BIO520 Bioinformatics 2005 EXAM2 You may use any books, notes
... Gene 1: 11 exons, plus strand. Gene 2: 5 exons, minus strand, least likely to be correct. Gene 3: 1 exon (partial gene) The polyA site and Promoter are not exons. The gene on the minus strand (12-22kb) has poor Genscan probability scores for every exon and feature. d. How useful is an EST that match ...
... Gene 1: 11 exons, plus strand. Gene 2: 5 exons, minus strand, least likely to be correct. Gene 3: 1 exon (partial gene) The polyA site and Promoter are not exons. The gene on the minus strand (12-22kb) has poor Genscan probability scores for every exon and feature. d. How useful is an EST that match ...
Chapter 8 DNA: the universal molecule of life All living things share
... different cell types, at different times & rates, in different conditions & life stages. • Structural genes produce proteins for structure and function in an organism. • Regulator genes produce proteins to control the action of other genes – turn them ‘on’ or ‘off’. o DNA binding proteins bind to re ...
... different cell types, at different times & rates, in different conditions & life stages. • Structural genes produce proteins for structure and function in an organism. • Regulator genes produce proteins to control the action of other genes – turn them ‘on’ or ‘off’. o DNA binding proteins bind to re ...
Name_____________________________________ Which is the
... a. Gene regulatory proteins often recognize and bind to a short stretch of DNA sequence b. Gene regulatory protein is complete in its function and often acts by itself to regulate gene expression c. A need for dimerization may occur when a gene regulatory protein by itself does not have enough bindi ...
... a. Gene regulatory proteins often recognize and bind to a short stretch of DNA sequence b. Gene regulatory protein is complete in its function and often acts by itself to regulate gene expression c. A need for dimerization may occur when a gene regulatory protein by itself does not have enough bindi ...
Human Genome Project
... • The genome database has many tools to locate a gene of interest or search for potential traits of the gene. • Example–chromosomal map search result for the "breast cancer–causing gene" BRCA2: ...
... • The genome database has many tools to locate a gene of interest or search for potential traits of the gene. • Example–chromosomal map search result for the "breast cancer–causing gene" BRCA2: ...
壹 - 國立彰化師範大學圖書館
... preventing initiation of transcription, prior to the formation of the first phospodiester bond. So the function of the subunit is (A) binding of template DNA (B) binding of nucleotide substrate (C) promoter recognition (D) control of the binding of RNA polymerase to the promoter region 12. Which o ...
... preventing initiation of transcription, prior to the formation of the first phospodiester bond. So the function of the subunit is (A) binding of template DNA (B) binding of nucleotide substrate (C) promoter recognition (D) control of the binding of RNA polymerase to the promoter region 12. Which o ...
Variation in Inherited Characteristics
... organism has during its lifetime can affect its offspring only if the genes in its own sex cells are changed by the experience. Genetic information ...
... organism has during its lifetime can affect its offspring only if the genes in its own sex cells are changed by the experience. Genetic information ...
Chapter 8
... • Any bases that are improperly base-paired are removed and replaced by replication enzymes (proof-reading capability of DNA polymerase) – Light-repair enzymes – Nucleotide excision repair mechanism ...
... • Any bases that are improperly base-paired are removed and replaced by replication enzymes (proof-reading capability of DNA polymerase) – Light-repair enzymes – Nucleotide excision repair mechanism ...
QPX methods 117KB Aug 15 2012 08:14:13 PM
... biochemical pathways will be associated with changes in temperature? Specifically we are interested in virulence factors, mucus production, cell growth and responses to heat stress. HELP! Virulence factors and QPX and methods to id ...
... biochemical pathways will be associated with changes in temperature? Specifically we are interested in virulence factors, mucus production, cell growth and responses to heat stress. HELP! Virulence factors and QPX and methods to id ...
Study Guide for LS
... Substitution is when one base is substituted for another. Not all mutations are harmful. Some mutations are beneficial, and others have no effect at all. A mutation in DNA could also result in death or a genetic disorder. We have certain enzymes that repair most DNA mutations. Ultraviolet radiatio ...
... Substitution is when one base is substituted for another. Not all mutations are harmful. Some mutations are beneficial, and others have no effect at all. A mutation in DNA could also result in death or a genetic disorder. We have certain enzymes that repair most DNA mutations. Ultraviolet radiatio ...
Unit 5 Free Response
... The unit of genetic organization in all living organisms is the chromosome. a. Describe the structure and function of the parts of a eukaryotic chromosome. You may wish to include a diagram as part of your description. b. Describe the adaptive (evolutionary) significance of organizing genes into chr ...
... The unit of genetic organization in all living organisms is the chromosome. a. Describe the structure and function of the parts of a eukaryotic chromosome. You may wish to include a diagram as part of your description. b. Describe the adaptive (evolutionary) significance of organizing genes into chr ...
Keystone Vocabulary 61-70
... 62. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA): A biological macromolecule that encodes the genetic information for living organisms and is capable of self replication and the synthesis of ribonucleic acid (RNA) 63. Homologous Structure: A physical characteristic in different organisms that is similar because it w ...
... 62. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA): A biological macromolecule that encodes the genetic information for living organisms and is capable of self replication and the synthesis of ribonucleic acid (RNA) 63. Homologous Structure: A physical characteristic in different organisms that is similar because it w ...
1. The products of mitosis are .
... D. Proteins E. Microtubules F. Genes 10. Gene density can be high A. in telomeres B. anywhere on the chromosomes C. in centromeres D. in metaphase chromosomes E. in anaphase chromosomes ...
... D. Proteins E. Microtubules F. Genes 10. Gene density can be high A. in telomeres B. anywhere on the chromosomes C. in centromeres D. in metaphase chromosomes E. in anaphase chromosomes ...
1 - web.biosci.utexas.edu
... a. about 100,000 b. about 13,000 c. about three times that of E. coli d. about 8,000 less than humans 4. Which of the following contributes significantly to variation in nuclear genome size among plants. a. amounts of highly repetitive DNA b. amount of selfish DNA (e.g., such as transposons) c. freq ...
... a. about 100,000 b. about 13,000 c. about three times that of E. coli d. about 8,000 less than humans 4. Which of the following contributes significantly to variation in nuclear genome size among plants. a. amounts of highly repetitive DNA b. amount of selfish DNA (e.g., such as transposons) c. freq ...
Eucharyotic Chromatin Organization
... chromosome ever codes for mRNA that is actually translated. 2)The other 99% may be composed of intron genes, pseudogenes or transposons that are rarely transcribed ...
... chromosome ever codes for mRNA that is actually translated. 2)The other 99% may be composed of intron genes, pseudogenes or transposons that are rarely transcribed ...
Leukaemia Section ins(5;11)(q31;q13q23) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... DNA/RNA 13-15 kb mRNA. Protein 431 kDa; contains two DNA binding motifs (a AT hook, and Zinc fingers), a DNA methyl transferase motif, a bromodomain; transcriptional regulatory factor; nuclear localisation. ...
... DNA/RNA 13-15 kb mRNA. Protein 431 kDa; contains two DNA binding motifs (a AT hook, and Zinc fingers), a DNA methyl transferase motif, a bromodomain; transcriptional regulatory factor; nuclear localisation. ...
CAP5510 - Bioinformatics - UF CISE
... • A biological system is made up of components (e.g., proteins, genes, compounds) that interact with each other to affect one another. As a result they serve a set of functions of that system. • Internal factors can alter the networks. – E.g., gene expression and regulation. ...
... • A biological system is made up of components (e.g., proteins, genes, compounds) that interact with each other to affect one another. As a result they serve a set of functions of that system. • Internal factors can alter the networks. – E.g., gene expression and regulation. ...
This examination paper consists of 4 pages
... (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers) 1. Which of the following statements are true Transcriptomes consist of functional RNAs Genes can be disrupted by RNA interference The genetic code includes 1 termination codon 3’ ends of genes can be identified by rapid amplification of c ...
... (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers) 1. Which of the following statements are true Transcriptomes consist of functional RNAs Genes can be disrupted by RNA interference The genetic code includes 1 termination codon 3’ ends of genes can be identified by rapid amplification of c ...
Lab - Protein Synthesis
... The coding sequence (5’ 3’ “antisense”) of DNA below leads to the production of a specific protein. That makes it a gene. The gene was sequenced from samples taken from healthy human patients. As a genetic researcher you must first transcribe the sequence into an mRNA sequence. Then, using the gen ...
... The coding sequence (5’ 3’ “antisense”) of DNA below leads to the production of a specific protein. That makes it a gene. The gene was sequenced from samples taken from healthy human patients. As a genetic researcher you must first transcribe the sequence into an mRNA sequence. Then, using the gen ...
Biotechnology
... • Cross the parent with unknown genotype with an organism that is homozygous recessive for the trait. • Observe the offspring. • Numerous test crosses required to be sure you findings are correct. ...
... • Cross the parent with unknown genotype with an organism that is homozygous recessive for the trait. • Observe the offspring. • Numerous test crosses required to be sure you findings are correct. ...
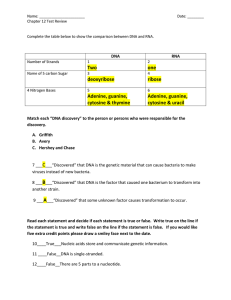
chapter 12 test review key
... 7 ___C___“Discovered” that DNA is the genetic material that can cause bacteria to make viruses instead of new bacteria. 8 ___B___“Discovered” that DNA is the factor that caused one bacterium to transform into ...
... 7 ___C___“Discovered” that DNA is the genetic material that can cause bacteria to make viruses instead of new bacteria. 8 ___B___“Discovered” that DNA is the factor that caused one bacterium to transform into ...
No Slide Title
... Hominds part 2 • Out of Africa: DNA clocks • Multiregionalism: the Neanderthal within us all ...
... Hominds part 2 • Out of Africa: DNA clocks • Multiregionalism: the Neanderthal within us all ...
File
... DNA is separated into single strands by gel DNA is negatively charged – migrates to positive ...
... DNA is separated into single strands by gel DNA is negatively charged – migrates to positive ...