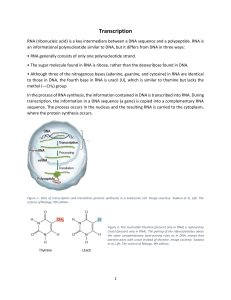
Protein Synthesis
... class.unl.edu/biochem/gp2/m_biology/animation/ gene/gene_a2.html http://207.207.4.198/pub/flash/26/transmenu_s.s wf (very good but need to skip some parts) ...
... class.unl.edu/biochem/gp2/m_biology/animation/ gene/gene_a2.html http://207.207.4.198/pub/flash/26/transmenu_s.s wf (very good but need to skip some parts) ...
Zoology 145 course
... Summary of RNA Transcription Mechanism 1) Transcription begins when the enzyme RNA polymerase binds to DNA at a promoter region. 2) The enzyme separates the DNA strands by breaking the hydrogen bonds, and then uses one strand of DNA as a template from which nucleotides are assembled into a strand o ...
... Summary of RNA Transcription Mechanism 1) Transcription begins when the enzyme RNA polymerase binds to DNA at a promoter region. 2) The enzyme separates the DNA strands by breaking the hydrogen bonds, and then uses one strand of DNA as a template from which nucleotides are assembled into a strand o ...
Chapter 14 2015 - Franklin College
... • Several ribosomes can translate the same message one after the other. • Increases the efficiency of protein production ...
... • Several ribosomes can translate the same message one after the other. • Increases the efficiency of protein production ...
Transcription and RNA processing
... prokaryotic and eukaryotic genes, transcription begins at a DNA sequence that is upstream (to the “left” on the DNA) of the first codon (i.e., at the promoter), and ends downstream (to the “right” on the DNA) of the termination codon. In eukaryotes, there is usually a “polyadenylation” sequence (AAU ...
... prokaryotic and eukaryotic genes, transcription begins at a DNA sequence that is upstream (to the “left” on the DNA) of the first codon (i.e., at the promoter), and ends downstream (to the “right” on the DNA) of the termination codon. In eukaryotes, there is usually a “polyadenylation” sequence (AAU ...
Chapter 36: RNA Synthesis and Regulation in Bacteria.
... 8. What is a consensus sequence? 9. What is the function of the σ unit of RNA polymerase? 10. RNA polymerase does not have a proofreading activity to correct errors resulting in a higher error frequency in the transcript than for DNA polymerase. Why is the higher frequency of RNA polymerase acceptab ...
... 8. What is a consensus sequence? 9. What is the function of the σ unit of RNA polymerase? 10. RNA polymerase does not have a proofreading activity to correct errors resulting in a higher error frequency in the transcript than for DNA polymerase. Why is the higher frequency of RNA polymerase acceptab ...
REVIEW SHEET FOR RNA AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... 3. Nucleotides, with the help of enzymes, move along one strand of the exposed gene and forms a molecule of mRNA (U pairs with A) 4. Multiple copies of mRNA are made according to the quantity of the order. They leave the nucleus and enter the cytoplasm via nuclear pairs. 5. An mRNA binds with a ribo ...
... 3. Nucleotides, with the help of enzymes, move along one strand of the exposed gene and forms a molecule of mRNA (U pairs with A) 4. Multiple copies of mRNA are made according to the quantity of the order. They leave the nucleus and enter the cytoplasm via nuclear pairs. 5. An mRNA binds with a ribo ...
Schedule
... change the order of base pairing (concept of codons shifted because of deletion / mutation) as the RNA is synthesised during transcription. This will affect the final mRNA product, changing the codon sequence (shortening the RNA possibly disrupting a section of coding RNA / exon). During translation ...
... change the order of base pairing (concept of codons shifted because of deletion / mutation) as the RNA is synthesised during transcription. This will affect the final mRNA product, changing the codon sequence (shortening the RNA possibly disrupting a section of coding RNA / exon). During translation ...
Judgement Statement – 2012
... change the order of base pairing (concept of codons shifted because of deletion / mutation) as the RNA is synthesised during transcription. This will affect the final mRNA product, changing the codon sequence (shortening the RNA possibly disrupting a section of coding RNA / exon). During translation ...
... change the order of base pairing (concept of codons shifted because of deletion / mutation) as the RNA is synthesised during transcription. This will affect the final mRNA product, changing the codon sequence (shortening the RNA possibly disrupting a section of coding RNA / exon). During translation ...
Chapter 10 (Sample questions)
... A charged tRNA enters the protein-synthesizing machinery at the ribosomes by recognition of its a. codon. b. anticodon. c. wobble. d. amino acid. e. none of the above. What is the minimum number of tRNA molecules required to produce a 60-amino acid polypeptide made up of only ten different kinds of ...
... A charged tRNA enters the protein-synthesizing machinery at the ribosomes by recognition of its a. codon. b. anticodon. c. wobble. d. amino acid. e. none of the above. What is the minimum number of tRNA molecules required to produce a 60-amino acid polypeptide made up of only ten different kinds of ...
as with reporter genes
... FOLLOWING GENE EXPRESSION – Pax6 AS AN EXAMPLE What is pax6? Pax6 encodes a transcription factor required for normal eye, nervous and pancreatic development. It binds to enhancer elements of Pax6regulated genes such as lens crystallin and those genes specifying a and b cells in the pancreas ...
... FOLLOWING GENE EXPRESSION – Pax6 AS AN EXAMPLE What is pax6? Pax6 encodes a transcription factor required for normal eye, nervous and pancreatic development. It binds to enhancer elements of Pax6regulated genes such as lens crystallin and those genes specifying a and b cells in the pancreas ...
Document
... RNA Synthesis Most of the work of making RNA takes place during transcription. In transcription, segments of DNA serve as templates to produce complementary RNA molecules. In prokaryotes, RNA synthesis and protein synthesis takes place in the cytoplasm. In eukaryotes, RNA is produced in the cell’s n ...
... RNA Synthesis Most of the work of making RNA takes place during transcription. In transcription, segments of DNA serve as templates to produce complementary RNA molecules. In prokaryotes, RNA synthesis and protein synthesis takes place in the cytoplasm. In eukaryotes, RNA is produced in the cell’s n ...
Transcription and Translation
... Protein Synthesis: Transcription • How does it happen? – After an enzyme targets the portion of the DNA that should be copied (initiation), the sections of DNA (genes) will temporarily unwind to allow mRNA to transcribe (copy). This will continue until an enzyme signals “the end” – mRNA leaves the ...
... Protein Synthesis: Transcription • How does it happen? – After an enzyme targets the portion of the DNA that should be copied (initiation), the sections of DNA (genes) will temporarily unwind to allow mRNA to transcribe (copy). This will continue until an enzyme signals “the end” – mRNA leaves the ...
transcription-and-translation-hl-notes2014-2
... – The amino acid attachment site is always the base triple CCA. – It is important to note that each tRNA molecule can attach to one specific amino acid, but an amino acid can have a few tRNA molecules with which is can ...
... – The amino acid attachment site is always the base triple CCA. – It is important to note that each tRNA molecule can attach to one specific amino acid, but an amino acid can have a few tRNA molecules with which is can ...
Gene Expression
... Each of the 20 amino acids found in proteins is uniquely specified by one or more codons The symbols used by the genetic code are the mRNA bases - Function as “letters” of the genetic alphabet - Genetic alphabet has only four “letters” (U, A, C, G) Codons in the genetic code are all three bases ...
... Each of the 20 amino acids found in proteins is uniquely specified by one or more codons The symbols used by the genetic code are the mRNA bases - Function as “letters” of the genetic alphabet - Genetic alphabet has only four “letters” (U, A, C, G) Codons in the genetic code are all three bases ...
Lecture 5
... RNA and protein construction • The nucleotide base sequence of mRNA is encoded from DNA and transmits sequences of bases used to determine the amino acid sequence of the protein. • mRNA (“Messenger RNA”) associates with the ribosome (mRNA and protein portion). • RNA (“Transfer RNA”) also required • ...
... RNA and protein construction • The nucleotide base sequence of mRNA is encoded from DNA and transmits sequences of bases used to determine the amino acid sequence of the protein. • mRNA (“Messenger RNA”) associates with the ribosome (mRNA and protein portion). • RNA (“Transfer RNA”) also required • ...
NEW revision booklt - Eduspace
... ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ What is similar about the two ? ______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ ...
... ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ What is similar about the two ? ______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ ...
File
... » When the ribosome reaches a termination codon on the mRNA (UAA, UAG or UGA) it will stop the translation process » The chain of amino acids, called a polypeptide, will be released. It then undergoes some posttranslational processing in the golgi bodies and is transported via the endoplasmic retic ...
... » When the ribosome reaches a termination codon on the mRNA (UAA, UAG or UGA) it will stop the translation process » The chain of amino acids, called a polypeptide, will be released. It then undergoes some posttranslational processing in the golgi bodies and is transported via the endoplasmic retic ...
DNA LIBRARIES
... entire genome of a given organism. • cDNA library-represents a sample of all the expressed mRNA’s from a particular cell type, particular tissue, or an entire organism which has been converted back to DNA. Thus represents the genes that were actively being transcribed (turned on). ...
... entire genome of a given organism. • cDNA library-represents a sample of all the expressed mRNA’s from a particular cell type, particular tissue, or an entire organism which has been converted back to DNA. Thus represents the genes that were actively being transcribed (turned on). ...
DNA, RNA, & Protein Synthesis Notes (12.3)
... Long strands of RNA nucleotides that are formed complementary to one strand of DNA Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) Associates with proteins to form ribosomes in the cytoplasm Transfer RNA (tRNA) Smaller segments of RNA nucleotides that transport amino acids to the ribosome ...
... Long strands of RNA nucleotides that are formed complementary to one strand of DNA Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) Associates with proteins to form ribosomes in the cytoplasm Transfer RNA (tRNA) Smaller segments of RNA nucleotides that transport amino acids to the ribosome ...
Gene Expression
... DNA in cells controls all sorts of things such as the color of your eyes, the color of your hair, and whether or not you can digest milk. These characteristics are called traits. DNA also controls your responses to stimuli in the environment to keep you alive. For example, when you are frightened, t ...
... DNA in cells controls all sorts of things such as the color of your eyes, the color of your hair, and whether or not you can digest milk. These characteristics are called traits. DNA also controls your responses to stimuli in the environment to keep you alive. For example, when you are frightened, t ...
SMIC Biology
... answers to questions. When time is up, peer leaders should bring up any items their groups were unable to resolve. Part 6: Scholarly Definitions Team leader: Divide the work amongst the group, including yourself. Your team should evaluate the definitions that follow by circling any parts that are in ...
... answers to questions. When time is up, peer leaders should bring up any items their groups were unable to resolve. Part 6: Scholarly Definitions Team leader: Divide the work amongst the group, including yourself. Your team should evaluate the definitions that follow by circling any parts that are in ...
Hot Seat - Protein Synthesis
... B. your skin cells activate only those genes needed to make skin whereas your muscle cells activate only those genes needed to make muscle C. your skin cells have different DNA codes than ...
... B. your skin cells activate only those genes needed to make skin whereas your muscle cells activate only those genes needed to make muscle C. your skin cells have different DNA codes than ...
Transcription and the Central Dogma
... • RNA polymerase is processive; once enzyme attaches to DNA, it can copy >10,000 nucleotides without falling off. • In eukaryotes, there are 3 RNA polymerases: – One for rRNA – One for tRNAs and some rRNA – One for all mRNAs and some small RNAs (involved in RNA processing) ...
... • RNA polymerase is processive; once enzyme attaches to DNA, it can copy >10,000 nucleotides without falling off. • In eukaryotes, there are 3 RNA polymerases: – One for rRNA – One for tRNAs and some rRNA – One for all mRNAs and some small RNAs (involved in RNA processing) ...
Activity
... place. The code, in DNA or mRNA, specifies the order in which the amino acids are joined together to form a polypeptide. The code words in mRNA, however, are not directly recognized by the corresponding amino acids. Another type of RNA called transfer RNA (tRNA) is needed to bring the mRNA and amino ...
... place. The code, in DNA or mRNA, specifies the order in which the amino acids are joined together to form a polypeptide. The code words in mRNA, however, are not directly recognized by the corresponding amino acids. Another type of RNA called transfer RNA (tRNA) is needed to bring the mRNA and amino ...
Messenger RNA

Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a large family of RNA molecules that convey genetic information from DNA to the ribosome, where they specify the amino acid sequence of the protein products of gene expression. Following transcription of primary transcript mRNA (known as pre-mRNA) by RNA polymerase, processed, mature mRNA is translated into a polymer of amino acids: a protein, as summarized in the central dogma of molecular biology.As in DNA, mRNA genetic information is in the sequence of nucleotides, which are arranged into codons consisting of three bases each. Each codon encodes for a specific amino acid, except the stop codons, which terminate protein synthesis. This process of translation of codons into amino acids requires two other types of RNA: Transfer RNA (tRNA), that mediates recognition of the codon and provides the corresponding amino acid, and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), that is the central component of the ribosome's protein-manufacturing machinery.The existence of mRNA was first suggested by Jacques Monod and François Jacob, and subsequently discovered by Jacob, Sydney Brenner and Matthew Meselson at the California Institute of Technology in 1961.