PDF
... morphogenetic inactivity of cell nuclei. This would seem paradoxical if the nuclei are supposed to be the sole site for RNA synthesis. This paradox might be resolved, however, if the 'early' RNA synthesis were partly or entirely independent of the cell nuclei. We attempted to clarify this point by m ...
... morphogenetic inactivity of cell nuclei. This would seem paradoxical if the nuclei are supposed to be the sole site for RNA synthesis. This paradox might be resolved, however, if the 'early' RNA synthesis were partly or entirely independent of the cell nuclei. We attempted to clarify this point by m ...
RNA PCR Kit (AMV)
... Use of this product is covered by one or more of the following US patents and corresponding patent claims outside the US: 5,789,224, 5,618,711, 6,127,155 and claims outside the US corresponding to expired US Patent No. 5,079,352. The purchase of this product includes a limited, non-transferable immu ...
... Use of this product is covered by one or more of the following US patents and corresponding patent claims outside the US: 5,789,224, 5,618,711, 6,127,155 and claims outside the US corresponding to expired US Patent No. 5,079,352. The purchase of this product includes a limited, non-transferable immu ...
Nucleic Acids - Farmasi Unand
... consist of a single polymer chain of nucleotides with the same bases as DNA, with the exception of thymine, which is replaced by uracil ( Figure 9). • These chains often contain singlestranded loops separated by short sections of a distorted double helix (Figure 11). These structures are known as ha ...
... consist of a single polymer chain of nucleotides with the same bases as DNA, with the exception of thymine, which is replaced by uracil ( Figure 9). • These chains often contain singlestranded loops separated by short sections of a distorted double helix (Figure 11). These structures are known as ha ...
NUCLEOTIDE and PROTEIN databases
... a wide range of web-based retrieval and analysis tools Is built primarily from the submission of sequence data from authors (i.e BankIt) and from bulk submission of high-throughput data from sequencing centre (i.e. Sequin) ...
... a wide range of web-based retrieval and analysis tools Is built primarily from the submission of sequence data from authors (i.e BankIt) and from bulk submission of high-throughput data from sequencing centre (i.e. Sequin) ...
The Role of the C-terminal Tail of the Ribosomal Protein S13 in Pr
... The ampicillin resistance cassette was amplified from the plasmid pND707 using the primers listed in appendix a (1‐5). The primers have 30 ~ 40 nt homologous to the rpsM gene, followed by the modified S13 CTD sequence, a stop codon, an E. coli SD sequence for translation of amp r ...
... The ampicillin resistance cassette was amplified from the plasmid pND707 using the primers listed in appendix a (1‐5). The primers have 30 ~ 40 nt homologous to the rpsM gene, followed by the modified S13 CTD sequence, a stop codon, an E. coli SD sequence for translation of amp r ...
Document
... directly interact with the mRNA, or it might indirectly affect the mRNA through interactions with other proteins. In either case, the net effect should be the stabilization in the presence of tyrosine of the RNA structure found in region 1 and the prevention of Tyr1 translation. The absence of such ...
... directly interact with the mRNA, or it might indirectly affect the mRNA through interactions with other proteins. In either case, the net effect should be the stabilization in the presence of tyrosine of the RNA structure found in region 1 and the prevention of Tyr1 translation. The absence of such ...
Hypoosmotic shock adaptation by prolactin involves upregulation of
... cerebellum (Hur et al. 2011). It is involved in various physiological functions, such as maintaining blood pressure (Warne and Balment 1995), antidiuretic functions (Henderson and Wales 1974; Amer and Brown ...
... cerebellum (Hur et al. 2011). It is involved in various physiological functions, such as maintaining blood pressure (Warne and Balment 1995), antidiuretic functions (Henderson and Wales 1974; Amer and Brown ...
Human Skeletal Muscle Expresses a Glycogen
... the phosphorylase phosphatase activity (30 –32). Phosphorylase a was shown to bind to a 16 –amino acid section at the extreme COOH-terminus of GL, a sequence that is absent from the other glycogen-targeting subunits, GM, R5, and R6 (13). Thus, stimulation of hepatic glycogenolysis by glucagon (actin ...
... the phosphorylase phosphatase activity (30 –32). Phosphorylase a was shown to bind to a 16 –amino acid section at the extreme COOH-terminus of GL, a sequence that is absent from the other glycogen-targeting subunits, GM, R5, and R6 (13). Thus, stimulation of hepatic glycogenolysis by glucagon (actin ...
Gene Expression
... Pairing of complementary bases is the key to the transfer of information from DNA to RNA and from RNA to protein Polarities of DNA, RNA, and polypeptides help guide the mechanisms of gene expression Gene expression requires input of energy and participation of specific proteins and macromolecular as ...
... Pairing of complementary bases is the key to the transfer of information from DNA to RNA and from RNA to protein Polarities of DNA, RNA, and polypeptides help guide the mechanisms of gene expression Gene expression requires input of energy and participation of specific proteins and macromolecular as ...
The RNA origin of transfer RNA aminoacylation and beyond
... respectively. P3 shown in box with question mark is a putative pair region. Proposed bases that form Watson–Crick pairs in r24min (G43 –U45) and tRNAs (A73 –C75) are underlined and the red-dashed arrow indicates their interactions. Putative bases involving the constitution of the Phe-binding site ar ...
... respectively. P3 shown in box with question mark is a putative pair region. Proposed bases that form Watson–Crick pairs in r24min (G43 –U45) and tRNAs (A73 –C75) are underlined and the red-dashed arrow indicates their interactions. Putative bases involving the constitution of the Phe-binding site ar ...
The nucleotide sequence and derived amino acid
... Although some limited sequence data have been obtained for the CA III isozyme of the rat (Carter et al., 1981), and what appears to be CA II cDNA from the mouse (Curtis, 1983), no extensive nucleotide or amino acid sequences are as yet available for a CA isozyme from any rodent species. In this resp ...
... Although some limited sequence data have been obtained for the CA III isozyme of the rat (Carter et al., 1981), and what appears to be CA II cDNA from the mouse (Curtis, 1983), no extensive nucleotide or amino acid sequences are as yet available for a CA isozyme from any rodent species. In this resp ...
INO1 - of /home/sholmes/web
... occurring after periphery localization is complete • These genes remain at the periphery long after the cells are returned to repressing conditions and mRNA expression returns to repressed levels, and this localization is inherited for several generations • Transcription by RNA polymerase II is not ...
... occurring after periphery localization is complete • These genes remain at the periphery long after the cells are returned to repressing conditions and mRNA expression returns to repressed levels, and this localization is inherited for several generations • Transcription by RNA polymerase II is not ...
Assessing Methods of Detecting Osteogenesis Imperfecta.
... Collagen is a triple helix of collagen proteins. This structure has great tensile strength, similar to wire cable, and this combined with the crystalline structure of bone minerals gives the structure a degree of flexibility. This combination of rigidity and flexibility is what gives bones their str ...
... Collagen is a triple helix of collagen proteins. This structure has great tensile strength, similar to wire cable, and this combined with the crystalline structure of bone minerals gives the structure a degree of flexibility. This combination of rigidity and flexibility is what gives bones their str ...
Dissecting the protein–RNA interface
... As of 11 November 2010, the PDB listed 824 structures of protein–RNA complexes that had been solved using X-ray crystallography (5). From this data set, 344 complexes were selected based on the following criteria: (i) structural resolution better than 3.0 Å and (ii) polypeptides and polyribonucleot ...
... As of 11 November 2010, the PDB listed 824 structures of protein–RNA complexes that had been solved using X-ray crystallography (5). From this data set, 344 complexes were selected based on the following criteria: (i) structural resolution better than 3.0 Å and (ii) polypeptides and polyribonucleot ...
Cell and Molecular Biology
... contrast, cycloheximide stops protein synthesis immediately. Analysis of the edeineinhibited lysate by density-gradient centrifugation showed that no polyribosomes remained by the time protein synthesis had stopped. Instead, all the globin mRNA accumulated in an abnormal 40S peak, which contained eq ...
... contrast, cycloheximide stops protein synthesis immediately. Analysis of the edeineinhibited lysate by density-gradient centrifugation showed that no polyribosomes remained by the time protein synthesis had stopped. Instead, all the globin mRNA accumulated in an abnormal 40S peak, which contained eq ...
Laalami S., Zig L. and H. Putzer - Institut de Biologie Physico
... divides only about once a day has an average mRNA halflife of only 2.4 min [23]. Under laboratory growth conditions, all known bacterial mRNA turnover rates are thus quite fast but also disparate with respect to their growth rate. This likely reflects evolutionary adaptation of each organism to its ...
... divides only about once a day has an average mRNA halflife of only 2.4 min [23]. Under laboratory growth conditions, all known bacterial mRNA turnover rates are thus quite fast but also disparate with respect to their growth rate. This likely reflects evolutionary adaptation of each organism to its ...
Developmental changes in barley microRNA expression profiles
... barley development, miR168-3p and miR1432-5p levels increase while the 5’U-miR156-5p level decreases (with exception for the 2-week-old barley). We have identified two miR156-5p izomiRs (called 5’U-miR156-5p [20 nt] and 5’UU-miR156-5p [21 nt]), which were expressed differently during barley developm ...
... barley development, miR168-3p and miR1432-5p levels increase while the 5’U-miR156-5p level decreases (with exception for the 2-week-old barley). We have identified two miR156-5p izomiRs (called 5’U-miR156-5p [20 nt] and 5’UU-miR156-5p [21 nt]), which were expressed differently during barley developm ...
Improving Virus C type 4 Interferon using Bioinformatics Techniques
... mRNA binds to a small ribosomal subunit near an AUG sequence in the mRNA. The AUG codon is called start codon, since it codes for the first amino acid (a methionine) to be made of the protein. The AUG codon base-pairs with the anticodon of tRNA carrying methionine. A large ribosomal subunit binds to ...
... mRNA binds to a small ribosomal subunit near an AUG sequence in the mRNA. The AUG codon is called start codon, since it codes for the first amino acid (a methionine) to be made of the protein. The AUG codon base-pairs with the anticodon of tRNA carrying methionine. A large ribosomal subunit binds to ...
Counting Small RNA in Pathogenic Bacteria
... either Yersinia pseudotuberculosis or Yersinia pestis bacteria express the small RNAs YSR35 or YSP8, with the copy number typically between 0 and 10 transcripts. The numbers of these RNA are both increased (by a factor of 2.5× for YSR35 and 3.5× for YSP8) upon a temperature shift from 25 to 37 °C, s ...
... either Yersinia pseudotuberculosis or Yersinia pestis bacteria express the small RNAs YSR35 or YSP8, with the copy number typically between 0 and 10 transcripts. The numbers of these RNA are both increased (by a factor of 2.5× for YSR35 and 3.5× for YSP8) upon a temperature shift from 25 to 37 °C, s ...
Evolution of Brachyury proteins: identification of a novel regulatory
... 2D–H, K–M, and O). The low endoderm induction activity displayed by the mouse and hemichordate orthologues was not reproducible, and was therefore considered negligible. By contrast, the low muscle induction observed upon misexpression of HyBra1 was obtained consistently. A randomization t test show ...
... 2D–H, K–M, and O). The low endoderm induction activity displayed by the mouse and hemichordate orthologues was not reproducible, and was therefore considered negligible. By contrast, the low muscle induction observed upon misexpression of HyBra1 was obtained consistently. A randomization t test show ...
SMN1
... snRNA. This unevenly alters the levels of specific endogenous snRNPs, such as those used to splice minor introns (particularly U11) from pre-mRNA. It remains to be determined what the downstream target genes of the affected snRNPs are and how this specifically affects motor neuron function (indicate ...
... snRNA. This unevenly alters the levels of specific endogenous snRNPs, such as those used to splice minor introns (particularly U11) from pre-mRNA. It remains to be determined what the downstream target genes of the affected snRNPs are and how this specifically affects motor neuron function (indicate ...
The Cleavage and Polyadenylation Specificity Factor in Xenopus
... During early development, specific mRNAs receive poly(A) in the cytoplasm. This cytoplasmic polyadenylation reaction correlates with, and in some cases causes, translational stimulation. Previously, it was suggested that a factor similar to the multisubunit nuclear cleavage and polyadenylation speci ...
... During early development, specific mRNAs receive poly(A) in the cytoplasm. This cytoplasmic polyadenylation reaction correlates with, and in some cases causes, translational stimulation. Previously, it was suggested that a factor similar to the multisubunit nuclear cleavage and polyadenylation speci ...
Chpt10_TxnRNAPol.doc
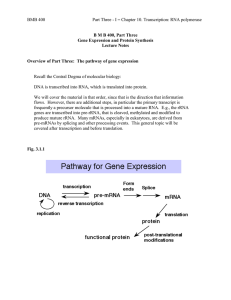
... Recall the Central Dogma of molecular biology: DNA is transcribed into RNA, which is translated into protein. We will cover the material in that order, since that is the direction that information flows. However, there are additional steps, in particular the primary transcript is frequently a precur ...
... Recall the Central Dogma of molecular biology: DNA is transcribed into RNA, which is translated into protein. We will cover the material in that order, since that is the direction that information flows. However, there are additional steps, in particular the primary transcript is frequently a precur ...
Messenger RNA

Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a large family of RNA molecules that convey genetic information from DNA to the ribosome, where they specify the amino acid sequence of the protein products of gene expression. Following transcription of primary transcript mRNA (known as pre-mRNA) by RNA polymerase, processed, mature mRNA is translated into a polymer of amino acids: a protein, as summarized in the central dogma of molecular biology.As in DNA, mRNA genetic information is in the sequence of nucleotides, which are arranged into codons consisting of three bases each. Each codon encodes for a specific amino acid, except the stop codons, which terminate protein synthesis. This process of translation of codons into amino acids requires two other types of RNA: Transfer RNA (tRNA), that mediates recognition of the codon and provides the corresponding amino acid, and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), that is the central component of the ribosome's protein-manufacturing machinery.The existence of mRNA was first suggested by Jacques Monod and François Jacob, and subsequently discovered by Jacob, Sydney Brenner and Matthew Meselson at the California Institute of Technology in 1961.