Nucleic acid
... • Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is formed by condensation of ribonucleotides. • RNA is a long, unbranched macromolecule and may contain 70 to several thousand nucleotides. RNA molecule is usually single stranded. • RNA contains adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C) and uracial (U). A-U, G-C in some double ...
... • Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is formed by condensation of ribonucleotides. • RNA is a long, unbranched macromolecule and may contain 70 to several thousand nucleotides. RNA molecule is usually single stranded. • RNA contains adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C) and uracial (U). A-U, G-C in some double ...
document
... Gene is part of genome Genome =full set of genetic information encoded by the chromosomes of an organism ...
... Gene is part of genome Genome =full set of genetic information encoded by the chromosomes of an organism ...
The human genome: a prospect for paediatrics
... million base pairs, has yet to be determined. As a typical protein comprises say, three hundred amino acids, only one thousand nucleotides are required on average for a structural gene's coding region. The human genome, therefore, has sufficient DNA to encode several million genes. It is probable, h ...
... million base pairs, has yet to be determined. As a typical protein comprises say, three hundred amino acids, only one thousand nucleotides are required on average for a structural gene's coding region. The human genome, therefore, has sufficient DNA to encode several million genes. It is probable, h ...
Class 10 Heredity and Evolution CBSE Solved Test paper-3
... Q. 4. Wings of bird and wings of insect-are these organs homologous or analogous? Give one suitable season to support your answer. Ans: They are analogous organs as both have developed from different origin and perform same function of flying. Q.5. Give one difference between eyes and eye spot.Which ...
... Q. 4. Wings of bird and wings of insect-are these organs homologous or analogous? Give one suitable season to support your answer. Ans: They are analogous organs as both have developed from different origin and perform same function of flying. Q.5. Give one difference between eyes and eye spot.Which ...
Recombinant DNA - Minneapolis Medical Research Foundation
... Do experiments involve the release into the environment of an organism containing recombinant DNA? Yes No If yes, has approval for this release been filed with state or federal regulating agency? (agency) (date filed) Send copy of approval when it is received ...
... Do experiments involve the release into the environment of an organism containing recombinant DNA? Yes No If yes, has approval for this release been filed with state or federal regulating agency? (agency) (date filed) Send copy of approval when it is received ...
Microbial Minimalism: Genome Reduction in Bacterial Pathogens
... genes that are dispensable, at least for growth in vitro. Based on a study in which single genes of M. genitalium were inactivated using transposon-mediated mutagenesis, at least 129 of that organism’s 484 ORFs were unnecessary for growth. Thus, a substantially smaller genome is plausible. It must b ...
... genes that are dispensable, at least for growth in vitro. Based on a study in which single genes of M. genitalium were inactivated using transposon-mediated mutagenesis, at least 129 of that organism’s 484 ORFs were unnecessary for growth. Thus, a substantially smaller genome is plausible. It must b ...
RNA
... Retro-Virus single-stranded RNA (viral genome) RNA-directed DNA synthesis by reverse transcriptase single-stranded DNA double-stranded DNA integrate into the host genome replication together with the host genome later, when it is necessary, express viral RNA and proteins packaging viru ...
... Retro-Virus single-stranded RNA (viral genome) RNA-directed DNA synthesis by reverse transcriptase single-stranded DNA double-stranded DNA integrate into the host genome replication together with the host genome later, when it is necessary, express viral RNA and proteins packaging viru ...
Chapt21 Lecture 13ed Pt 1
... function of DNA and RNA. • How is DNA replicated? • Describe transcription and translation in detail. • Describe the genetic code. • Review protein structure and function. • What are the 4 levels of regulating gene expression? ...
... function of DNA and RNA. • How is DNA replicated? • Describe transcription and translation in detail. • Describe the genetic code. • Review protein structure and function. • What are the 4 levels of regulating gene expression? ...
The Avery and Hershey-Chase Experiments
... • The DNA-digesting enzyme DNase destroyed all transforming activity ...
... • The DNA-digesting enzyme DNase destroyed all transforming activity ...
DNA and the Genetic Code
... Translation Translation is the process where ribosomes decode mRNA to produce amino acids. mRNA is decoded in three-base sections called codons. The codons code for one of 20 amino acids. There are 64 different codons (43 ) so several different codons can specify the same amino acid, or none at all ...
... Translation Translation is the process where ribosomes decode mRNA to produce amino acids. mRNA is decoded in three-base sections called codons. The codons code for one of 20 amino acids. There are 64 different codons (43 ) so several different codons can specify the same amino acid, or none at all ...
A Novel Interacting Protein With The DNA Mismatch Repair Gene
... DNA mismatch repair (MMR) is associated with hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC), the most common known genetic cancer susceptibility syndrome. We are investigating protein interactions between the DNA MMR protein PMS2 and Clone PMS2-Interactor 1 to explain the dominant negative (DN) ...
... DNA mismatch repair (MMR) is associated with hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC), the most common known genetic cancer susceptibility syndrome. We are investigating protein interactions between the DNA MMR protein PMS2 and Clone PMS2-Interactor 1 to explain the dominant negative (DN) ...
Genome Organization
... - It is found in almost all eukaryotes. - It consists of short sequences, typically 2 to 200 bp in length, repeated many times in one or more tandem arrays. - The bulk of the sequences seem to be located in a fraction of chromatin called heterochromatin. When its location is determined, it is found ...
... - It is found in almost all eukaryotes. - It consists of short sequences, typically 2 to 200 bp in length, repeated many times in one or more tandem arrays. - The bulk of the sequences seem to be located in a fraction of chromatin called heterochromatin. When its location is determined, it is found ...
DNA notes 2015 - OG
... - DNA makes a copy of itself - Important during meiosis & mitosis – DNA gets passed on to daughter cells • DNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the parent strands and checks the strand for errors • Each double helix now has 1 old strand & 1 new strand •This is called SEMI-CONSERVATIVE • If the origina ...
... - DNA makes a copy of itself - Important during meiosis & mitosis – DNA gets passed on to daughter cells • DNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the parent strands and checks the strand for errors • Each double helix now has 1 old strand & 1 new strand •This is called SEMI-CONSERVATIVE • If the origina ...
Genetic Diseases and Gene Therapy
... • Concept maps allow you to organize lots of information into a form that is easily understood. • Concept maps allow you to visualize connections within the information. ...
... • Concept maps allow you to organize lots of information into a form that is easily understood. • Concept maps allow you to visualize connections within the information. ...
11. Genetic engineering case study 1 - Human Insulin
... • Plasmids are cut by restriction enzymes that has its target site (where it cuts) in the middle of tetracycline resistance gene • This means that if the required gene is taken up, the gene for tetracycline resistance is broken up and fails to work, but the gene for ampicillin resistance does still ...
... • Plasmids are cut by restriction enzymes that has its target site (where it cuts) in the middle of tetracycline resistance gene • This means that if the required gene is taken up, the gene for tetracycline resistance is broken up and fails to work, but the gene for ampicillin resistance does still ...
Response from Women`s and Children`s Health Network Institutional
... We are in support of option 4. We consider that methods SDN-1 and SDN-2 result in genetic modification that are (1) indistinguishable from naturally occurring mutations, and hence natural habitats (2) in line with outcomes produced from other exempt technologies, such as radiation and chemical metho ...
... We are in support of option 4. We consider that methods SDN-1 and SDN-2 result in genetic modification that are (1) indistinguishable from naturally occurring mutations, and hence natural habitats (2) in line with outcomes produced from other exempt technologies, such as radiation and chemical metho ...
Nucleic Acid Chemistry
... – As opens up, DNA polymerase binds – Makes new DNA 5’ - 3’ • Same direction as opening of helix ...
... – As opens up, DNA polymerase binds – Makes new DNA 5’ - 3’ • Same direction as opening of helix ...
Lesson 3
... • Sometimes mistakes happen when DNA is being copied • These mistakes, called mutations, are any permanent change in the DNA sequence of a gene or chromosome • Incorrect proteins are made • Some mutations result in a missing or extra chromosome ...
... • Sometimes mistakes happen when DNA is being copied • These mistakes, called mutations, are any permanent change in the DNA sequence of a gene or chromosome • Incorrect proteins are made • Some mutations result in a missing or extra chromosome ...
An Amazing Sequence Arrangement at the 5’ Ends of
... The notion of the cistron, the genetic unit of function that one thought corresponded to a polypeptide chain, now must be replaced by that of a transcription unit containing regions which will be lost from the mature messenger -- which I suggest we call introns (for intragenic regions) -- alternatin ...
... The notion of the cistron, the genetic unit of function that one thought corresponded to a polypeptide chain, now must be replaced by that of a transcription unit containing regions which will be lost from the mature messenger -- which I suggest we call introns (for intragenic regions) -- alternatin ...
LECTURE #3: DNA History and Scientists
... • Deoxyribose nucleic acid type of nucleic acid – What is the other type of nucleic acid? • RNA • DNA function – to hold genetic code – Genetic code = genetic instructions to make proteins • DNA is found in nucleus of eukaryotic cells • Found in nucleoid region in prokaryotes ...
... • Deoxyribose nucleic acid type of nucleic acid – What is the other type of nucleic acid? • RNA • DNA function – to hold genetic code – Genetic code = genetic instructions to make proteins • DNA is found in nucleus of eukaryotic cells • Found in nucleoid region in prokaryotes ...
Genetic Update Conferences - 2002 - yhs
... 95% of our genes have the capacity to have their exons spliced together in different alternative ways - one gene produces more than one protein! Titin Gene 80,780 bp - 178 Exons - 177 Introns Dystrophin Gene: 2.4 million bp - 79 Exons - 78 Introns Human Genome = 231,667 Exons - average gene has over ...
... 95% of our genes have the capacity to have their exons spliced together in different alternative ways - one gene produces more than one protein! Titin Gene 80,780 bp - 178 Exons - 177 Introns Dystrophin Gene: 2.4 million bp - 79 Exons - 78 Introns Human Genome = 231,667 Exons - average gene has over ...
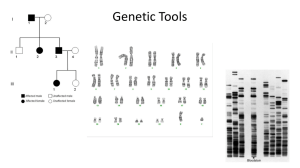
Genetic Tools
... • Mr. and Mrs. Raider are deeply worried about their child who seems to be developing at a slower rate. They are concerned for the child’s health just like any other parent and have come to you for help. ...
... • Mr. and Mrs. Raider are deeply worried about their child who seems to be developing at a slower rate. They are concerned for the child’s health just like any other parent and have come to you for help. ...
Biology 101 Chapter 14 Fill-in-the
... with C instead of T during DNA replication. this spontaneous mutation is a base-pair (3)____ substitution_______. Sickle-cell anemia is a genetic disease whose cause has been traced to a single DNA base pair; the result is that one (4) __ amino acid____ is substituted for another in the beta chain o ...
... with C instead of T during DNA replication. this spontaneous mutation is a base-pair (3)____ substitution_______. Sickle-cell anemia is a genetic disease whose cause has been traced to a single DNA base pair; the result is that one (4) __ amino acid____ is substituted for another in the beta chain o ...