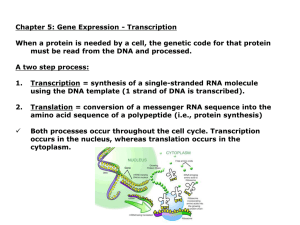
jan4
... Review of the Central Dogma (cont.) Eukaryotic genes are interrupted by introns (noncoding information). They must be removed from the RNA before translation in a process called “splicing.” exons introns ...
... Review of the Central Dogma (cont.) Eukaryotic genes are interrupted by introns (noncoding information). They must be removed from the RNA before translation in a process called “splicing.” exons introns ...
Oct. 14th
... The Hox gene family are examples of homeotic genes. Homeotic genes are genes that when mutant cause a change in the spatial position of structures (change in address). ...
... The Hox gene family are examples of homeotic genes. Homeotic genes are genes that when mutant cause a change in the spatial position of structures (change in address). ...
`RNA world`.
... •Enzymes facilitate the formation of a transition state, thereby lowering the activation energy. ...
... •Enzymes facilitate the formation of a transition state, thereby lowering the activation energy. ...
Protein Synthesis Powerpoint
... brings it to the ribosome. It is made during first step called transcription. - rRNA= Ribosomal RNA: combines with proteins to make the structure of the ribosome. - tRNA= Transfer RNA: carries an amino acid to the ribosome to be able to synthesize the protein during translation. ...
... brings it to the ribosome. It is made during first step called transcription. - rRNA= Ribosomal RNA: combines with proteins to make the structure of the ribosome. - tRNA= Transfer RNA: carries an amino acid to the ribosome to be able to synthesize the protein during translation. ...
5X All-In-One RT MasterMix
... OneScript® RTase with its superior catalytic prowess. Nullifying the RNase H activity which is intrinsic to native RTase helps prevent RNA degradation during first-strand cDNA synthesis resulting in higher yields and an increase in the achievable length of synthesized cDNA. OneScript® RTase also con ...
... OneScript® RTase with its superior catalytic prowess. Nullifying the RNase H activity which is intrinsic to native RTase helps prevent RNA degradation during first-strand cDNA synthesis resulting in higher yields and an increase in the achievable length of synthesized cDNA. OneScript® RTase also con ...
File
... – Altering the DNA sequence by one or two bases produced a different amino acid sequence due to disruption in the reading frame • Adding a base at one point and deleting a base at another point disrupted the reading frame between the ...
... – Altering the DNA sequence by one or two bases produced a different amino acid sequence due to disruption in the reading frame • Adding a base at one point and deleting a base at another point disrupted the reading frame between the ...
Supplementary Documents (doc 60K)
... TFs (HNF4A, PPARG, MITF, CREM, FLI1, KDM5B and RUNX1) were among the top 10 in at least two datasets, and these were further analyzed with Kinase Enrichment Analysis (KEA) to identify the protein kinases that regulate these seven TFs.2 ...
... TFs (HNF4A, PPARG, MITF, CREM, FLI1, KDM5B and RUNX1) were among the top 10 in at least two datasets, and these were further analyzed with Kinase Enrichment Analysis (KEA) to identify the protein kinases that regulate these seven TFs.2 ...
DNA Splicing
... The resulting different mRNAs may be translated into different protein isoforms; thus, a single gene may code for multiple proteins.” A mechanism by which different forms of mature mRNAs are generated from the same gene. Alternative splicing is a regulatory mechanism by which variations in the incor ...
... The resulting different mRNAs may be translated into different protein isoforms; thus, a single gene may code for multiple proteins.” A mechanism by which different forms of mature mRNAs are generated from the same gene. Alternative splicing is a regulatory mechanism by which variations in the incor ...
bcdcdbcaab - kehsscience.org
... RNA is usually double-stranded and contains the base thymine. RNA is usually single-stranded and contains the base uracil. RNA is longer than DNA and uses five bases to encode information. RNA is made in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells and stays there to carry out its functions. ...
... RNA is usually double-stranded and contains the base thymine. RNA is usually single-stranded and contains the base uracil. RNA is longer than DNA and uses five bases to encode information. RNA is made in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells and stays there to carry out its functions. ...
Figure S2.
... Figure S2. NELF-E potentiates expression of the slp1[PESE]-lacZ reporter. Fluorescent double in situ hybridization was used to compare the expression of a reporter gene containing a slp1 cis-regulatory element extending from 3.9 to 1.8 kb upstream of the slp1 promoter fused to a 129 bp slp1 basal pr ...
... Figure S2. NELF-E potentiates expression of the slp1[PESE]-lacZ reporter. Fluorescent double in situ hybridization was used to compare the expression of a reporter gene containing a slp1 cis-regulatory element extending from 3.9 to 1.8 kb upstream of the slp1 promoter fused to a 129 bp slp1 basal pr ...
Nucleic acids and their protein partners
... without the help of proteins. Electrostatics is a dominant force in RNA folding, but recent theoretical, computational, and experimental investigations have revealed the interplay of counterions, RNA structure and folding pathways. New structural methods, including timeresolved footprinting, small-a ...
... without the help of proteins. Electrostatics is a dominant force in RNA folding, but recent theoretical, computational, and experimental investigations have revealed the interplay of counterions, RNA structure and folding pathways. New structural methods, including timeresolved footprinting, small-a ...
Chapter 8: Microbial Genetics 1. Gene Expression Gene Expression
... Regulation of Transcription The focal point is whether or not RNA polymerase binds the promoter of a gene and initiates transcription which depends on: 1) Affinity of RNA polymerase for a given promoter • some promoters are “strong” and bind RNA polymerase with high affinity • some promoters are “we ...
... Regulation of Transcription The focal point is whether or not RNA polymerase binds the promoter of a gene and initiates transcription which depends on: 1) Affinity of RNA polymerase for a given promoter • some promoters are “strong” and bind RNA polymerase with high affinity • some promoters are “we ...
Slide 1
... What makes RNA so powerful? • It can fold up • Some of its bases can catalyze chemical reactions • It is highly specific (i.e., complementary) tRNA ...
... What makes RNA so powerful? • It can fold up • Some of its bases can catalyze chemical reactions • It is highly specific (i.e., complementary) tRNA ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein.
... A type of RNA called small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA) aids in processing pre-rRNA transcripts in the nucleolus, a process necessary for ribosome formation. Recent research has also revealed the presence of small, single-stranded and double-stranded RNA molecules that play important roles in regulati ...
... A type of RNA called small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA) aids in processing pre-rRNA transcripts in the nucleolus, a process necessary for ribosome formation. Recent research has also revealed the presence of small, single-stranded and double-stranded RNA molecules that play important roles in regulati ...
2. recombinant gene
... What are they good for? - (1) examination of gene function; (2) economically important GMOs, (3) gene therapy in future ...
... What are they good for? - (1) examination of gene function; (2) economically important GMOs, (3) gene therapy in future ...
Protein Synthesis Overview
... • Each gene on a strand of DNA is read in 3 base sequences called codons • A codon designates an amino acid • An amino acid may have more than one codon • There are 20 amino acids, but 64 possible codons • Some codons tell the ribosome to stop ...
... • Each gene on a strand of DNA is read in 3 base sequences called codons • A codon designates an amino acid • An amino acid may have more than one codon • There are 20 amino acids, but 64 possible codons • Some codons tell the ribosome to stop ...
Gene expression: Transcription
... tRNA genes also occur in repeated copies throughout the genome, and may contain introns. ...
... tRNA genes also occur in repeated copies throughout the genome, and may contain introns. ...
Analyzing Factorially designed microarray experiments
... must satisfy a number of constraints and hence are not suitable for outlier detection However, outlier detection is important since the presence of outliers will inflate the estimated variance and hence decrease our ability to detect significant effects ...
... must satisfy a number of constraints and hence are not suitable for outlier detection However, outlier detection is important since the presence of outliers will inflate the estimated variance and hence decrease our ability to detect significant effects ...
Water Flea Boasts Whopper Gene Count
... (lincRNAs), 2300 to 17,200 bases long, that Guttman, Rinn, and their colleagues have are coded for in DNA between genes. Until also looked for patterns of coexpression recently, researchers knew of only about a between protein-coding genes and lincRNAs dozen lincRNAs, notably XIST, an RNA that in 21 ...
... (lincRNAs), 2300 to 17,200 bases long, that Guttman, Rinn, and their colleagues have are coded for in DNA between genes. Until also looked for patterns of coexpression recently, researchers knew of only about a between protein-coding genes and lincRNAs dozen lincRNAs, notably XIST, an RNA that in 21 ...
Applications of RNA minimum free energy computations
... Non-coding RNA (ncRNA) (Eddy, 2001; Eddy, 2002) is transcribed from genomic DNA and plays a biologically important role, although it is not translated into protein. Examples include tRNA, rRNA, XIST (which in mammalian males suppresses expression of genes on the X chromosome) (Brown et al., 1992), m ...
... Non-coding RNA (ncRNA) (Eddy, 2001; Eddy, 2002) is transcribed from genomic DNA and plays a biologically important role, although it is not translated into protein. Examples include tRNA, rRNA, XIST (which in mammalian males suppresses expression of genes on the X chromosome) (Brown et al., 1992), m ...
Chapter 17 Nucleotides, Nucleic Acids, and Heredity
... Micro RNA (miRNA): another type of small RNA ◦ 20-22 nucleotides long ◦ Important in the timing of an organism’s development. ◦ They inhibit translation of mRNA into protein and promote the degredation of mRNA Small Interfering RNA (siRNA): eliminate expression of an undersirable gene, such as one t ...
... Micro RNA (miRNA): another type of small RNA ◦ 20-22 nucleotides long ◦ Important in the timing of an organism’s development. ◦ They inhibit translation of mRNA into protein and promote the degredation of mRNA Small Interfering RNA (siRNA): eliminate expression of an undersirable gene, such as one t ...
chapter14
... codon in the mRNA. The mRNA transcript and the new polypeptide chain are released from the ribosome. The two ribosomal subunits separate from each other. Translation is now complete. Either the chain will join the pool of proteins in the cytoplasm or it will enter rough ER of the endomembrane system ...
... codon in the mRNA. The mRNA transcript and the new polypeptide chain are released from the ribosome. The two ribosomal subunits separate from each other. Translation is now complete. Either the chain will join the pool of proteins in the cytoplasm or it will enter rough ER of the endomembrane system ...
Lecture 1 - Doolittle Lab
... In 1964 the Nirenberg lab introduced a new strategy that gave definitive answers. They used synthetic trinucelotides corresponding to the various codons in combination with amino acyl-tRNAs. ...
... In 1964 the Nirenberg lab introduced a new strategy that gave definitive answers. They used synthetic trinucelotides corresponding to the various codons in combination with amino acyl-tRNAs. ...
molbiolcell.org
... microRNAs (miRNAs) or other endogenous small RNAs. Within cells, either 21–24 –nucleotide short interfering RNA (siRNA) fragments derived from longer dsRNA or miRNAs (Hammond et al., 2001; Hutvagner and Zamore, 2002; Mourelatos et al., 2002; Doi et al., 2003) can be incorporated into the RISC togeth ...
... microRNAs (miRNAs) or other endogenous small RNAs. Within cells, either 21–24 –nucleotide short interfering RNA (siRNA) fragments derived from longer dsRNA or miRNAs (Hammond et al., 2001; Hutvagner and Zamore, 2002; Mourelatos et al., 2002; Doi et al., 2003) can be incorporated into the RISC togeth ...
RNA interference
RNA interference (RNAi) is a biological process in which RNA molecules inhibit gene expression, typically by causing the destruction of specific mRNA molecules. Historically, it was known by other names, including co-suppression, post-transcriptional gene silencing (PTGS), and quelling. Only after these apparently unrelated processes were fully understood did it become clear that they all described the RNAi phenomenon. Andrew Fire and Craig C. Mello shared the 2006 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their work on RNA interference in the nematode worm Caenorhabditis elegans, which they published in 1998.Two types of small ribonucleic acid (RNA) molecules – microRNA (miRNA) and small interfering RNA (siRNA) – are central to RNA interference. RNAs are the direct products of genes, and these small RNAs can bind to other specific messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules and either increase or decrease their activity, for example by preventing an mRNA from producing a protein. RNA interference has an important role in defending cells against parasitic nucleotide sequences – viruses and transposons. It also influences development.The RNAi pathway is found in many eukaryotes, including animals, and is initiated by the enzyme Dicer, which cleaves long double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) molecules into short double-stranded fragments of ~20 nucleotide siRNAs. Each siRNA is unwound into two single-stranded RNAs (ssRNAs), the passenger strand and the guide strand. The passenger strand is degraded and the guide strand is incorporated into the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). The most well-studied outcome is post-transcriptional gene silencing, which occurs when the guide strand pairs with a complementary sequence in a messenger RNA molecule and induces cleavage by Argonaute, the catalytic component of the RISC complex. In some organisms, this process spreads systemically, despite the initially limited molar concentrations of siRNA.RNAi is a valuable research tool, both in cell culture and in living organisms, because synthetic dsRNA introduced into cells can selectively and robustly induce suppression of specific genes of interest. RNAi may be used for large-scale screens that systematically shut down each gene in the cell, which can help to identify the components necessary for a particular cellular process or an event such as cell division. The pathway is also used as a practical tool in biotechnology, medicine and insecticides.