RNA polymerase II is the key enzyme in the process of transcription
... 5. RXR acts as a partner for nuclear receptors such as Vitamin D receptor (VDR), thyroid hormone receptor (TR) and PPAR. These dimers bind to related ciselements in responsive promoters. Explain how discrimination between responsive elements for these factors is obtained? How is it possible to chang ...
... 5. RXR acts as a partner for nuclear receptors such as Vitamin D receptor (VDR), thyroid hormone receptor (TR) and PPAR. These dimers bind to related ciselements in responsive promoters. Explain how discrimination between responsive elements for these factors is obtained? How is it possible to chang ...
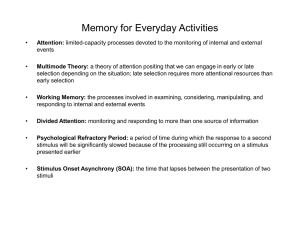
Memory for Everyday Activities
... Multimode Theory: a theory of attention positing that we can engage in early or late selection depending on the situation; late selection requires more attentional resources than early selection ...
... Multimode Theory: a theory of attention positing that we can engage in early or late selection depending on the situation; late selection requires more attentional resources than early selection ...
RNA polymerase II is the key enzyme in the process of transcription
... 5. RXR acts as a partner for nuclear receptors such as Vitamin D receptor (VDR), thyroid hormone receptor (TR) and PPAR. These dimers bind to related ciselements in responsive promoters. Explain how discrimination between responsive elements for these factors is obtained? How is it possible to chang ...
... 5. RXR acts as a partner for nuclear receptors such as Vitamin D receptor (VDR), thyroid hormone receptor (TR) and PPAR. These dimers bind to related ciselements in responsive promoters. Explain how discrimination between responsive elements for these factors is obtained? How is it possible to chang ...
Biology 303 EXAM II 3/14/00 NAME
... Considering the location of genetic material in the interphase nucleus, certain chromosomal territories appear to exist. Specifically, A. each chromosome appears to occupy a discrete domain. B. gene-poor regions of chromosomes are located outside the nucleus, whereas gene-rich regions are located in ...
... Considering the location of genetic material in the interphase nucleus, certain chromosomal territories appear to exist. Specifically, A. each chromosome appears to occupy a discrete domain. B. gene-poor regions of chromosomes are located outside the nucleus, whereas gene-rich regions are located in ...
RNA-Seq is a sequencing technique applied to transcript analysis
... next-generation sequencing technology, and can be applied to the study of gene expression. Since the development of next-generation sequencing technology, RNA-Seq data are generally considered to have advantages over conventional microarray (microarray) gene expression data, including the large dyna ...
... next-generation sequencing technology, and can be applied to the study of gene expression. Since the development of next-generation sequencing technology, RNA-Seq data are generally considered to have advantages over conventional microarray (microarray) gene expression data, including the large dyna ...
What happens to the repressor when lactose is present?
... ___________ or ___________. sequence is found directly before the RNA Polymerase starting point for __________________. This region is known as the TATA _______ Box ...
... ___________ or ___________. sequence is found directly before the RNA Polymerase starting point for __________________. This region is known as the TATA _______ Box ...
to get the file - Chair of Computational Biology
... The genomes of several plants have been sequenced, and those of many others are under way. But genetic information alone cannot fully address the fundamental question of how genes are differentially expressed during cell differentiation and plant development, as the DNA sequences in all cells in a p ...
... The genomes of several plants have been sequenced, and those of many others are under way. But genetic information alone cannot fully address the fundamental question of how genes are differentially expressed during cell differentiation and plant development, as the DNA sequences in all cells in a p ...
Voices - Indiana University Bloomington
... the chromatin-marking patterns. Other studies have demonstrated that thousands of regulatory regions undergo activation or decommissioning even during transitions between closely developmentally related cell types. It seems highly likely that the information content within regulatory parts of the ge ...
... the chromatin-marking patterns. Other studies have demonstrated that thousands of regulatory regions undergo activation or decommissioning even during transitions between closely developmentally related cell types. It seems highly likely that the information content within regulatory parts of the ge ...
What Do Studies of Insect Polyphenisms Tell Us about
... act to change phenotype. The complexity of these mechanisms and their outcomes makes understanding the fundamental biology involved difficult. Insects provide an ideal model system to study the role of epigenetics in environmentally induced phenotypic change. Most insects methylate their DNA [1] as ...
... act to change phenotype. The complexity of these mechanisms and their outcomes makes understanding the fundamental biology involved difficult. Insects provide an ideal model system to study the role of epigenetics in environmentally induced phenotypic change. Most insects methylate their DNA [1] as ...
Regulation of Gene Expression
... • a coding region with five genes for enzymes required for tryptophan synthesis • a regulatory region with a promoter and an operator ...
... • a coding region with five genes for enzymes required for tryptophan synthesis • a regulatory region with a promoter and an operator ...
PowerPoint-Präsentation
... selectable marker flanked by homologous sequences. The chromosomal segment is replaced by this URA3 containing fragment after integration by homologous recombination. (B) The URA3 marker introduced in the YFG1 locus, can be excised if URA3 is also flanked by direct repeats of DNA, preferably not ori ...
... selectable marker flanked by homologous sequences. The chromosomal segment is replaced by this URA3 containing fragment after integration by homologous recombination. (B) The URA3 marker introduced in the YFG1 locus, can be excised if URA3 is also flanked by direct repeats of DNA, preferably not ori ...
TRANSFORMATION
... Boiled S + live R injected into mice -> pneumonia -> death This was not expected because boiled S and live R were harmless by themselves Took blood samples and found live S in the dead mice Concluded that some factor, a "transforming principle", from the dead S had converted some R bacteria ...
... Boiled S + live R injected into mice -> pneumonia -> death This was not expected because boiled S and live R were harmless by themselves Took blood samples and found live S in the dead mice Concluded that some factor, a "transforming principle", from the dead S had converted some R bacteria ...
Must Knows - Gene Regulation and Biotechnology
... 2) What type of operon is shown—inducible or repressible—and how do you know? 3) What is the role of molecule #5 in regulating the operon shown above? 4) Why is a catabolic operon (one that contains genes for enzymes used to break down molecules) usually an inducible operon? 5) Why is an anabolic op ...
... 2) What type of operon is shown—inducible or repressible—and how do you know? 3) What is the role of molecule #5 in regulating the operon shown above? 4) Why is a catabolic operon (one that contains genes for enzymes used to break down molecules) usually an inducible operon? 5) Why is an anabolic op ...
2.5 Genetics - Elaine Galvin
... A haploid sex cell which is capable of fusion The fusion of 2[haploid] gametes to form a [diploid] zygote An alternative form of a gene Has identical alleles [for a trait] Has different alleles [for a trait] The genetic make-up of an individual Physical appearance of an organism One allele masks the ...
... A haploid sex cell which is capable of fusion The fusion of 2[haploid] gametes to form a [diploid] zygote An alternative form of a gene Has identical alleles [for a trait] Has different alleles [for a trait] The genetic make-up of an individual Physical appearance of an organism One allele masks the ...
Answered copy of exam 3
... C) At least 3 DNA viruses are associated with increased risk of cancer in humans. List 2 of them. Epstein Barr ...
... C) At least 3 DNA viruses are associated with increased risk of cancer in humans. List 2 of them. Epstein Barr ...
Document
... • Where is it located? • How many splice forms do you find – According to the UCSC gene controls – According to ENSEMBL gene controls ...
... • Where is it located? • How many splice forms do you find – According to the UCSC gene controls – According to ENSEMBL gene controls ...
Beckwith-Wiedemann and Russel
... EGL is an academic, not-for-profit organization and a global leader in genetic testing. Associated with the prestigious Emory University School of Medicine, EGL has fully integrated biochemical, cytogenetics, and molecular laboratories, employing the latest technologies for one of the most comprehen ...
... EGL is an academic, not-for-profit organization and a global leader in genetic testing. Associated with the prestigious Emory University School of Medicine, EGL has fully integrated biochemical, cytogenetics, and molecular laboratories, employing the latest technologies for one of the most comprehen ...
Gene Regulation Summary Slide Questions with
... 2. What is the difference between negative and positive regulation? Negative regulation is done by a repressor to impede the gene; positive regulation is done by an activator which enhances the pol/promoter interaction. A corepressor enhances the binding of a repressor, so that it repressors further ...
... 2. What is the difference between negative and positive regulation? Negative regulation is done by a repressor to impede the gene; positive regulation is done by an activator which enhances the pol/promoter interaction. A corepressor enhances the binding of a repressor, so that it repressors further ...
Gene Section CITED4 (Cbp/p300 interacting transactivator, with Glu/Asp
... DNA sequence is located at chromosome 1p. ...
... DNA sequence is located at chromosome 1p. ...
Document
... 17) CDS is an abbreviation for ________________________. 18a) Can all CDS’ be said to contain an ORF? (yes, no-circle one) 18b) Can all ORFs be said to contain a CDS? (yes, no-circle one) ...
... 17) CDS is an abbreviation for ________________________. 18a) Can all CDS’ be said to contain an ORF? (yes, no-circle one) 18b) Can all ORFs be said to contain a CDS? (yes, no-circle one) ...
Part 1: Prokaryotic Regulation Questions to answer
... provides a eukaryotic cell with the ability to regulate gene expression: a. nucleosomes b. DNA methylation c. Transcription factors/enhancers d. alternative splicing e. mRNA degradation f. RNA interference (RNAi) g. Protein processing and degradation. ...
... provides a eukaryotic cell with the ability to regulate gene expression: a. nucleosomes b. DNA methylation c. Transcription factors/enhancers d. alternative splicing e. mRNA degradation f. RNA interference (RNAi) g. Protein processing and degradation. ...
Solutions - MsHughesPsychology
... 5. Explain the role of the neuron in terms of memory formation. __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 1 mark 6. Distinguish between the two types of amnesia. ______________ ...
... 5. Explain the role of the neuron in terms of memory formation. __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 1 mark 6. Distinguish between the two types of amnesia. ______________ ...
1 Bi/CNS/NB 150 Problem Set 5 Due: Tuesday, Nov. 24, at 4:30 pm
... responsible for them in humans. Iconic memory (< 1 s) is short-term sensory memory stored in the regions dedicated to the sensory modality. Short-term memory (< 30 s) is limited to a small amount of information and a short period of time but is in an active and readily available state. STM is stored ...
... responsible for them in humans. Iconic memory (< 1 s) is short-term sensory memory stored in the regions dedicated to the sensory modality. Short-term memory (< 30 s) is limited to a small amount of information and a short period of time but is in an active and readily available state. STM is stored ...
Control of Gene Express in Prokaryotes
... • Promoter region-controls access to the structural genes, located between the promoter and structural genes, contains the operator site. • Operator Site -region where the repressor attaches • Regulatory genes-codes for repressor proteins • Polycistronic mRNA-transcript for several polypeptides ...
... • Promoter region-controls access to the structural genes, located between the promoter and structural genes, contains the operator site. • Operator Site -region where the repressor attaches • Regulatory genes-codes for repressor proteins • Polycistronic mRNA-transcript for several polypeptides ...
Bild 1
... Supplemental Digital Content 1 - Figure 1. Global Gene Expression Analysis of Similarities in Biopsies. A data set consisting of ten biopsies from one patient projected by correspondence analysis to reveal similarities in global gene expression levels between different samples. Genes and samples tha ...
... Supplemental Digital Content 1 - Figure 1. Global Gene Expression Analysis of Similarities in Biopsies. A data set consisting of ten biopsies from one patient projected by correspondence analysis to reveal similarities in global gene expression levels between different samples. Genes and samples tha ...