Gene Section AKT3 (v-akt murine thymoma viral oncogene
... Location: 1q44 Note: Location in the mouse: chromosome 1 in band H4-H6. ...
... Location: 1q44 Note: Location in the mouse: chromosome 1 in band H4-H6. ...
basic characterisation of hiPSC.
... Basic characterization of hiPSC BSCC will provide a basic characterization of hiPSC including: ...
... Basic characterization of hiPSC BSCC will provide a basic characterization of hiPSC including: ...
Practice Midterm 2
... B) signal reception, signal transduction, and cellular response. C) signal reception, nucleus disintegration, and new cell generation. D) the alpha, beta, and gamma stages. E) signal reception, cellular response, ...
... B) signal reception, signal transduction, and cellular response. C) signal reception, nucleus disintegration, and new cell generation. D) the alpha, beta, and gamma stages. E) signal reception, cellular response, ...
Functional Characterization of Soybean Transcription Factor
... major targets to increase the tolerance of plants to stresses, since these proteins control the expression of several genes simultaneously. Members of the bZIP family of transcription factors are characterized by having a leucine zipper domain which is a basic DNA binding domain. Previous research d ...
... major targets to increase the tolerance of plants to stresses, since these proteins control the expression of several genes simultaneously. Members of the bZIP family of transcription factors are characterized by having a leucine zipper domain which is a basic DNA binding domain. Previous research d ...
Ch 2: Genetics and Prenatal Development
... 11. _______________________________ is when eggs and sperm are fertilized in a petri dish then placed in the mother’s uterus for further development. 12. During ____________________ the cell copies its own chromosome. 13. During____________________ sperm and egg cells form. 14. The sex cell is calle ...
... 11. _______________________________ is when eggs and sperm are fertilized in a petri dish then placed in the mother’s uterus for further development. 12. During ____________________ the cell copies its own chromosome. 13. During____________________ sperm and egg cells form. 14. The sex cell is calle ...
09-13-11 st bio3 notes
... -describe how cells are connected and how they communicate with each other -describe nine important landmarks (organelles) in eukaryotic cells ___ Cell Theory: 1. All living organisms are made up of one or more cells 2. All cells arise from other pre-existing cells Cell: smallest unit of life that c ...
... -describe how cells are connected and how they communicate with each other -describe nine important landmarks (organelles) in eukaryotic cells ___ Cell Theory: 1. All living organisms are made up of one or more cells 2. All cells arise from other pre-existing cells Cell: smallest unit of life that c ...
Chapter Notes
... -Forms a helix structure (a twisted ladder). This structure was first described by Watson and Crick. When a cell is ready to divide, each strand of loosely coiled DNA folds up further into a compact, Xshaped structure called a chromosome. Chromosomes within the nucleus are found in pairs. Most human ...
... -Forms a helix structure (a twisted ladder). This structure was first described by Watson and Crick. When a cell is ready to divide, each strand of loosely coiled DNA folds up further into a compact, Xshaped structure called a chromosome. Chromosomes within the nucleus are found in pairs. Most human ...
Thesis Proposal Format
... Cripto and Cancer The human cripto gene is a growth factor of the EGF-CFC family that is found only in vertebrates. It is a small protein that is rich in cysteines. (1) It has an EGF-like domain and a Cripto/Frl/Criptic (CFC) domain that have been found to be conserved across species. It was the fir ...
... Cripto and Cancer The human cripto gene is a growth factor of the EGF-CFC family that is found only in vertebrates. It is a small protein that is rich in cysteines. (1) It has an EGF-like domain and a Cripto/Frl/Criptic (CFC) domain that have been found to be conserved across species. It was the fir ...
7.013 Sp 05 Section Self-quiz
... 3 b) How do prokaryotic cells differ from eukaryotic cells? (Note the prokaryotic cell is much much smaller than the eukaryotic cell but they are both drawn so that you can see and compare interanal components.) ...
... 3 b) How do prokaryotic cells differ from eukaryotic cells? (Note the prokaryotic cell is much much smaller than the eukaryotic cell but they are both drawn so that you can see and compare interanal components.) ...
spring 2000 exam 1
... 11. Cancer in situ (benign cancer) a. is highly metastatic b. is usually contained in a capsule within the tissue of origin. c. contains cells that most likely have not been affected by any mutations to oncogenes or tumor suppressor genes. d. consists of cells that have lost their ability to adhere ...
... 11. Cancer in situ (benign cancer) a. is highly metastatic b. is usually contained in a capsule within the tissue of origin. c. contains cells that most likely have not been affected by any mutations to oncogenes or tumor suppressor genes. d. consists of cells that have lost their ability to adhere ...
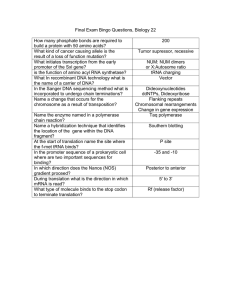
How many phosphate bonds are required to build a protein with 50
... What kind of cancer causing allele is the result of a loss of function mutation? What initiates transcription from the early promoter of the Sxl gene? is the function of amino acyl RNA synthetase? What In recombinant DNA technology what is the name of a carrier of DNA? In the Sanger DNA sequencing m ...
... What kind of cancer causing allele is the result of a loss of function mutation? What initiates transcription from the early promoter of the Sxl gene? is the function of amino acyl RNA synthetase? What In recombinant DNA technology what is the name of a carrier of DNA? In the Sanger DNA sequencing m ...
Name
... In the space at the left, write the letter of the term, number, or phrase that best answers each question. 1. How many chromosomes are found in human body cells? A. 11 B. 23 C. 46 D. 92 2. Which describes a gene? A. chromosome pair B. chromosome trait C. DNA segment D. haploid cell 3. How is an alle ...
... In the space at the left, write the letter of the term, number, or phrase that best answers each question. 1. How many chromosomes are found in human body cells? A. 11 B. 23 C. 46 D. 92 2. Which describes a gene? A. chromosome pair B. chromosome trait C. DNA segment D. haploid cell 3. How is an alle ...
(1) Division and differentiation in human cells
... DIFFERENTIATION IN HUMAN CELLS (F) Cancer Cells ...
... DIFFERENTIATION IN HUMAN CELLS (F) Cancer Cells ...
Leukaemia Section t(8;12)(q24;q22) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... B-cell translocation gene 1 (BTG1) is an antiproliferative gene; it regulates cell growth and differentiation. BTG1 is strongly expressed in the G0/G1 phases of the cell cycle, and then downregulated during the G1 phase. Overexpression of BTG1 results in a retardation of cell proliferation. Potentia ...
... B-cell translocation gene 1 (BTG1) is an antiproliferative gene; it regulates cell growth and differentiation. BTG1 is strongly expressed in the G0/G1 phases of the cell cycle, and then downregulated during the G1 phase. Overexpression of BTG1 results in a retardation of cell proliferation. Potentia ...
DNA Repilication and Transmission
... There are two types: autosomes and sex chromosomes (allosomes). The autosomes occur as homologous pairs, but only a female’s allosomes are homologous. The chromosomes of a person constitute one’s karyotype. ...
... There are two types: autosomes and sex chromosomes (allosomes). The autosomes occur as homologous pairs, but only a female’s allosomes are homologous. The chromosomes of a person constitute one’s karyotype. ...
The Major Histocompatibility Complex
... code for the two subunits of the heterodimeric antigen receptor on the surface of the T cell; its complete deduced primary structure is presented. ...
... code for the two subunits of the heterodimeric antigen receptor on the surface of the T cell; its complete deduced primary structure is presented. ...
Neoplasia Etiology genetic Neoplasia is defined as: "an abnormal
... Growth Factors: Genes that encode growth factors may become oncogenic. Growth Factor Receptors: most are transmembrane proteins that cause phosphorylation of proteins on the cytoplasmic side when activated. Point mutations in the ret protooncogene (codes for receptor associated with glial cells) are ...
... Growth Factors: Genes that encode growth factors may become oncogenic. Growth Factor Receptors: most are transmembrane proteins that cause phosphorylation of proteins on the cytoplasmic side when activated. Point mutations in the ret protooncogene (codes for receptor associated with glial cells) are ...
Big Picture wkst
... d. prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus. _____ 7. Carbon-based molecules such as proteins and nucleic acids play important roles in living things because of their a. simple molecular structures. b. ability to dissolve other substances. c. unique bonding ability. d. high specific heat. _____ 8. What are ...
... d. prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus. _____ 7. Carbon-based molecules such as proteins and nucleic acids play important roles in living things because of their a. simple molecular structures. b. ability to dissolve other substances. c. unique bonding ability. d. high specific heat. _____ 8. What are ...
Gene Section SASH1 (SAM and SH3 domain containing 1)
... Other names: SH3D6A, dJ323M4, dJ323M4.1 HGNC (Hugo): SASH1 Location: 6q24.3 ...
... Other names: SH3D6A, dJ323M4, dJ323M4.1 HGNC (Hugo): SASH1 Location: 6q24.3 ...
Gene Section MTA3 (metastasis associated 1 family, member 3)
... Epithelial cancer Deregulation of MTA3 expression in epithelial breast cancer, endometrial cancer, and ovarian cancer is associated with cancer progression by promoting the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). It is principally believed that reduced expression of MTA3 allows higher expression le ...
... Epithelial cancer Deregulation of MTA3 expression in epithelial breast cancer, endometrial cancer, and ovarian cancer is associated with cancer progression by promoting the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). It is principally believed that reduced expression of MTA3 allows higher expression le ...
Review Questions 1. A rabbit`s fur can be all different colors. The
... a. Galileo wrote a book proving the sun is the center of the universe not the Earth. This is the heliocentric model. b. Rachel Carson performed experiments determining that DDT, a pesticide, was softening the shells of birds and caused a decline in the bird populations. c. Jane Goodall’s observation ...
... a. Galileo wrote a book proving the sun is the center of the universe not the Earth. This is the heliocentric model. b. Rachel Carson performed experiments determining that DDT, a pesticide, was softening the shells of birds and caused a decline in the bird populations. c. Jane Goodall’s observation ...
Lecture #9 Date
... lifetime Plants: morphogenesis and growth of overall size occur throughout lifetime of plant; apical meristems (perpetually embryonic regions), responsible for plant’s continual growth ...
... lifetime Plants: morphogenesis and growth of overall size occur throughout lifetime of plant; apical meristems (perpetually embryonic regions), responsible for plant’s continual growth ...
Monkemeier March 19, 2015 Honors Biology Unit 8: Cell
... 2. List the three processes that must occur in order for any type of cell to divide (reproduce). 3. WHY do prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells reproduce using different processes? 4. Do prokaryotic cells reproduce faster than eukaryotic cells? 5. Compare the genetic material of a prokaryote to th ...
... 2. List the three processes that must occur in order for any type of cell to divide (reproduce). 3. WHY do prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells reproduce using different processes? 4. Do prokaryotic cells reproduce faster than eukaryotic cells? 5. Compare the genetic material of a prokaryote to th ...