Gene_March_2005 - Buffalo Ontology Site
... The recipes (genes) determine whether you’re a man or a woman, your eye color, how many arms and legs you have, how many wings and tentacles you have. Exact copy of entire set of cookbooks (= chromosomes) contained in nuclei of almost all your cells 23 pairs of chromosomes in each cell 25,000 genes ...
... The recipes (genes) determine whether you’re a man or a woman, your eye color, how many arms and legs you have, how many wings and tentacles you have. Exact copy of entire set of cookbooks (= chromosomes) contained in nuclei of almost all your cells 23 pairs of chromosomes in each cell 25,000 genes ...
Chapter 12 Molecular Genetics
... helicase Strands kept apart by single-stranded binding proteins Add “starter” RNA segment by RNA primase Add new nucleotides by DNA polymerase This is only the highlights; there are many other enzymes involved ...
... helicase Strands kept apart by single-stranded binding proteins Add “starter” RNA segment by RNA primase Add new nucleotides by DNA polymerase This is only the highlights; there are many other enzymes involved ...
Individuals DON`T evolve…
... Individuals survive orevolve… don’t survive… Individuals DON’T Populations evolve Individuals reproduce or don’t… Individuals are selected ...
... Individuals survive orevolve… don’t survive… Individuals DON’T Populations evolve Individuals reproduce or don’t… Individuals are selected ...
word
... RNA) that encodes for the gene of interest – at least 20 nucleotides in length a) Sometimes many probes are needed because the amino acid sequence in question can be encoded by numerous nucleotide sequences (this is called a degenerate “probe”) b) A database (expressed sequence tag) is available tha ...
... RNA) that encodes for the gene of interest – at least 20 nucleotides in length a) Sometimes many probes are needed because the amino acid sequence in question can be encoded by numerous nucleotide sequences (this is called a degenerate “probe”) b) A database (expressed sequence tag) is available tha ...
DNA Structure and replication notes
... There must be a complete copy of the DNA genome in every cell For this to happen the DNA must be copied before a cell divides so that a copy of the DNA can go into each of the new cells. ...
... There must be a complete copy of the DNA genome in every cell For this to happen the DNA must be copied before a cell divides so that a copy of the DNA can go into each of the new cells. ...
The structure of a d5SICS-dNaM pairing - Digital USD
... The structure of a d5SICS-dNaM pairing. A comparison of d5SICSdNaM and pyrimidine-pyrimidine bonding via dC-dG. As can be seen, the d5SICS-dNaM has no hydrogen bonding between nucleosides and is completely stabilized by hydrophobic interactions. ...
... The structure of a d5SICS-dNaM pairing. A comparison of d5SICSdNaM and pyrimidine-pyrimidine bonding via dC-dG. As can be seen, the d5SICS-dNaM has no hydrogen bonding between nucleosides and is completely stabilized by hydrophobic interactions. ...
Eukaryotic vs. Prokaryotic genes Eukaryotic Genes
... called introns. Each contiguous portion of a coding sequence is called an exon. – mnemonic: EXons are EXpressed, INtrons are INserts into genes. ...
... called introns. Each contiguous portion of a coding sequence is called an exon. – mnemonic: EXons are EXpressed, INtrons are INserts into genes. ...
Nucleic Acids - University of Idaho
... other hand, consist of two fused rings, and so are classified as purines. One of the important features of the nitrogenous bases of nucleic acids is that they are able to hydrogen bond with one another. Hydrogen bonding in nucleic acids occurs between the two strands of DNA molecules, or between DNA ...
... other hand, consist of two fused rings, and so are classified as purines. One of the important features of the nitrogenous bases of nucleic acids is that they are able to hydrogen bond with one another. Hydrogen bonding in nucleic acids occurs between the two strands of DNA molecules, or between DNA ...
genetics-1 - MacsScienceSpace
... that could develop into a normal human male? a) phosphate groups b) deoxyribose sugars c) nitrogenous base d) ribose sugars\ Base your answers to the next two questions on the chart below and on your knowledge of biology. ...
... that could develop into a normal human male? a) phosphate groups b) deoxyribose sugars c) nitrogenous base d) ribose sugars\ Base your answers to the next two questions on the chart below and on your knowledge of biology. ...
DNA
... • Replication – creation of new exact copies of DNA to be used in newly made cells Packet page # ...
... • Replication – creation of new exact copies of DNA to be used in newly made cells Packet page # ...
References - Proceedings of the Royal Society B
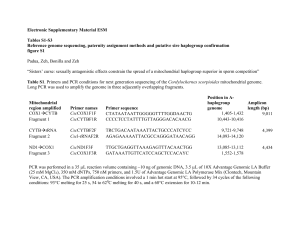
... CYTB are located approximately opposite one another in the circular mitochondrial genome, and primers from these two genes can be used to amplify the entire genome in two fragments of similar length. In order to span the entire genome, 35 primer pairs were designed, with ~ 100-bp overlap between con ...
... CYTB are located approximately opposite one another in the circular mitochondrial genome, and primers from these two genes can be used to amplify the entire genome in two fragments of similar length. In order to span the entire genome, 35 primer pairs were designed, with ~ 100-bp overlap between con ...
Workshop-2010 - An-Najah Blogs - An
... of clinical and environmental species of the genera Enterococcus, Lactobacillus and Streptococcus • The use of partial sequences of pheS, rpoA and atpA genes provides a rapid and low cost tool for species identification ...
... of clinical and environmental species of the genera Enterococcus, Lactobacillus and Streptococcus • The use of partial sequences of pheS, rpoA and atpA genes provides a rapid and low cost tool for species identification ...
1. To research…
... Sickle Cell Anemia is a genetic disorder caused by a mutation in the DNA. People with Sickle Cell have red blood cells with sickle shaped hemoglobin that cannot hold as much oxygen. They get out of breath easily and have a lot of pain. Below is the base sequence for the normal protein for normal hem ...
... Sickle Cell Anemia is a genetic disorder caused by a mutation in the DNA. People with Sickle Cell have red blood cells with sickle shaped hemoglobin that cannot hold as much oxygen. They get out of breath easily and have a lot of pain. Below is the base sequence for the normal protein for normal hem ...
Leukaemia Section t(12;22)(p13;q11-12) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... RAEB evolving towards ANLL; ‘atypical CML’; may occur secondary to genotoxic exposure. Epidemiology Yet poorly known; median age: 22 yrs (range 8-60; n=11 cases herein reviewed); male predominance so far ...
... RAEB evolving towards ANLL; ‘atypical CML’; may occur secondary to genotoxic exposure. Epidemiology Yet poorly known; median age: 22 yrs (range 8-60; n=11 cases herein reviewed); male predominance so far ...
DNA - The Double Helix
... particular protein which in turn codes for a trait. Hence you hear it commonly referred to as the gene for baldness or the gene for blue eyes. Meanwhile, DNA is the chemical that genes and chromosomes are made of. DNA is called a nucleic acid because it was first found in the nucleus. We now know th ...
... particular protein which in turn codes for a trait. Hence you hear it commonly referred to as the gene for baldness or the gene for blue eyes. Meanwhile, DNA is the chemical that genes and chromosomes are made of. DNA is called a nucleic acid because it was first found in the nucleus. We now know th ...
syllabus components
... analyze human pedigrees for patterns of inheritance; understand the concept of gene linkage; calculate recombination frequencies between two genes and use this to construct gene maps; describe chromosomal structure; list chromosomal abnormalities and their effects on development; compare and contras ...
... analyze human pedigrees for patterns of inheritance; understand the concept of gene linkage; calculate recombination frequencies between two genes and use this to construct gene maps; describe chromosomal structure; list chromosomal abnormalities and their effects on development; compare and contras ...
lay-person-summary
... also dictate whether or not an individual gets asthma but more research is needed in that area. ...
... also dictate whether or not an individual gets asthma but more research is needed in that area. ...
DOC - San Juan College
... analyze human pedigrees for patterns of inheritance; understand the concept of gene linkage; calculate recombination frequencies between two genes and use this to construct gene maps; describe chromosomal structure; list chromosomal abnormalities and their effects on development; compare and contras ...
... analyze human pedigrees for patterns of inheritance; understand the concept of gene linkage; calculate recombination frequencies between two genes and use this to construct gene maps; describe chromosomal structure; list chromosomal abnormalities and their effects on development; compare and contras ...
A common ancestor
... from a common ancestor • 1000 nucleotides (~333 aa) – 41000 or 10600 different sequences – ~1079 atoms in the universe ...
... from a common ancestor • 1000 nucleotides (~333 aa) – 41000 or 10600 different sequences – ~1079 atoms in the universe ...
Various Career Options Available
... where, and under what conditions genes are expressed. Proteomics study of protein expression in time and space, more important than gene expression studies to whats actually happening in the cell. Structural genomics 3-D structures of one or more proteins from each protein family, clues to functio ...
... where, and under what conditions genes are expressed. Proteomics study of protein expression in time and space, more important than gene expression studies to whats actually happening in the cell. Structural genomics 3-D structures of one or more proteins from each protein family, clues to functio ...
Protein Synthesis
... 17. UAG is a stop codon. What might happen if the uracil in this codon was changed to cytosine? Glutamine would have been added to the polypeptide chain. 18. List the four different sets of DNA nucleotide sequences that code for the amino acid Valine. Explain why this redundancy in the genetic code ...
... 17. UAG is a stop codon. What might happen if the uracil in this codon was changed to cytosine? Glutamine would have been added to the polypeptide chain. 18. List the four different sets of DNA nucleotide sequences that code for the amino acid Valine. Explain why this redundancy in the genetic code ...