RG 7 - Cell Cycle and Mitosis
... furrow and completing cellular division in animal cells. 11. Describe how a new cell wall is formed during plant cell division. 12. In which eukaryotic organisms can mitosis function as a method of reproduction? Is this type of reproduction sexual or asexual? Why? 13. Review alternation of generatio ...
... furrow and completing cellular division in animal cells. 11. Describe how a new cell wall is formed during plant cell division. 12. In which eukaryotic organisms can mitosis function as a method of reproduction? Is this type of reproduction sexual or asexual? Why? 13. Review alternation of generatio ...
mbv4160_mbv9160_exam_2011_final
... 2) Explain in brief Knudsons two hit hypothesis 3) List known mechanisms by which tumor suppressor genes can be inactivated II TP53 “the guardian of the genome” and cell cycle 4) Explain in brief how a single mutation in the tumor suppressor gene TP53 can have a dominant negative effect 5) Explain i ...
... 2) Explain in brief Knudsons two hit hypothesis 3) List known mechanisms by which tumor suppressor genes can be inactivated II TP53 “the guardian of the genome” and cell cycle 4) Explain in brief how a single mutation in the tumor suppressor gene TP53 can have a dominant negative effect 5) Explain i ...
Endosymbiotic Theory for the Evolution of Eukaryotic Cells
... Endosymbiotic Theory for the Evolution of Eukaryotic Cells The theory that eukaryotic cells arose from a symbiotic relationship formed when a _____________________________ ________________________________. A mutually beneficial relationship evolved into membrane-bound organelles. ...
... Endosymbiotic Theory for the Evolution of Eukaryotic Cells The theory that eukaryotic cells arose from a symbiotic relationship formed when a _____________________________ ________________________________. A mutually beneficial relationship evolved into membrane-bound organelles. ...
Cell Reproduction
... number of cells is increased without changing the information contained in the DNA or the amount of DNA in those cells. ...
... number of cells is increased without changing the information contained in the DNA or the amount of DNA in those cells. ...
Name
... Dr. Yi-Ching Wang studies the molecular mechanisms involved in lung tumorigenesis. Dr. Wang investigates the etiological association of alterations in tumor suppressor genes and oncogenes with lung tumorigenesis. The alteration analyses include the following aspects: gene mutation and polymorphism, ...
... Dr. Yi-Ching Wang studies the molecular mechanisms involved in lung tumorigenesis. Dr. Wang investigates the etiological association of alterations in tumor suppressor genes and oncogenes with lung tumorigenesis. The alteration analyses include the following aspects: gene mutation and polymorphism, ...
Warm up
... 46:What happens during Meiosis? a:Each sex cell loses half of its chromosome B:Sex cells copies itself to form 4 new chromosomes. 47:What is mutation? a:any change in a gene or chromosome B:any change in the phenotype. 48: The mistaken idea that living things arise from nonliving sources is known as ...
... 46:What happens during Meiosis? a:Each sex cell loses half of its chromosome B:Sex cells copies itself to form 4 new chromosomes. 47:What is mutation? a:any change in a gene or chromosome B:any change in the phenotype. 48: The mistaken idea that living things arise from nonliving sources is known as ...
Cell characteristics
... A physical basis for mitotic clock is the DNA at the tip of chromosome. Other external factors that control mitosis are the kinases ( proteins) and cyclins , hormones and growth factors. Internal factors that control the mitosis are the surface area ratio between cell and membrane and the cell ...
... A physical basis for mitotic clock is the DNA at the tip of chromosome. Other external factors that control mitosis are the kinases ( proteins) and cyclins , hormones and growth factors. Internal factors that control the mitosis are the surface area ratio between cell and membrane and the cell ...
Gene Section GSDMA (gasdermin A) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... GSDMA protein is expressed in pit cells of the gastric epithelium, where it is involved in maintenance of homeostasis by its apoptosis induction ability under TGF-beta signaling. Its expression was also observed in epithelial cells of the esophagus, skin and mammary ...
... GSDMA protein is expressed in pit cells of the gastric epithelium, where it is involved in maintenance of homeostasis by its apoptosis induction ability under TGF-beta signaling. Its expression was also observed in epithelial cells of the esophagus, skin and mammary ...
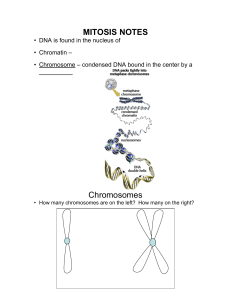
Mitosis Notes
... • Nuclear membrane • Chromatin condenses to form • Microtubules form spindle fibers, attach to ...
... • Nuclear membrane • Chromatin condenses to form • Microtubules form spindle fibers, attach to ...
Inheritance dominoes Punnett square diagram carriers family trees
... membranes and is caused by a recessive allele ...
... membranes and is caused by a recessive allele ...
Cancer is generally understood as a genetic or cellular disease
... and Pathology, University of Rome “La Sapienza” Cancer is generally understood as a genetic or cellular disease, which results either from the overexpression or lack of expression of certain genes and related proteins. However, intensive research on cancer, along the lines depicted by the current ep ...
... and Pathology, University of Rome “La Sapienza” Cancer is generally understood as a genetic or cellular disease, which results either from the overexpression or lack of expression of certain genes and related proteins. However, intensive research on cancer, along the lines depicted by the current ep ...
No Slide Title
... Oncogenes --> a cancer-causing gene, any of several mutant genes that cause cells to exhibit rapid, uncontrolled proliferation Discovered in tumor-causing viruses Very similar to normal genes in the body called proto-oncogenes (growth regulating genes) ...
... Oncogenes --> a cancer-causing gene, any of several mutant genes that cause cells to exhibit rapid, uncontrolled proliferation Discovered in tumor-causing viruses Very similar to normal genes in the body called proto-oncogenes (growth regulating genes) ...
The Big Picture: A Review of Biology
... 12. What are the 2 ways things are transported across the cell membrane? Give 2 examples of both. 13. What is the process by which organisms use energy from sunlight to make their own food (glucose)? 14. What is the process that breaks down glucose in order to make energy for an organism? And give t ...
... 12. What are the 2 ways things are transported across the cell membrane? Give 2 examples of both. 13. What is the process by which organisms use energy from sunlight to make their own food (glucose)? 14. What is the process that breaks down glucose in order to make energy for an organism? And give t ...
Gene Section LPHN2 (latrophilin 2) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... Representation of the genomic structure of LPHH1. Black blocks represent core exons which are present in the majority of gene transcripts. The yellow blocks represent alternatively spliced coding exons which may be incorporated variably in transcripts derived from different cell types/tissues or as ...
... Representation of the genomic structure of LPHH1. Black blocks represent core exons which are present in the majority of gene transcripts. The yellow blocks represent alternatively spliced coding exons which may be incorporated variably in transcripts derived from different cell types/tissues or as ...
Leukaemia Section t(12;15)(p13;q25) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... activation, leading to constitutive elevation of cyclin D1, and increased cell cycle progression. ETV6NTRK3 also leads to constitutive activation of two of the major effector pathways of NTRK3: the RasMAPK mitogenic pathway and the phosphatidyl inositol-3-kinase (PI3K) pathway leading to activation ...
... activation, leading to constitutive elevation of cyclin D1, and increased cell cycle progression. ETV6NTRK3 also leads to constitutive activation of two of the major effector pathways of NTRK3: the RasMAPK mitogenic pathway and the phosphatidyl inositol-3-kinase (PI3K) pathway leading to activation ...
Syllabus
... This laboratory for majors in Chemical Biology and Biochemistry and Molecular Biology is designed to have students learn the theory and practicality of modern laboratory science by investigation of unknown properties of the yeast kinesin Cin8. The course breadth covers Molecular and Cell Biology wit ...
... This laboratory for majors in Chemical Biology and Biochemistry and Molecular Biology is designed to have students learn the theory and practicality of modern laboratory science by investigation of unknown properties of the yeast kinesin Cin8. The course breadth covers Molecular and Cell Biology wit ...
Investigating the role of FAM109A/CCSER1 in cell division and
... 1. Analysis of the function and regulation of FAM109A in cell division Although a preliminary study indicated a requirement for FAM109 in cell division (3), its exact function(s) are still unknown. Thus, to fully understand the role(s) of FAM109A in cell division we will deplete th ...
... 1. Analysis of the function and regulation of FAM109A in cell division Although a preliminary study indicated a requirement for FAM109 in cell division (3), its exact function(s) are still unknown. Thus, to fully understand the role(s) of FAM109A in cell division we will deplete th ...
Chapter 13: The Cell Cycle
... Nucleoid disappears 2 sister chromatids Mitotic spindle forms Centrosome Animals – Centrioles moves apart to poles ...
... Nucleoid disappears 2 sister chromatids Mitotic spindle forms Centrosome Animals – Centrioles moves apart to poles ...
Post-doc researcher - Labex GR-Ex
... Full-time position founded by the Canceropole Ile-de-France for 2 years available in the Department Development/Reproduction/cancer in the team headed by Dr Patrick Mayeux named “Signaling and apoptosis in normal and pathological hematopoiesis” in the group of Pr. Michaela FONTENAY dedicated to func ...
... Full-time position founded by the Canceropole Ile-de-France for 2 years available in the Department Development/Reproduction/cancer in the team headed by Dr Patrick Mayeux named “Signaling and apoptosis in normal and pathological hematopoiesis” in the group of Pr. Michaela FONTENAY dedicated to func ...
Gene Section ATF3 (activating transcription factor 3) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... transcription factors and both homodimerize and heterodimerize with other members of CREB/ATF family, including C/EBPg, CHOP/DDIT3, ATF2, Jun, JunB, p21SNFT/JDP1, and Nrf2/NFE2L2. ATF3 and various heterodimers containing ATF3 has been shown to bind to a consensus cAMP response element (5'-GTGACGT[AC ...
... transcription factors and both homodimerize and heterodimerize with other members of CREB/ATF family, including C/EBPg, CHOP/DDIT3, ATF2, Jun, JunB, p21SNFT/JDP1, and Nrf2/NFE2L2. ATF3 and various heterodimers containing ATF3 has been shown to bind to a consensus cAMP response element (5'-GTGACGT[AC ...