Key Terms Cell Reproduction
... 8. Starting with one diploid cell, how many haploid sperm cells have formed after both phases of meiosis have been completed? 9. How are sex cells different from other cells in the body? 10. What happens during fertilization? ...
... 8. Starting with one diploid cell, how many haploid sperm cells have formed after both phases of meiosis have been completed? 9. How are sex cells different from other cells in the body? 10. What happens during fertilization? ...
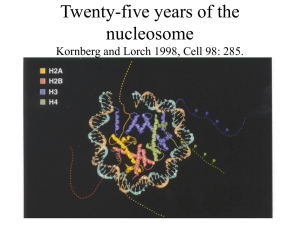
Twenty-five years of the nucleosome Kornberg and Lorch 1998, Cell
... 2. Immunocytochemistry- observe phospho-H3 throughout chromosomes during cell division Thus, this must play a role is chromosome condensation during mitosis 3. Models1. Phosphorylation + acetylation allows activation of gene expression, depending on context 2. Phospho-H3 loosens chromatin, enhancin ...
... 2. Immunocytochemistry- observe phospho-H3 throughout chromosomes during cell division Thus, this must play a role is chromosome condensation during mitosis 3. Models1. Phosphorylation + acetylation allows activation of gene expression, depending on context 2. Phospho-H3 loosens chromatin, enhancin ...
here
... Some genes either do not have clear homologues in mice, or were not on the array. Those are listed here. ...
... Some genes either do not have clear homologues in mice, or were not on the array. Those are listed here. ...
BIOL 245 Endocrine System 1 I. Hormones A. From endocrine
... A. From endocrine glands B. Target tissues C. Classes 1. protein based a. glycoproteins: b. polypeptides 2. biogenic amines (monoamines) - amino acid-based: - tyrosine derived: 3. steroids (cholesterol-based) a. cortisol b. sex steroids D. Synthesis and transport 1. steroids a. bound to hydrophilic ...
... A. From endocrine glands B. Target tissues C. Classes 1. protein based a. glycoproteins: b. polypeptides 2. biogenic amines (monoamines) - amino acid-based: - tyrosine derived: 3. steroids (cholesterol-based) a. cortisol b. sex steroids D. Synthesis and transport 1. steroids a. bound to hydrophilic ...
Cell Division - Glasgow Science Centre
... 2. Cell division is a means in which the number of cells in an organism increases (T) 3. The cytoplasm controls the cell’s activities (F – Nucleus) 4. The nucleus of the cell carries chromosomes that are essential in growth and development (T) 5. A chromosome is made up of two halves, each half is c ...
... 2. Cell division is a means in which the number of cells in an organism increases (T) 3. The cytoplasm controls the cell’s activities (F – Nucleus) 4. The nucleus of the cell carries chromosomes that are essential in growth and development (T) 5. A chromosome is made up of two halves, each half is c ...
college-prep biology midterm review
... The definition of the word biology The areas of biology we’ll study this year and their definitions The differences between a hypothesis, theory, and a law The steps of the scientific method the contents of the safety contract how to make tables and graphs according to the handout given in class How ...
... The definition of the word biology The areas of biology we’ll study this year and their definitions The differences between a hypothesis, theory, and a law The steps of the scientific method the contents of the safety contract how to make tables and graphs according to the handout given in class How ...
Chapter 9 answers
... manage to hold together until cell division and mitosis occurred, the two daughter cells would have two different copies of the DNA; one would have the old version, with cytosine, the second would have the new version with adenine. Second, if it were to be read by an mRNA molecule, one of the codons ...
... manage to hold together until cell division and mitosis occurred, the two daughter cells would have two different copies of the DNA; one would have the old version, with cytosine, the second would have the new version with adenine. Second, if it were to be read by an mRNA molecule, one of the codons ...
cells? - Madeira City Schools
... F plasmid – contains genes that enable cell to form a “mating bridge” with a cell that does not have the plasmid. R plasmid – contains genes that make it resistant to antibiotics What is the difference between F+ cells and F- cells? F+ cells contain the F plasmid and therefore are donors during conj ...
... F plasmid – contains genes that enable cell to form a “mating bridge” with a cell that does not have the plasmid. R plasmid – contains genes that make it resistant to antibiotics What is the difference between F+ cells and F- cells? F+ cells contain the F plasmid and therefore are donors during conj ...
12.5 Gene Regulation
... • Cell differentiation: when the embryo is developing, the cells are not just going to divide, they will turn into specialized cells – Each of these specialized cells will have specialized structure and function ...
... • Cell differentiation: when the embryo is developing, the cells are not just going to divide, they will turn into specialized cells – Each of these specialized cells will have specialized structure and function ...
The Role of NF-kB in Cancer Cell Growth
... NF-B is a transcription factor that serves as a master switch for turning on certain immune and inflammatory responses. NF-B alters cell behavior in many ways; it inhibits apoptosis (programmed cell death), increases cell proliferation, and increases inflammatory and immune response. Recent eviden ...
... NF-B is a transcription factor that serves as a master switch for turning on certain immune and inflammatory responses. NF-B alters cell behavior in many ways; it inhibits apoptosis (programmed cell death), increases cell proliferation, and increases inflammatory and immune response. Recent eviden ...
lecture - McLoon Lab
... G1 phase during which proteins that initiate or block division are expressed Restriction point - a condition in which a cell is destined to progress through mitosis regardless of any changes in its environment S ...
... G1 phase during which proteins that initiate or block division are expressed Restriction point - a condition in which a cell is destined to progress through mitosis regardless of any changes in its environment S ...
Powerpoint Presentation: Gene Therapy
... Normal gene inserted into the genome to replace non-functional gene Trials began in 1990 Cystic fibrosis gene moderately successful ...
... Normal gene inserted into the genome to replace non-functional gene Trials began in 1990 Cystic fibrosis gene moderately successful ...
PowerPoint 簡報
... All organisms consist of cells that multiply through cell division. An adult human being has approximately 100 000 billion cells, all originating from a single cell, the fertilized egg cell. In adults there is also an enormous number of continuously dividing cells replacing those dying. Before a cel ...
... All organisms consist of cells that multiply through cell division. An adult human being has approximately 100 000 billion cells, all originating from a single cell, the fertilized egg cell. In adults there is also an enormous number of continuously dividing cells replacing those dying. Before a cel ...
Concept 9.2 The Cell Cycle Multiplies Cells
... 6. centromere 7. cell cycle 8. interphase 9. mitotic phase 10. mitosis 11. cytokinesis Concept 9.1: All cells come from cells I. Repair and Growth A. The___________________________________ layer of your skin is actually a layer of dead cells B. Underneath the outer layer is a layer of ______________ ...
... 6. centromere 7. cell cycle 8. interphase 9. mitotic phase 10. mitosis 11. cytokinesis Concept 9.1: All cells come from cells I. Repair and Growth A. The___________________________________ layer of your skin is actually a layer of dead cells B. Underneath the outer layer is a layer of ______________ ...
Use the first two meiosis diagrams to show independent assortment
... B. an enzyme in cell membranes that converts ATP into cAMP C. enzymes that transfer phosphate groups from ATP to a protein ...
... B. an enzyme in cell membranes that converts ATP into cAMP C. enzymes that transfer phosphate groups from ATP to a protein ...
Receptor tyrosine kinases: role in cancer
... erlotinib) show modest antitumour activity when administered as single agents in unselected patient populations with non-small-cell lung carcinoma, but they show a positive clinical response in a subset of patients that harbour somatic mutations in the EGFR gene and whose tumours may be dependent on ...
... erlotinib) show modest antitumour activity when administered as single agents in unselected patient populations with non-small-cell lung carcinoma, but they show a positive clinical response in a subset of patients that harbour somatic mutations in the EGFR gene and whose tumours may be dependent on ...
Questions and missing material
... – Generally half of the function /activity is enough for maintenance of normal functions (recessive) – Not produced at all or protein is immediately degraded = null-allele – dominant-negative effect: defective protein disturbs the function of normal protein ...
... – Generally half of the function /activity is enough for maintenance of normal functions (recessive) – Not produced at all or protein is immediately degraded = null-allele – dominant-negative effect: defective protein disturbs the function of normal protein ...
“The Nucleus: Not Just a Sack of Chromosomes”
... Contains most of the cell’s genetic material It’s function is to maintain the integrity of these genes and to control the activities of the cell Found only in eukaryotic cells ...
... Contains most of the cell’s genetic material It’s function is to maintain the integrity of these genes and to control the activities of the cell Found only in eukaryotic cells ...
Molecular Biology of Cancer
... Why is bcr-abl an oncogene? • The abl gene codes for a membrane receptor with protein tyrosine kinase activity (Abl). • A protein tyrosine kinase puts phosphate groups on the amino acid tyrosine in proteins. • The Abl protein is at the beginning of a signal transduction pathway that leads to activa ...
... Why is bcr-abl an oncogene? • The abl gene codes for a membrane receptor with protein tyrosine kinase activity (Abl). • A protein tyrosine kinase puts phosphate groups on the amino acid tyrosine in proteins. • The Abl protein is at the beginning of a signal transduction pathway that leads to activa ...
Heredity and Genetics Vocabulary (Part 1)
... chromosomes of an organism, which is found only in the reproductive organs of a plant or animal. ...
... chromosomes of an organism, which is found only in the reproductive organs of a plant or animal. ...
Researchers Find "Immortality" Enzyme in Cancer Cells Cancer
... The telomere is made up of DNA segments that help control the accuracy of genetic reproduction when a cell divides to create a new cell. In cancer cells, it is thought that the telomere does not erode with each cell division, thus enabling cancer cells, in a sense, to be "immortal." Telomeres in can ...
... The telomere is made up of DNA segments that help control the accuracy of genetic reproduction when a cell divides to create a new cell. In cancer cells, it is thought that the telomere does not erode with each cell division, thus enabling cancer cells, in a sense, to be "immortal." Telomeres in can ...
PDF
... signaling systems, but the references to history continue throughout the book and provide interesting tidbits that ground our current terminology in the past. The multifunctional serine/threonine protein kinase GSK3, for example, has its name because it phosphorylates a certain residue known as site ...
... signaling systems, but the references to history continue throughout the book and provide interesting tidbits that ground our current terminology in the past. The multifunctional serine/threonine protein kinase GSK3, for example, has its name because it phosphorylates a certain residue known as site ...