Goal 3: Learner will develop an understanding of the continuity of
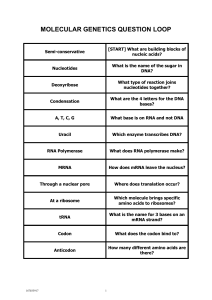
... 13. During DNA replication, how many pieces of DNA are made? What does the term semi-conservative mean? 14. What is the end result of DNA replication? 15. When does DNA replication occur during the cell cycle? 16. What kind of weak bonds hold the two strands of DNA together? Why is it important that ...
... 13. During DNA replication, how many pieces of DNA are made? What does the term semi-conservative mean? 14. What is the end result of DNA replication? 15. When does DNA replication occur during the cell cycle? 16. What kind of weak bonds hold the two strands of DNA together? Why is it important that ...
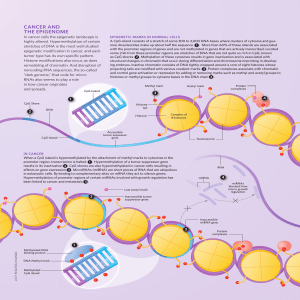
CaNCer aND THe ePIGeNOMe
... epigenetic modification in cancer, and each tumor type has its own specific pattern. Histone modifications also occur, as does remodeling of chromatin. And disruption of noncoding RNA sequences, the so-called “dark genome,” that code for microRNAs also seems to play a role in how cancer originates a ...
... epigenetic modification in cancer, and each tumor type has its own specific pattern. Histone modifications also occur, as does remodeling of chromatin. And disruption of noncoding RNA sequences, the so-called “dark genome,” that code for microRNAs also seems to play a role in how cancer originates a ...
VERTEBRATE GENOME EVOLUTION AND FUNCTION …
... Activation and induction of reporter genes after site-directed, stable integration in erythroid cells ...
... Activation and induction of reporter genes after site-directed, stable integration in erythroid cells ...
Learning Guide:
... 5. Explain what would happen to the process of gene expression if the gene for RNA polymerase was mutated. 6. Each amino acid has a tRNA synthetase enzyme that is responsible for attaching it to a tRNA molecule. Explain what would happen if there was a mutation in the gene encoding one of these enzy ...
... 5. Explain what would happen to the process of gene expression if the gene for RNA polymerase was mutated. 6. Each amino acid has a tRNA synthetase enzyme that is responsible for attaching it to a tRNA molecule. Explain what would happen if there was a mutation in the gene encoding one of these enzy ...
Go to - Net Start Class
... wishes them to view this also. (2 is replication & transcription: 4 is 3’; 5’ ends) Forward arrow on the controls moves to the next page. Questions the students need to answer are on the next page. You could also have them answer in their journals. ...
... wishes them to view this also. (2 is replication & transcription: 4 is 3’; 5’ ends) Forward arrow on the controls moves to the next page. Questions the students need to answer are on the next page. You could also have them answer in their journals. ...
What is DNA?
... process of Mitosis. • Replication is the process by which DNA duplicate in order to form two identical cells • Cells need to reproduce to create new cells for growth, repair of tissue, (healing) and to produce other things our body needs. • Why do the body cells have to be identical? ...
... process of Mitosis. • Replication is the process by which DNA duplicate in order to form two identical cells • Cells need to reproduce to create new cells for growth, repair of tissue, (healing) and to produce other things our body needs. • Why do the body cells have to be identical? ...
Click Here For Worksheet
... 1. What percent of your genes are found in your nucleus?__________________________________________ 2. How many genes does a human cell have?___________________________________ 3. Which is not a base that makes up DNA? (Circle One) A. Adenine ...
... 1. What percent of your genes are found in your nucleus?__________________________________________ 2. How many genes does a human cell have?___________________________________ 3. Which is not a base that makes up DNA? (Circle One) A. Adenine ...
Recombinant DNA - Richmond School District
... restriction enzyme. (this leaves the human DNA and the plasmid DNA with the same “sticky ends”) ...
... restriction enzyme. (this leaves the human DNA and the plasmid DNA with the same “sticky ends”) ...
DNA experiments exercise
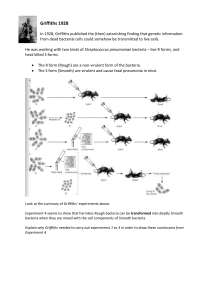
... Experiment 4 seems to show that harmless Rough bacteria can be transformed into deadly Smooth bacteria when they are mixed with the cell components of Smooth bacteria. Explain why Griffiths needed to carry out experiments 1 to 3 in order to draw these conclusions from Experiment 4. ...
... Experiment 4 seems to show that harmless Rough bacteria can be transformed into deadly Smooth bacteria when they are mixed with the cell components of Smooth bacteria. Explain why Griffiths needed to carry out experiments 1 to 3 in order to draw these conclusions from Experiment 4. ...
`Central Dogma` of Molecular Biology
... More Terms & Background Concepts Splicing: enzyme- (and intron-) controlled snipping of DNA segment to be transcribed to RNA. ‘Alternative splicings’ mean that the same Gene could code for multiple proteins depending on where snips are made. Markers: locations along DNA sequence at which known avai ...
... More Terms & Background Concepts Splicing: enzyme- (and intron-) controlled snipping of DNA segment to be transcribed to RNA. ‘Alternative splicings’ mean that the same Gene could code for multiple proteins depending on where snips are made. Markers: locations along DNA sequence at which known avai ...
DNA Review Cards
... Describe the process of transcription. What is a mutagen? What is the primary enzyme in transcription. Give examples of mutagens. What type of cell must a mutation occur in to be passed on to offspring? ...
... Describe the process of transcription. What is a mutagen? What is the primary enzyme in transcription. Give examples of mutagens. What type of cell must a mutation occur in to be passed on to offspring? ...
Protein - UDKeystone
... • Definition: more than two alleles • (more than 2 alleles exist in a population not an individual) Ex: rabbit’s coat color Ex: human’s blood type ...
... • Definition: more than two alleles • (more than 2 alleles exist in a population not an individual) Ex: rabbit’s coat color Ex: human’s blood type ...
File
... collection of genes an organism has. Ex: Human Genome Project- scientists now know the sequence of 20,500 genes! Gene technology helps scientists study genomes of organisms ...
... collection of genes an organism has. Ex: Human Genome Project- scientists now know the sequence of 20,500 genes! Gene technology helps scientists study genomes of organisms ...
Ross - Tree Improvement Program
... region of DNA that affects a trait of interest • “Gene” means a region of DNA that encodes some product needed by the cell. • “Regulatory sequences” control expression of genes, but are not always near the genes they control ...
... region of DNA that affects a trait of interest • “Gene” means a region of DNA that encodes some product needed by the cell. • “Regulatory sequences” control expression of genes, but are not always near the genes they control ...
Document
... Use one of the above terms to best complete each sentence #1-15 below. (2 pts. each) 1. _____cDNA_______ is a DNA copy of an RNA molecule. 2. ___reverse transcriptase__ is an RNA-dependent DNA polymerase. 3. Knockout mice are created by replacing a normal gene segment with a modified segment within ...
... Use one of the above terms to best complete each sentence #1-15 below. (2 pts. each) 1. _____cDNA_______ is a DNA copy of an RNA molecule. 2. ___reverse transcriptase__ is an RNA-dependent DNA polymerase. 3. Knockout mice are created by replacing a normal gene segment with a modified segment within ...
Product Information Sheet - Sigma
... well as participation by another form of RNA, ribosomal RNA. DNA provides the means of transmitting heritable information from one generation of cells or higher organism to the next via the gene and genome. A gene is a sequence of DNA nucleotides that specify the order of amino acids that are incorp ...
... well as participation by another form of RNA, ribosomal RNA. DNA provides the means of transmitting heritable information from one generation of cells or higher organism to the next via the gene and genome. A gene is a sequence of DNA nucleotides that specify the order of amino acids that are incorp ...
a14DNAGenMat
... DNA: Structure and Replication • DNA – Was known to be a chemical in cells by the end of the nineteenth century. – Has the capacity to store genetic information. ...
... DNA: Structure and Replication • DNA – Was known to be a chemical in cells by the end of the nineteenth century. – Has the capacity to store genetic information. ...
DNA- Experiments and People
... Grow E. coli bacteria with radioactive 15N (its heavier than 14N) so bacteria incorporate heavy N into their DNA Then grow in media with only 14N Centrifuge DNA at different times to separate by size. (The more 15N it has the heavier it is) Pattern shows which model is correct ...
... Grow E. coli bacteria with radioactive 15N (its heavier than 14N) so bacteria incorporate heavy N into their DNA Then grow in media with only 14N Centrifuge DNA at different times to separate by size. (The more 15N it has the heavier it is) Pattern shows which model is correct ...
DNA People - Biology Junction
... Grow E. coli bacteria with radioactive 15N (its heavier than 14N) so bacteria incorporate heavy N into their DNA Then grow in media with only 14N Centrifuge DNA at different times to separate by size. (The more 15N it has the heavier it is) Pattern shows which model is correct ...
... Grow E. coli bacteria with radioactive 15N (its heavier than 14N) so bacteria incorporate heavy N into their DNA Then grow in media with only 14N Centrifuge DNA at different times to separate by size. (The more 15N it has the heavier it is) Pattern shows which model is correct ...