The importance of alternative splicing in the drug discovery process
... selecting an antibody for a desired therapeutic role, alternative splicing must be considered. If, for example, Pre-mRNA one wants to eliminate totally a certain protein, the antibody should be designed against the region common to all splice variants of it; otherwise, the antibody will miss some of ...
... selecting an antibody for a desired therapeutic role, alternative splicing must be considered. If, for example, Pre-mRNA one wants to eliminate totally a certain protein, the antibody should be designed against the region common to all splice variants of it; otherwise, the antibody will miss some of ...
Calcitonin
... Calcitonin is a 32-amino acid polypeptide hormone that is produced in humans primarily by the parafollicular (also known as C-cells) of the thyroid, and in many other animals in the ultimobranchia body. It acts to reduce blood calcium (Ca2+), opposing the effects of parathyroid hormone(PTH). It has ...
... Calcitonin is a 32-amino acid polypeptide hormone that is produced in humans primarily by the parafollicular (also known as C-cells) of the thyroid, and in many other animals in the ultimobranchia body. It acts to reduce blood calcium (Ca2+), opposing the effects of parathyroid hormone(PTH). It has ...
Metabolic rate depression in animals
... becomes intermittent, and kidney filtration rate is reduced. Organisms do not eat so the energetic costs of digestion, nutrient absorption, and peristalsis are eliminated. A substantial part of total energy savings comes from the suppression of these physiological activities. Metabolic rate is also i ...
... becomes intermittent, and kidney filtration rate is reduced. Organisms do not eat so the energetic costs of digestion, nutrient absorption, and peristalsis are eliminated. A substantial part of total energy savings comes from the suppression of these physiological activities. Metabolic rate is also i ...
Identification of a C-terminal Poly(A)-binding Protein (PABP)
... sufficient to confer viability to cells depleted of the normal PABP gene (11). In Xenopus oocytes, RRMs can stimulate translation when tethered to reporter mRNA (18). As to the C terminus, although it does not bind RNA, it enables PABP to multimerize on poly(A) (12). Recently it was shown to include ...
... sufficient to confer viability to cells depleted of the normal PABP gene (11). In Xenopus oocytes, RRMs can stimulate translation when tethered to reporter mRNA (18). As to the C terminus, although it does not bind RNA, it enables PABP to multimerize on poly(A) (12). Recently it was shown to include ...
Get PDF - Wiley Online Library
... The poly(A) tail is bound by the poly(A)-binding protein (PABP), which is necessary for efficient translation (for reviews, see Jacobson, 1996; Sachs et al., 1997). In yeast, eIF4G was found to associate with PABP (Tarun and Sachs, 1996). The PABP-binding site was mapped to an N-terminal region prox ...
... The poly(A) tail is bound by the poly(A)-binding protein (PABP), which is necessary for efficient translation (for reviews, see Jacobson, 1996; Sachs et al., 1997). In yeast, eIF4G was found to associate with PABP (Tarun and Sachs, 1996). The PABP-binding site was mapped to an N-terminal region prox ...
Alternative Splicing
... splice sites (AG) are accessible to give two different mature mRNAs and therefore two different protein products (Protein Z and Protein Y). The splicing regulator (X) binds to a splice site which is located within a coding region of the pre-mRNA. This splice site is now no longer accessible to the s ...
... splice sites (AG) are accessible to give two different mature mRNAs and therefore two different protein products (Protein Z and Protein Y). The splicing regulator (X) binds to a splice site which is located within a coding region of the pre-mRNA. This splice site is now no longer accessible to the s ...
Document
... splice isoforms of known transcripts … – Frey et al Science, March 2006 … the number of new proteincoding genes found by us has been revised from 5154 to 2222… – FANTOM/RIKEN Consortium Science, March 2006 Brendan Frey ...
... splice isoforms of known transcripts … – Frey et al Science, March 2006 … the number of new proteincoding genes found by us has been revised from 5154 to 2222… – FANTOM/RIKEN Consortium Science, March 2006 Brendan Frey ...
Kallikrein-like prorenin-converting enzymes in inbred
... Kallikreins are a group of serine proteases and are distinguished by having serine residue at their active site. Their general function is to convert inactive pro-peptide into its biologically active form. In recent years, emerging evidence indicates that some kallikrein–kinin enzymes also play a ro ...
... Kallikreins are a group of serine proteases and are distinguished by having serine residue at their active site. Their general function is to convert inactive pro-peptide into its biologically active form. In recent years, emerging evidence indicates that some kallikrein–kinin enzymes also play a ro ...
Interfering RNA
... • showing of antisense targets across mRNA may be sufficient, but not all antisense targets are open to siRNA • intron targets may not be active for siRNA but may be for antisense – identify all elements claimed and their support in the description – identify species explicitly or implicitly disclos ...
... • showing of antisense targets across mRNA may be sufficient, but not all antisense targets are open to siRNA • intron targets may not be active for siRNA but may be for antisense – identify all elements claimed and their support in the description – identify species explicitly or implicitly disclos ...
Predictable Alteration of Sequence Recognition by RNA
... can be found in all eukaryotes, from humans to algae, although they differ greatly in number between organisms. This protein family has massively expanded in terrestrial plants, which contain from ;100 (Physcomitrella) to over 1000 (Selaginella) PPR proteins (Fujii and Small, 2011). PPR proteins are ...
... can be found in all eukaryotes, from humans to algae, although they differ greatly in number between organisms. This protein family has massively expanded in terrestrial plants, which contain from ;100 (Physcomitrella) to over 1000 (Selaginella) PPR proteins (Fujii and Small, 2011). PPR proteins are ...
Interpreting the Genetic Code
... The genetic code appears to be Non-random in nature and designed with considerable safeguards against harmful point mutations An evolutionary model suggests at least at some level of randomness in assignment of amino acids to codons No mechanism exists for genetic code evolution Thus variation in th ...
... The genetic code appears to be Non-random in nature and designed with considerable safeguards against harmful point mutations An evolutionary model suggests at least at some level of randomness in assignment of amino acids to codons No mechanism exists for genetic code evolution Thus variation in th ...
Interpreting the Genetic Code
... The net effect of wobble base pairing is to reduce the number of tRNAs that must be produced by a cell In reality cells do not make 61 different tRNAs, one for each codon Many tRNAs have anticodons that anneal to several different codons Codons are known for which there are more than one tRNA, altho ...
... The net effect of wobble base pairing is to reduce the number of tRNAs that must be produced by a cell In reality cells do not make 61 different tRNAs, one for each codon Many tRNAs have anticodons that anneal to several different codons Codons are known for which there are more than one tRNA, altho ...
December 9, 2005 12:54 WSPC/INSTRUCTION FILE jbcb1 THE
... quadrant) and FYW (in three quadrants). In other words, reverse codon pairs tend to code for evolutionary similar amino acids, and each quadrant is enriched for amino acids with similar biochemical properties. The new scheme of the genetic code has now its optimal form (Fig. 2). It shows five differ ...
... quadrant) and FYW (in three quadrants). In other words, reverse codon pairs tend to code for evolutionary similar amino acids, and each quadrant is enriched for amino acids with similar biochemical properties. The new scheme of the genetic code has now its optimal form (Fig. 2). It shows five differ ...
7.1 The lac Operon
... Walter Gilbert and Benno Müller-Hill succeeded in partially purifying the lac repressor. The most sensitive assay available to them was binding a labeled synthetic inducer (isopropylthiogalactoside, or IPTG) to the repressor. But, with a crude extract of wild-type cells, the repressor was in such lo ...
... Walter Gilbert and Benno Müller-Hill succeeded in partially purifying the lac repressor. The most sensitive assay available to them was binding a labeled synthetic inducer (isopropylthiogalactoside, or IPTG) to the repressor. But, with a crude extract of wild-type cells, the repressor was in such lo ...
Molecular Beacon Product Sheet
... binding of single stranded oligos to specific targets based on structural conformation. Aptamers are single-stranded RNA or DNA oligonucleotides 15 to 60 base in length that bind with high affinity to specific molecular targets; most aptamers to proteins bind with Kds (equilibrium constant) in the r ...
... binding of single stranded oligos to specific targets based on structural conformation. Aptamers are single-stranded RNA or DNA oligonucleotides 15 to 60 base in length that bind with high affinity to specific molecular targets; most aptamers to proteins bind with Kds (equilibrium constant) in the r ...
Characterization of the amino acid response element within the
... is a sodium-dependent, secondary active transporter that is expressed in all nucleated mammalian cells [1–4]. The level of System A activity is usually quite low in cells that are slowly dividing or in metabolic homoeostasis. However, System A transport activity is up-regulated in response to amino ...
... is a sodium-dependent, secondary active transporter that is expressed in all nucleated mammalian cells [1–4]. The level of System A activity is usually quite low in cells that are slowly dividing or in metabolic homoeostasis. However, System A transport activity is up-regulated in response to amino ...
... products from our artificial polyproteins are not produced by proteolysis. We propose that the FMDV 2A sequence, rather than representing a proteolytic element, modifies the activity of the ribosome to promote hydrolysis of the peptidyl(2A)-tRNAGly ester linkage, thereby releasing the polypeptide fr ...
RNA-based regulation of genes of tryptophan synthesis
... most plants, and indole in many bacte- FIGURE 2. Organization of the trp operon of E. coli. The genes of E. coli required for ria. Thus the regulatory strategies tryptophan biosynthesis from chorismate are organized in a single operon, or transcriptional unit (Yanofsky and Crawford 1987; Yanofsky 20 ...
... most plants, and indole in many bacte- FIGURE 2. Organization of the trp operon of E. coli. The genes of E. coli required for ria. Thus the regulatory strategies tryptophan biosynthesis from chorismate are organized in a single operon, or transcriptional unit (Yanofsky and Crawford 1987; Yanofsky 20 ...
RNA 3`-terminal phosphate cyclases and cyclase
... nucleases) or RNA-based (for example, hairpin and hammerhead ribozymes). The protein-based nucleases include bacterial and fungal ribonucleases, such as colicin D or MazF and RNases T1 or T2, as well as ribonucleases of the RNaseA/angiogenin, and inositol-requiring enzyme-1 (Ire-1; an endoribonuclea ...
... nucleases) or RNA-based (for example, hairpin and hammerhead ribozymes). The protein-based nucleases include bacterial and fungal ribonucleases, such as colicin D or MazF and RNases T1 or T2, as well as ribonucleases of the RNaseA/angiogenin, and inositol-requiring enzyme-1 (Ire-1; an endoribonuclea ...
Figure 1000G Allele Frequencies
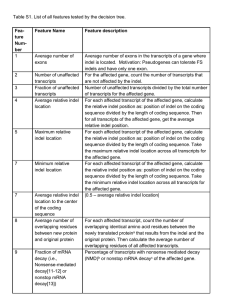
... 3’UTR exon, and the premature termination codon is in the last exon, or in the last 50 nucleotides in the second to last exon; 2) If the last coding exon is flanked by more than one 3’ UTR exon, and the premature termination codon is in the last 50 coding nucleotides of the last coding exon. See Fig ...
... 3’UTR exon, and the premature termination codon is in the last exon, or in the last 50 nucleotides in the second to last exon; 2) If the last coding exon is flanked by more than one 3’ UTR exon, and the premature termination codon is in the last 50 coding nucleotides of the last coding exon. See Fig ...
Can the Origin of the Genetic Code Be Explained - BIO
... affinities. To do this, they looked for RNA strands that bound certain amino acids preferentially, from a class of RNA molecules now dubbed aptamers. Using the directed evolution method SELEX, in which large pools of random RNA strands are synthesized and then sifted for particular functions (in thi ...
... affinities. To do this, they looked for RNA strands that bound certain amino acids preferentially, from a class of RNA molecules now dubbed aptamers. Using the directed evolution method SELEX, in which large pools of random RNA strands are synthesized and then sifted for particular functions (in thi ...
The 2009 Nobel Prize in Chemistry and KEK`s Photon Factory
... available for imaging, but there was still one critical limitation: ribosome crystals would be destroyed after just one exposure. Because ribosomes have a complex structure with no repeating patterns or symmetry, Prof. Yonath needed to take images from every angle to discern their exact structure. “ ...
... available for imaging, but there was still one critical limitation: ribosome crystals would be destroyed after just one exposure. Because ribosomes have a complex structure with no repeating patterns or symmetry, Prof. Yonath needed to take images from every angle to discern their exact structure. “ ...
Nonconventional Initiation Complex Assembly by STAT and NF
... -> ΔStat1 or ΔRela (NF-κB p65) genes suppressed iNOS mRNA induction B. IFN-I receptor (Ifnar1-/- mice) & the NF-κB pathway (Rela-/- & Ikbkb-/- mice, deficient for NF-κB p65 and the IKKβ kinase, respectively) & the ISGF3 ( subunits STAT1, STAT2, IRF9 ) ...
... -> ΔStat1 or ΔRela (NF-κB p65) genes suppressed iNOS mRNA induction B. IFN-I receptor (Ifnar1-/- mice) & the NF-κB pathway (Rela-/- & Ikbkb-/- mice, deficient for NF-κB p65 and the IKKβ kinase, respectively) & the ISGF3 ( subunits STAT1, STAT2, IRF9 ) ...
Application of small interfering RNAs modified by unlocked nucleic
... the specificity of the approach. Some of the most potent modification patterns were selected and the corresponding control siRNAs without homology to the host or viral genome were synthesized. Fig. 4 shows that neither the modified nor the unmodified 22 nt or 21 nt control siRNAs (light grey bars) had a ...
... the specificity of the approach. Some of the most potent modification patterns were selected and the corresponding control siRNAs without homology to the host or viral genome were synthesized. Fig. 4 shows that neither the modified nor the unmodified 22 nt or 21 nt control siRNAs (light grey bars) had a ...
The Euglena gracilis chloroplast rpoB gene
... We are interested in the relationship between chloroplast genes for RNA polymerase subunits and the known chloroplast polymerase activities. Antibodies against fusion proteins that contained fragments of the chloroplast genes rpoA from spinach, rpoB from tobacco, and rpoC2 from Euglena, were able to ...
... We are interested in the relationship between chloroplast genes for RNA polymerase subunits and the known chloroplast polymerase activities. Antibodies against fusion proteins that contained fragments of the chloroplast genes rpoA from spinach, rpoB from tobacco, and rpoC2 from Euglena, were able to ...
Messenger RNA

Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a large family of RNA molecules that convey genetic information from DNA to the ribosome, where they specify the amino acid sequence of the protein products of gene expression. Following transcription of primary transcript mRNA (known as pre-mRNA) by RNA polymerase, processed, mature mRNA is translated into a polymer of amino acids: a protein, as summarized in the central dogma of molecular biology.As in DNA, mRNA genetic information is in the sequence of nucleotides, which are arranged into codons consisting of three bases each. Each codon encodes for a specific amino acid, except the stop codons, which terminate protein synthesis. This process of translation of codons into amino acids requires two other types of RNA: Transfer RNA (tRNA), that mediates recognition of the codon and provides the corresponding amino acid, and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), that is the central component of the ribosome's protein-manufacturing machinery.The existence of mRNA was first suggested by Jacques Monod and François Jacob, and subsequently discovered by Jacob, Sydney Brenner and Matthew Meselson at the California Institute of Technology in 1961.