Reading DNA - teacherknowledge
... to attach to these three nucleotides. (Ex. If your first three nucleotides are AUG, write UAC on the cresent. • Now find the amino acid, based on the mRNA sequence that the tRNA will bring with it. Use the Amino Acid Key below to determine which amino acid these 3 chemical bases code for. Because we ...
... to attach to these three nucleotides. (Ex. If your first three nucleotides are AUG, write UAC on the cresent. • Now find the amino acid, based on the mRNA sequence that the tRNA will bring with it. Use the Amino Acid Key below to determine which amino acid these 3 chemical bases code for. Because we ...
transcription
... There are 5 types of RNA, each encoded by its own type of gene: mRNA -(80 % in eucaryoyes) Messenger RNA: Encodes the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide. tRNA - (15 % in eucaryoyes) Transfer RNA: Brings amino acids to ribosomes during translation. mRNA - (5 % in eucaryoyes) Ribosomal RNA: with r ...
... There are 5 types of RNA, each encoded by its own type of gene: mRNA -(80 % in eucaryoyes) Messenger RNA: Encodes the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide. tRNA - (15 % in eucaryoyes) Transfer RNA: Brings amino acids to ribosomes during translation. mRNA - (5 % in eucaryoyes) Ribosomal RNA: with r ...
gene expression - cloudfront.net
... DNA molecules pass inherited information to RNA, more specifically, messenger RNA (mRNA) which in turn codes for proteins. The flow of information is represented as: DNA ...
... DNA molecules pass inherited information to RNA, more specifically, messenger RNA (mRNA) which in turn codes for proteins. The flow of information is represented as: DNA ...
GENETICS and the DNA code NOTES BACKGROUND DNA is the
... “letters,” codes for an amino acid, the building block of proteins. Like DNA, RNA is a nucleic acid made of repeated nucleotides. An RNA nucleotide consists of ribose sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogen base. RNA is very similar to DNA, but differs in a few important structural details: in the ...
... “letters,” codes for an amino acid, the building block of proteins. Like DNA, RNA is a nucleic acid made of repeated nucleotides. An RNA nucleotide consists of ribose sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogen base. RNA is very similar to DNA, but differs in a few important structural details: in the ...
Gene Expression Worksheet
... 2. Where does the replication of DNA occur inside the cell and what part of the cell cycle? ...
... 2. Where does the replication of DNA occur inside the cell and what part of the cell cycle? ...
Slide 1 - E-Learning/An-Najah National University
... The class of RNA found in ribosomes is called ribosomal RNA (rRNA). During polypeptide synthesis, rRNA provides the site where polypeptides are assembled. Transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules both transport the amino acids to the ribosome for use in building the polypeptides and position each amino aci ...
... The class of RNA found in ribosomes is called ribosomal RNA (rRNA). During polypeptide synthesis, rRNA provides the site where polypeptides are assembled. Transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules both transport the amino acids to the ribosome for use in building the polypeptides and position each amino aci ...
Gene Expression
... • All cells in the human body have the same DNA and the same set of genes, yet different cells look different and do different jobs. • Cells have systems to regulate which genes are “turned on” (transcribed) and which are not. ...
... • All cells in the human body have the same DNA and the same set of genes, yet different cells look different and do different jobs. • Cells have systems to regulate which genes are “turned on” (transcribed) and which are not. ...
Gene Regulation -
... Mutations in the I gene that prevent the repressor protein from interacting with lactose, but still bind to the operator and permanently turn off all transcription. These are called i mutations for superrepressors. ...
... Mutations in the I gene that prevent the repressor protein from interacting with lactose, but still bind to the operator and permanently turn off all transcription. These are called i mutations for superrepressors. ...
PartFourSumm_ThemesInRegulation.doc
... in which the extent of translation of a leader peptide determines whether or not a -independent terminator of transcription is used. An example from mammals is the HIV virus, in which a Tat protein acting at a TAR element close to the 5' end of the mRNA will determine the efficiency of elongation p ...
... in which the extent of translation of a leader peptide determines whether or not a -independent terminator of transcription is used. An example from mammals is the HIV virus, in which a Tat protein acting at a TAR element close to the 5' end of the mRNA will determine the efficiency of elongation p ...
C - NCSU Bioinformatics Research Center
... • Polypeptides having a three dimensional structure. ...
... • Polypeptides having a three dimensional structure. ...
Gene Regulation
... demonstrate negative control because active repressors can only have negative effects on transcription. •Positive gene control occurs when an activator molecule interacts directly with the genome to switch transcription on or enhance transcription. ...
... demonstrate negative control because active repressors can only have negative effects on transcription. •Positive gene control occurs when an activator molecule interacts directly with the genome to switch transcription on or enhance transcription. ...
Chapter 22
... Retroposons of the viral superfamily are transposons that mobilize via an RNA that does not form an infectious particle. Some retroposons directly resemble retroviruses in their use of LTRs, whereas others do not have LTRs. Other elements can be found that were generated by an RNA-mediated transposi ...
... Retroposons of the viral superfamily are transposons that mobilize via an RNA that does not form an infectious particle. Some retroposons directly resemble retroviruses in their use of LTRs, whereas others do not have LTRs. Other elements can be found that were generated by an RNA-mediated transposi ...
Pochonia chlamydosporia - Biological Engineering
... the fungal polyketides, is produced by Pochonia chlamydosporia. It inhibits the Hsp90 molecular chaperone, another important target for cancer chemotherapy. Recently, gene clusters for biosynthesis of radicicol from Pochonia chlamydosporia were sequenced. However, the function of each enzyme is stil ...
... the fungal polyketides, is produced by Pochonia chlamydosporia. It inhibits the Hsp90 molecular chaperone, another important target for cancer chemotherapy. Recently, gene clusters for biosynthesis of radicicol from Pochonia chlamydosporia were sequenced. However, the function of each enzyme is stil ...
Genetic Code
... this tRNA, and which amino acid also bound in the active site of that enzyme, then you would know which amino acid will be found on this tRNA. And then you'd know what amino acid would go into the polypeptide when the mRNA had the codon UGG, which is complementary to this tRNA's anticodon. To make t ...
... this tRNA, and which amino acid also bound in the active site of that enzyme, then you would know which amino acid will be found on this tRNA. And then you'd know what amino acid would go into the polypeptide when the mRNA had the codon UGG, which is complementary to this tRNA's anticodon. To make t ...
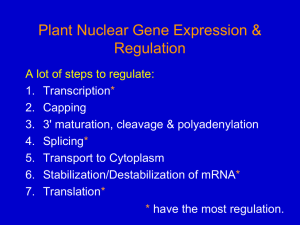
Nuclear gene expression 1
... 2. Pol II - synthesizes mRNA precursors, some snRNAs 3. Pol III- synthesizes 5S rRNAs, tRNAs, small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs) All 3 polymerases are multi-subunit; have some large, unique subunits; and 5 small, shared subunits (at least in yeast). ...
... 2. Pol II - synthesizes mRNA precursors, some snRNAs 3. Pol III- synthesizes 5S rRNAs, tRNAs, small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs) All 3 polymerases are multi-subunit; have some large, unique subunits; and 5 small, shared subunits (at least in yeast). ...
Chapter Outline
... time it takes various mRNA molecules to pass through nuclear pores. 5. The DNA that is not transcribed into a protein is used to form small RNA (sRNA) molecules and regulate gene expression by: a. Altering DNA compaction so some genes are inaccessible to the transcription machinery of the cell. b. P ...
... time it takes various mRNA molecules to pass through nuclear pores. 5. The DNA that is not transcribed into a protein is used to form small RNA (sRNA) molecules and regulate gene expression by: a. Altering DNA compaction so some genes are inaccessible to the transcription machinery of the cell. b. P ...
Bench Guide
... number of different functions. Messenger RNA (mRNA), transcribed from DNA, serves as a template for synthesis of proteins. Protein synthesis is carried out by ribosomes, which consist of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and proteins. Amino acids for protein synthesis are delivered to the ribosome on transfer RN ...
... number of different functions. Messenger RNA (mRNA), transcribed from DNA, serves as a template for synthesis of proteins. Protein synthesis is carried out by ribosomes, which consist of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and proteins. Amino acids for protein synthesis are delivered to the ribosome on transfer RN ...
DNA Worksheet
... 23. Use the amino acid chart in your notes to translate the sequence of codons (from #16) and write the ...
... 23. Use the amino acid chart in your notes to translate the sequence of codons (from #16) and write the ...
The CENTRAL DOGMA Make a Protein – Transcription and
... Reading a Copy of DNA instructions to Assemble a Polypeptide - Translation Cells read DNA in small portions (genes) to create a protein. To do this, the cell must first make a copy of the gene’s code to send to the protein-building organelle, the ribosome. This process is called transcription. This ...
... Reading a Copy of DNA instructions to Assemble a Polypeptide - Translation Cells read DNA in small portions (genes) to create a protein. To do this, the cell must first make a copy of the gene’s code to send to the protein-building organelle, the ribosome. This process is called transcription. This ...
Document
... Consists of two nucleotide chains/strands wrapped around each other in a spiral helix A on one strand matches T on the other Similarly G and C pair between strands When the strands are separated, they can each regenerate their partner & thus copy the information they encode A codon consists of 3 seq ...
... Consists of two nucleotide chains/strands wrapped around each other in a spiral helix A on one strand matches T on the other Similarly G and C pair between strands When the strands are separated, they can each regenerate their partner & thus copy the information they encode A codon consists of 3 seq ...
DNA and RNA - Mrs-Lamberts-Biology
... • The language of proteins is amino acids. • mRNA attaches to the ribosomes with the recipe for the protein. • The tRNA molecule with the anticodon to the mRNA codon brings the amino acid called for by the recipe to the ribosomes. ...
... • The language of proteins is amino acids. • mRNA attaches to the ribosomes with the recipe for the protein. • The tRNA molecule with the anticodon to the mRNA codon brings the amino acid called for by the recipe to the ribosomes. ...
Biology 105: Biology Science for Life with Physiology, 3rd Ed., Belk
... replication; 14 frameshift mutation;15 galls;16 germ-line gene therapy; 17 gene gun; 18 gene therapy; 19 generally recognized as safe (GRAS); 20 genetically modified organism (GMO); 21 genetic code; 22 genome;23 helicase; 24 in vitro; 25 messenger RNA (mRNA); 26 model organisms; 27 mutations; 28 nit ...
... replication; 14 frameshift mutation;15 galls;16 germ-line gene therapy; 17 gene gun; 18 gene therapy; 19 generally recognized as safe (GRAS); 20 genetically modified organism (GMO); 21 genetic code; 22 genome;23 helicase; 24 in vitro; 25 messenger RNA (mRNA); 26 model organisms; 27 mutations; 28 nit ...
Transcription and Translation
... It is needed to get the DNA message out of the nucleus so the ribosomes know what protein to make! Without transcription, the ribosome would have no idea what proteins the body needed and would not make any. You could NOT replace the hair that we loose every day; could NOT grow long fingernails; be ...
... It is needed to get the DNA message out of the nucleus so the ribosomes know what protein to make! Without transcription, the ribosome would have no idea what proteins the body needed and would not make any. You could NOT replace the hair that we loose every day; could NOT grow long fingernails; be ...
Document
... B) (4pts) What are the two most likely splice patterns you would observe in the mRNA (use exon numbers for answers)? ...
... B) (4pts) What are the two most likely splice patterns you would observe in the mRNA (use exon numbers for answers)? ...
Messenger RNA

Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a large family of RNA molecules that convey genetic information from DNA to the ribosome, where they specify the amino acid sequence of the protein products of gene expression. Following transcription of primary transcript mRNA (known as pre-mRNA) by RNA polymerase, processed, mature mRNA is translated into a polymer of amino acids: a protein, as summarized in the central dogma of molecular biology.As in DNA, mRNA genetic information is in the sequence of nucleotides, which are arranged into codons consisting of three bases each. Each codon encodes for a specific amino acid, except the stop codons, which terminate protein synthesis. This process of translation of codons into amino acids requires two other types of RNA: Transfer RNA (tRNA), that mediates recognition of the codon and provides the corresponding amino acid, and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), that is the central component of the ribosome's protein-manufacturing machinery.The existence of mRNA was first suggested by Jacques Monod and François Jacob, and subsequently discovered by Jacob, Sydney Brenner and Matthew Meselson at the California Institute of Technology in 1961.