Lecture 8: RNA-sequence analysis: Expression, isoforms
... isoforms using constraints • Goal is to quantify isoforms and determine significance of differential expression • Common RNA-seq expression metrics are ...
... isoforms using constraints • Goal is to quantify isoforms and determine significance of differential expression • Common RNA-seq expression metrics are ...
A model for mis-sense error in protein synthesis: mis
... have been used by nature for synthesizing proteins. The specific sequence of the amino acids in a given protein is directed by the corresponding sequence of codons (triplets of nucleotide monomers) on the corresponding template messenger RNA (mRNA). The template-directed polymerization of a protein, ...
... have been used by nature for synthesizing proteins. The specific sequence of the amino acids in a given protein is directed by the corresponding sequence of codons (triplets of nucleotide monomers) on the corresponding template messenger RNA (mRNA). The template-directed polymerization of a protein, ...
You`re one in a googol: optimizing genes for protein expression
... into the same amino acid sequence. These sequences are not all equally useful however; the exact sequence chosen can have profound effects on the expression of the encoded protein. Despite the importance of protein-coding sequences, there has been little systematic study to identify parameters that ...
... into the same amino acid sequence. These sequences are not all equally useful however; the exact sequence chosen can have profound effects on the expression of the encoded protein. Despite the importance of protein-coding sequences, there has been little systematic study to identify parameters that ...
Chapter 7 Operons: Fine Control of Bacterial Transcription Bacterial
... • Ribosomes stall at tandem tryptophan codons in leader peptide • Stalled ribosome position influences way mRNA folds • Prevents formation of hairpin; hairpin part of transcription termination signal which caused attenuation if lots of trp and translation of leader. ...
... • Ribosomes stall at tandem tryptophan codons in leader peptide • Stalled ribosome position influences way mRNA folds • Prevents formation of hairpin; hairpin part of transcription termination signal which caused attenuation if lots of trp and translation of leader. ...
in Power-Point Format
... • Ribosomes stall at tandem tryptophan codons in leader peptide • Stalled ribosome position influences way mRNA folds • Prevents formation of hairpin; hairpin part of transcription termination signal which caused attenuation if lots of trp and translation of leader. ...
... • Ribosomes stall at tandem tryptophan codons in leader peptide • Stalled ribosome position influences way mRNA folds • Prevents formation of hairpin; hairpin part of transcription termination signal which caused attenuation if lots of trp and translation of leader. ...
Graph Theory Patterns in the Genetic Codes
... The underlying structure of the genetic code has been suggested to influence mRNA sequences through evolutionary selection of RNA secondary structures (SEFFENS and DIGBY , 1999). That study found that mRNA sequences are thermodynamically more stable than expected for secondary structure folding. Cal ...
... The underlying structure of the genetic code has been suggested to influence mRNA sequences through evolutionary selection of RNA secondary structures (SEFFENS and DIGBY , 1999). That study found that mRNA sequences are thermodynamically more stable than expected for secondary structure folding. Cal ...
PDF 743ko
... in Halocynthia. This was further confirmed in C. intestinalis and savigny (Satou et al., 2002). Macho1 codes for a transcription factor of the Zic family (important for vertebrate neuronal differentiation) and has a general influence on posterior tissue differentiation. Its influence in ascidian emb ...
... in Halocynthia. This was further confirmed in C. intestinalis and savigny (Satou et al., 2002). Macho1 codes for a transcription factor of the Zic family (important for vertebrate neuronal differentiation) and has a general influence on posterior tissue differentiation. Its influence in ascidian emb ...
Posttranscriptional Control of Chloroplast Gene Expression
... systems with chloroplast extracts (13). As it turns out, most chloroplast 3⬘ ends are produced by RNA processing rather than by transcription termination. In most cases, an endonucleolytic cleavage downstream of the mature 3⬘ end is followed by 3⬘-exonucleolytic resection to a stem-loop at the 3⬘ en ...
... systems with chloroplast extracts (13). As it turns out, most chloroplast 3⬘ ends are produced by RNA processing rather than by transcription termination. In most cases, an endonucleolytic cleavage downstream of the mature 3⬘ end is followed by 3⬘-exonucleolytic resection to a stem-loop at the 3⬘ en ...
Prostaglandin E2 Regulates the Level and Stability of
... cells. Transfection experiments with a human COX-2 promoter construct revealed a minor element of p38 MAPK-dependent transcriptional control after IL-1 stimulation. p38 MAPK synergized with the cAMP/cAMP-dependent protein kinase cascade to transactivate the COX-2 promoter. When human synovial fibro ...
... cells. Transfection experiments with a human COX-2 promoter construct revealed a minor element of p38 MAPK-dependent transcriptional control after IL-1 stimulation. p38 MAPK synergized with the cAMP/cAMP-dependent protein kinase cascade to transactivate the COX-2 promoter. When human synovial fibro ...
Novel Ciliate Genetic Code Variants Including the Reassignment of
... (Mukai et al. 2016). Sequence analysis of ciliate tRNAs and future experimental studies may shed a light on this intriguing possibility and disclose the molecular machinery used by ciliates to discriminate between stop codons at different positions. Potential possibilities include interactions betwe ...
... (Mukai et al. 2016). Sequence analysis of ciliate tRNAs and future experimental studies may shed a light on this intriguing possibility and disclose the molecular machinery used by ciliates to discriminate between stop codons at different positions. Potential possibilities include interactions betwe ...
ELEM_CouvC_V1n3 copy
... vast deposits of montmorillonite clays up to 16 m thick. The simple crystal structure of clays consists of layers of corner-linked SiO4 tetrahedra bound to layers of edgelinked AlO6 octahedra (FIG. 1). These sheets bind to each other like “a deck of cards” by van der Waals forces and interlayer cati ...
... vast deposits of montmorillonite clays up to 16 m thick. The simple crystal structure of clays consists of layers of corner-linked SiO4 tetrahedra bound to layers of edgelinked AlO6 octahedra (FIG. 1). These sheets bind to each other like “a deck of cards” by van der Waals forces and interlayer cati ...
RNA Splicing
... sequence,it follows an alternative splicing pattern. • In some cases, the ultimate pattern of expression is dictated by the primary transcript, because the use of different startpoints or the generation of alternative 3' ends alters the pattern of splicing. ...
... sequence,it follows an alternative splicing pattern. • In some cases, the ultimate pattern of expression is dictated by the primary transcript, because the use of different startpoints or the generation of alternative 3' ends alters the pattern of splicing. ...
as a PDF
... CUG in Candida albicans (Santos et al., 1997) or of tryptophan by UGA in mitochondria (Barrell et al., 1979). In addition to such reassignment, which affects all genes of a given organism, alternative ways of reading the genetic code have been described that are programmed by signals present in spec ...
... CUG in Candida albicans (Santos et al., 1997) or of tryptophan by UGA in mitochondria (Barrell et al., 1979). In addition to such reassignment, which affects all genes of a given organism, alternative ways of reading the genetic code have been described that are programmed by signals present in spec ...
Highly Efficient Micro RNA Enrichment
... Highly Efficient Micro RNA Enrichment Procedure using Solid Phase Reverse Immobilization Magnetic Bead Technology Bee Na Lee,Ph.D. Sr. Application Scientist, Beckman Coulter Life Sciences ...
... Highly Efficient Micro RNA Enrichment Procedure using Solid Phase Reverse Immobilization Magnetic Bead Technology Bee Na Lee,Ph.D. Sr. Application Scientist, Beckman Coulter Life Sciences ...
Reactivation of Creatine Kinase by Dithiothreitol Prior to Use
... addition of sucrose during the preparation and storage of cell extracts could to some extent prevent the loss of the biological activity of the creatine kinase (Favre and Trepo, 2001). It has been shown that the biological activity of denatured CK could be restored after treatment with dithiothreito ...
... addition of sucrose during the preparation and storage of cell extracts could to some extent prevent the loss of the biological activity of the creatine kinase (Favre and Trepo, 2001). It has been shown that the biological activity of denatured CK could be restored after treatment with dithiothreito ...
A defense-offense multi-layered regulatory switch in a pathogenic
... The wiring diagram of the DSS (Figure 1) was converted into a set of coupled ordinary differential equations (ODEs) under the assumption of mass action kinetics for all reactions. The model describes the temporal variation in the levels of all relevant molecular types, where NX is the number of mole ...
... The wiring diagram of the DSS (Figure 1) was converted into a set of coupled ordinary differential equations (ODEs) under the assumption of mass action kinetics for all reactions. The model describes the temporal variation in the levels of all relevant molecular types, where NX is the number of mole ...
appendix ii - Shodhganga
... c) To build a strand of mRNA using DNA as a template. d) To build a strand of DNA using mRNA as a template. 18. What does a molecule of transfer RNA carry? a) An amino acid molecule b) Enzyme for protein synthesis c) Information from the DNA d) Sequence of codons. 19. Which statement describes the b ...
... c) To build a strand of mRNA using DNA as a template. d) To build a strand of DNA using mRNA as a template. 18. What does a molecule of transfer RNA carry? a) An amino acid molecule b) Enzyme for protein synthesis c) Information from the DNA d) Sequence of codons. 19. Which statement describes the b ...
The Bacterial Toxin RelE Displays Codon
... of protein synthesis by RelE in vivo. We have found that although RelE does not degrade free RNA, it cleaves mRNA in the ribosomal A site with high codon specificity. Among stop codons UAG is cleaved with fast, UAA intermediate and UGA slow rate, while UCG and CAG are cleaved most rapidly among sens ...
... of protein synthesis by RelE in vivo. We have found that although RelE does not degrade free RNA, it cleaves mRNA in the ribosomal A site with high codon specificity. Among stop codons UAG is cleaved with fast, UAA intermediate and UGA slow rate, while UCG and CAG are cleaved most rapidly among sens ...
The trp Operon
... answer to this question lies in the fact that genetic information is not simply inherited and automatically used in every cell all the time. Each cell is using or expressing only a small portion of the total genes that it contains. The finger cells are not expressing the gene for insulin production. ...
... answer to this question lies in the fact that genetic information is not simply inherited and automatically used in every cell all the time. Each cell is using or expressing only a small portion of the total genes that it contains. The finger cells are not expressing the gene for insulin production. ...
Mineral Catalysis and Prebiotic Synthesis: Montmorillonite
... vast deposits of montmorillonite clays up to 16 m thick. The simple crystal structure of clays consists of layers of corner-linked SiO4 tetrahedra bound to layers of edgelinked AlO6 octahedra (FIG. 1). These sheets bind to each other like “a deck of cards” by van der Waals forces and interlayer cati ...
... vast deposits of montmorillonite clays up to 16 m thick. The simple crystal structure of clays consists of layers of corner-linked SiO4 tetrahedra bound to layers of edgelinked AlO6 octahedra (FIG. 1). These sheets bind to each other like “a deck of cards” by van der Waals forces and interlayer cati ...
M2 RNA Pol Ⅰ genes
... 1. Which one of the following statements about eukaryotic RNA polymerases I, II and III is false? A RNA Pol II is very sensitive toα-amanitin. B RNA Pol II is located in th~ nucleoplasm. C RNA Pol III transcribes th~ genes for tRNA. D eukaryotic cells contain other RNA polymerases in addition to RNA ...
... 1. Which one of the following statements about eukaryotic RNA polymerases I, II and III is false? A RNA Pol II is very sensitive toα-amanitin. B RNA Pol II is located in th~ nucleoplasm. C RNA Pol III transcribes th~ genes for tRNA. D eukaryotic cells contain other RNA polymerases in addition to RNA ...
Interactions of Elongation Factor 1 Cell Protrusions with F-Actin and
... sorting of -actin protein to this region. -Actin has been suggested to be an important player in leading edge dynamics by virtue of its isoform-specific interaction with other proteins (such as ezrin and -Cap73; Shuster et al., 1996). The sorting of -actin mRNA requires transport and then select ...
... sorting of -actin protein to this region. -Actin has been suggested to be an important player in leading edge dynamics by virtue of its isoform-specific interaction with other proteins (such as ezrin and -Cap73; Shuster et al., 1996). The sorting of -actin mRNA requires transport and then select ...
Drosophila Genetics Simulation
... Genetics is the scientific study of heredity. Scientists substitute simple organisms for humans when studying inherited diseases and disorders. About 60% of the genes that are known to cause human disease have a recognizable match in the genetic code of the common fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) ...
... Genetics is the scientific study of heredity. Scientists substitute simple organisms for humans when studying inherited diseases and disorders. About 60% of the genes that are known to cause human disease have a recognizable match in the genetic code of the common fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) ...
Bacterial Regulation
... (a) Lactose present, glucose scarce (cAMP level high): abundant lac mRNA synthesized. If glucose is scarce, the high level of cAMP activates CAP, and the lac operon produces large amounts of mRNA for the lactose pathway. Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... (a) Lactose present, glucose scarce (cAMP level high): abundant lac mRNA synthesized. If glucose is scarce, the high level of cAMP activates CAP, and the lac operon produces large amounts of mRNA for the lactose pathway. Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
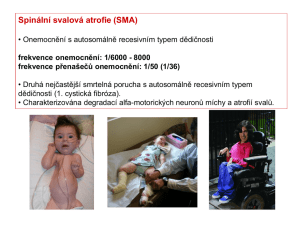
Snímek 1
... snRNA. This unevenly alters the levels of specific endogenous snRNPs, such as those used to splice minor introns (particularly U11) from pre-mRNA. It remains to be determined what the downstream target genes of the affected snRNPs are and how this specifically affects motor neuron function (indicate ...
... snRNA. This unevenly alters the levels of specific endogenous snRNPs, such as those used to splice minor introns (particularly U11) from pre-mRNA. It remains to be determined what the downstream target genes of the affected snRNPs are and how this specifically affects motor neuron function (indicate ...
Messenger RNA

Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a large family of RNA molecules that convey genetic information from DNA to the ribosome, where they specify the amino acid sequence of the protein products of gene expression. Following transcription of primary transcript mRNA (known as pre-mRNA) by RNA polymerase, processed, mature mRNA is translated into a polymer of amino acids: a protein, as summarized in the central dogma of molecular biology.As in DNA, mRNA genetic information is in the sequence of nucleotides, which are arranged into codons consisting of three bases each. Each codon encodes for a specific amino acid, except the stop codons, which terminate protein synthesis. This process of translation of codons into amino acids requires two other types of RNA: Transfer RNA (tRNA), that mediates recognition of the codon and provides the corresponding amino acid, and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), that is the central component of the ribosome's protein-manufacturing machinery.The existence of mRNA was first suggested by Jacques Monod and François Jacob, and subsequently discovered by Jacob, Sydney Brenner and Matthew Meselson at the California Institute of Technology in 1961.