Quick Vocabulary Lesson 1 Lesson 2 dominant trait
... genetics study of how traits are passed from parents to offspring ...
... genetics study of how traits are passed from parents to offspring ...
Genes
... Both exons and introns are transcribed into premature mRNA. Introns are excised and exons are brought together before mRNA leaves nucleus and enters cytoplasm for translation. Activator proteins bound to enhancer transiently bind to RNApII by looping out intervening DNA. Folding DNA enables protei ...
... Both exons and introns are transcribed into premature mRNA. Introns are excised and exons are brought together before mRNA leaves nucleus and enters cytoplasm for translation. Activator proteins bound to enhancer transiently bind to RNApII by looping out intervening DNA. Folding DNA enables protei ...
Molecular Genetics Outcome Checklist
... _____ I can describe how a DNA molecule is able to replicate itself semi-conservatively using molecules such as helicase & DNA polymerase. _____ I can describe the differences in DNA synthesis by polymerase in the leading and lagging strands of DNA replication. _____ I understand how a DNA sequence ...
... _____ I can describe how a DNA molecule is able to replicate itself semi-conservatively using molecules such as helicase & DNA polymerase. _____ I can describe the differences in DNA synthesis by polymerase in the leading and lagging strands of DNA replication. _____ I understand how a DNA sequence ...
Biotechnology Free Response Questions part II
... (b) Cells regulate both protein synthesis and protein activity. Discuss TWO specific mechanisms of protein regulation in eukaryotic cells. (c) The central dogma does not apply to some viruses. Select a specific virus or type of virus and explain how it deviates from the central dogma. ...
... (b) Cells regulate both protein synthesis and protein activity. Discuss TWO specific mechanisms of protein regulation in eukaryotic cells. (c) The central dogma does not apply to some viruses. Select a specific virus or type of virus and explain how it deviates from the central dogma. ...
It all started in the 700s when Chinese used fingerprints to launch
... of significant documents. Afterward, a new field entitled Forensic Science was formed by merging Mathematics, Chemistry, Physics and Biology, toward the designing of novel techniques that will assist in cracking crimes. Sherlock Homes said: ‘’it has long been an axiom of mine that the little things ...
... of significant documents. Afterward, a new field entitled Forensic Science was formed by merging Mathematics, Chemistry, Physics and Biology, toward the designing of novel techniques that will assist in cracking crimes. Sherlock Homes said: ‘’it has long been an axiom of mine that the little things ...
Gene Technology Study Guide Describe three ways genetic
... Recombinant DNA is formed by joining DNA molecules from two different species Fragments of DNA that have complementary sticky ends can join with each other The risk associated with vaccines prepared from dead or weakened pathogenic microbes is that a few remaining live or unweakened microbes c ...
... Recombinant DNA is formed by joining DNA molecules from two different species Fragments of DNA that have complementary sticky ends can join with each other The risk associated with vaccines prepared from dead or weakened pathogenic microbes is that a few remaining live or unweakened microbes c ...
Chapter 16 Research Discovery of DNA`s Structure and Function
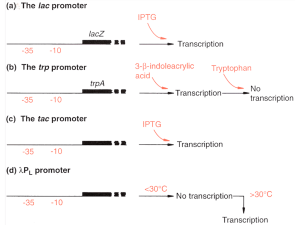
... ➢ Operator - segment of DNA that operates as the switch ➢ Promoter - RNA polymerase can bind with the DNA to begin transcription ➢ Genes - nucleotide sequences that encode subunits of the enzyme Repressor Protein - binds to the operator and blocks the attachment of RNA polymerase to the promoter, p ...
... ➢ Operator - segment of DNA that operates as the switch ➢ Promoter - RNA polymerase can bind with the DNA to begin transcription ➢ Genes - nucleotide sequences that encode subunits of the enzyme Repressor Protein - binds to the operator and blocks the attachment of RNA polymerase to the promoter, p ...
Genetics Introduction:
... o Watson and Crick discovered 3D structure of DNA o Molecular structure of DNA is double helix comprised of a linear sequence of paired nucleotide bases and a sugar phosphate backbone o Nucleotides= building blocks= phosphate + sugar (5C deoxyribose) + base (adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine) o 2 ...
... o Watson and Crick discovered 3D structure of DNA o Molecular structure of DNA is double helix comprised of a linear sequence of paired nucleotide bases and a sugar phosphate backbone o Nucleotides= building blocks= phosphate + sugar (5C deoxyribose) + base (adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine) o 2 ...
Genetics 3500 winter Test ii_ansers
... cell division. Binding of a growth factor to a growth factor receptor on the membrane triggers activation of RAS. In its inactive state RAS has GDP bound to it . RAS is activated when GTP is bound to RAS displacing the GDP. Activation ras then activated other proteins such as RAF leading to a signal ...
... cell division. Binding of a growth factor to a growth factor receptor on the membrane triggers activation of RAS. In its inactive state RAS has GDP bound to it . RAS is activated when GTP is bound to RAS displacing the GDP. Activation ras then activated other proteins such as RAF leading to a signal ...
Intro to Genetics
... • The DNA Sequence shows how a species changes over time • If a mutation (typo) occurs within the DNA sequence, genes can change causing alleles and traits to change ...
... • The DNA Sequence shows how a species changes over time • If a mutation (typo) occurs within the DNA sequence, genes can change causing alleles and traits to change ...
Name Date Class
... 3. Where in the treated cells is CFTR actually produced? 4. The cold viruses used in gene therapy for cystic fibrosis are genetically engineered so they cannot reproduce, and thus cannot cause a viral infection in the patient. Because of this, the therapy does not lead to a permanent cure for cystic ...
... 3. Where in the treated cells is CFTR actually produced? 4. The cold viruses used in gene therapy for cystic fibrosis are genetically engineered so they cannot reproduce, and thus cannot cause a viral infection in the patient. Because of this, the therapy does not lead to a permanent cure for cystic ...
Gene Section AF1q (ALL1 fused gene from chromosome 1q)
... probes are welcome : contact [email protected]. ...
... probes are welcome : contact [email protected]. ...
What are transcription factors?
... The process of STAT3, a transcription factor, binding to a regulatory/non-coding region (in yellow) of a gene is shown. This process occurs in the nucleus. In step 1, STAT3 recognizes a specific DNA sequence (the regulatory/non-coding region that only it can bind to), and binds to it. In step 2, a s ...
... The process of STAT3, a transcription factor, binding to a regulatory/non-coding region (in yellow) of a gene is shown. This process occurs in the nucleus. In step 1, STAT3 recognizes a specific DNA sequence (the regulatory/non-coding region that only it can bind to), and binds to it. In step 2, a s ...
Ch 17 Evolution of Populations
... Sometimes crossing-over involves an unequal swapping of DNA so that one chromosome in the pair gets extra DNA. ...
... Sometimes crossing-over involves an unequal swapping of DNA so that one chromosome in the pair gets extra DNA. ...
17.4_Molecular_Evolution
... Sometimes crossing-over involves an unequal swapping of DNA so that one chromosome in the pair gets extra DNA. ...
... Sometimes crossing-over involves an unequal swapping of DNA so that one chromosome in the pair gets extra DNA. ...
DNA - Ellis Benjamin
... • Gene therapy – replacing faulty genes • Block gene expression to silence harmful gene or study gene function – Antisense RNA, gene knockouts ...
... • Gene therapy – replacing faulty genes • Block gene expression to silence harmful gene or study gene function – Antisense RNA, gene knockouts ...
Gene 5102-96
... Assignment (10 points): For each item of evidence, explain why that evidence, by itself, is not sufficient. Your explanation should consist of a feasible alternative explanation for the finding (independent of the other results). Note there are 5 items, 3 on the following page. 1. A BLASTx search of ...
... Assignment (10 points): For each item of evidence, explain why that evidence, by itself, is not sufficient. Your explanation should consist of a feasible alternative explanation for the finding (independent of the other results). Note there are 5 items, 3 on the following page. 1. A BLASTx search of ...
DNA Recombination
... In order to remove a gene from one cell and insert it into another cell, the gene must be cut from the original chromosome and implanted into the one in the recipient cell. This is accomplished by using special chemicals called restriction enzymes. These enzymes recognize a specific sequence of nucl ...
... In order to remove a gene from one cell and insert it into another cell, the gene must be cut from the original chromosome and implanted into the one in the recipient cell. This is accomplished by using special chemicals called restriction enzymes. These enzymes recognize a specific sequence of nucl ...
Topic 6
... Protein A is a bacterial protein that binds tightly to IgG Streptavidin binds biotin strongly (Kd~10-15). MBP = maltose binding protein GST = glutathione-S-transferase ...
... Protein A is a bacterial protein that binds tightly to IgG Streptavidin binds biotin strongly (Kd~10-15). MBP = maltose binding protein GST = glutathione-S-transferase ...
Assignment 3 - OpenWetWare
... 4. Mutations in a gene can lead to changes in the protein sequence. This can occur in many different ways including the insertion of nucleotides, loss of nucleotides, or the conversion of one sequence to another. For example in sickle-cell disease, the replacement of A by T at the 17th nucleotide of ...
... 4. Mutations in a gene can lead to changes in the protein sequence. This can occur in many different ways including the insertion of nucleotides, loss of nucleotides, or the conversion of one sequence to another. For example in sickle-cell disease, the replacement of A by T at the 17th nucleotide of ...
Quiz 3 Key - UW Canvas
... Quiz 3 KEY NOTE: This key is for version A – look carefully if you have version B! 1. (4 pts) For each of the following molecules or structures, write the letter for the category of biological macromolecule it is or is made of. IF IT CONSISTS OF TWO TYPES, write both letters. Categories may be used ...
... Quiz 3 KEY NOTE: This key is for version A – look carefully if you have version B! 1. (4 pts) For each of the following molecules or structures, write the letter for the category of biological macromolecule it is or is made of. IF IT CONSISTS OF TWO TYPES, write both letters. Categories may be used ...
Cloze passage 3
... p) A biologist who worked with fruit fly to identify sex-linkage q) The features or traits of an organism are controlled by both genes and the ……………. r) The base complementary to thymine s) A model we used to represent chromosomes t) A biological name for a family tree u) A colourblind male need onl ...
... p) A biologist who worked with fruit fly to identify sex-linkage q) The features or traits of an organism are controlled by both genes and the ……………. r) The base complementary to thymine s) A model we used to represent chromosomes t) A biological name for a family tree u) A colourblind male need onl ...
Mutations are heritable alteration in DNA sequence Most common
... Genetic rearrangements o Homologous Recombination Mechanism by which similar strands of double-stranded DNA interact, resulting in inter-strand exchange of bases is the basis for crossing over and gene conversion ...
... Genetic rearrangements o Homologous Recombination Mechanism by which similar strands of double-stranded DNA interact, resulting in inter-strand exchange of bases is the basis for crossing over and gene conversion ...