Genetics BIO.B.1.2.1 Describe how the process of DNA replication
... The genetic code for all organisms is the same – meaning that in ALL organisms the same mRNA code will code for the same amino acids. An organism’s proteins are different because the DNA specifies a different number, order and type of amino acids for each protein to be made. ...
... The genetic code for all organisms is the same – meaning that in ALL organisms the same mRNA code will code for the same amino acids. An organism’s proteins are different because the DNA specifies a different number, order and type of amino acids for each protein to be made. ...
BioBoot Camp Genetics
... The genetic code for all organisms is the same – meaning that in ALL organisms the same mRNA code will code for the same amino acids. An organism’s proteins are different because the DNA specifies a different number, order and type of amino acids for each protein to be made. ...
... The genetic code for all organisms is the same – meaning that in ALL organisms the same mRNA code will code for the same amino acids. An organism’s proteins are different because the DNA specifies a different number, order and type of amino acids for each protein to be made. ...
Biotechnology Need To Know List
... The technique used to make many copies of a gene What genetic engineering involves The technique of DNA sequencing How a recombinant plasmid gets inside a bacterial cell What is most often used as a genetic marker in plasmids The advantage of producing transgenic plants The technique of cloning (she ...
... The technique used to make many copies of a gene What genetic engineering involves The technique of DNA sequencing How a recombinant plasmid gets inside a bacterial cell What is most often used as a genetic marker in plasmids The advantage of producing transgenic plants The technique of cloning (she ...
PowerPoint - Land of Biology
... Because a section of DNA is cut out of one genome and the combined with another genome it is referred to as: RECOMBINANT DNA Because the process is so similar to video and audio tape splicing, this type of genetic engineering is called Gene Splicing. ...
... Because a section of DNA is cut out of one genome and the combined with another genome it is referred to as: RECOMBINANT DNA Because the process is so similar to video and audio tape splicing, this type of genetic engineering is called Gene Splicing. ...
Chapter 12 Study Guide
... In eukaryotes, proteins that attract RNA polymerase bind to ____________________ sequences in DNA. According to the principle of ____________________, hydrogen bonds can form only between adenine and thymine, and between guanine and cytosine. Chromatin contains proteins called ____________________. ...
... In eukaryotes, proteins that attract RNA polymerase bind to ____________________ sequences in DNA. According to the principle of ____________________, hydrogen bonds can form only between adenine and thymine, and between guanine and cytosine. Chromatin contains proteins called ____________________. ...
Now - The Rest of the Genome
... knew that a few genes encoded RNA molecules that never became proteins. Instead, they had other jobs, like helping build proteins in the ribosome. But these exceptions did not seem important enough to cause scientists to question their definitions. “The way biology works is different from mathematic ...
... knew that a few genes encoded RNA molecules that never became proteins. Instead, they had other jobs, like helping build proteins in the ribosome. But these exceptions did not seem important enough to cause scientists to question their definitions. “The way biology works is different from mathematic ...
SAMPLE PAPER CLASS XII MM:70 TIME : 3 HRS General
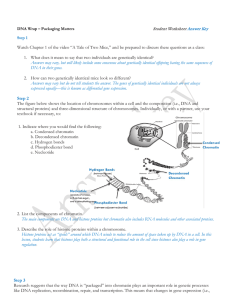
... a)How such a long DNA molecule is packed within the chromosome. b)What are codons and what are their property? c)What are monocistronic and polycistronic genes? d)What value do you learn from a eukaryotic DNA molecule? SECTION E (5 Marks) 1)If a desired gene is identified in an organism for some exp ...
... a)How such a long DNA molecule is packed within the chromosome. b)What are codons and what are their property? c)What are monocistronic and polycistronic genes? d)What value do you learn from a eukaryotic DNA molecule? SECTION E (5 Marks) 1)If a desired gene is identified in an organism for some exp ...
Chromosomes
... • UGA encodes tryptophan not stop-codon • AGA and AGG are stop-codons (they specify arginine in the nuclear genetic code) ...
... • UGA encodes tryptophan not stop-codon • AGA and AGG are stop-codons (they specify arginine in the nuclear genetic code) ...
IMPLICATIONS OF ANTHROPGENY FOR MEDICINE AND
... found from Africa to Indonesia. May have been the first hominin Selection: Allele frequency change over time caused by the to leave Africa. H. erectus DNA may be retrievable from other different replication rate of specific alleles. species due to archaic admixture. ...
... found from Africa to Indonesia. May have been the first hominin Selection: Allele frequency change over time caused by the to leave Africa. H. erectus DNA may be retrievable from other different replication rate of specific alleles. species due to archaic admixture. ...
Biology (Bio 315) S
... developmentally regulated genes which results in the activation of their transcription.* B. adds methyl groups to the DNA of regulatory regions of developmentally regulated genes which results in the activation of their transcription. C. produces a high mutation rate in regulatory regions of develop ...
... developmentally regulated genes which results in the activation of their transcription.* B. adds methyl groups to the DNA of regulatory regions of developmentally regulated genes which results in the activation of their transcription. C. produces a high mutation rate in regulatory regions of develop ...
Lecture 1/3/2006
... Basic concepts of molecular genetics, microarray technology, sources of variability, motivation of the need for statistical analysis Introduction to programming and data analysis using R and Bioconductor. Basics of probability theory (random events, probability, random variables, probability distrib ...
... Basic concepts of molecular genetics, microarray technology, sources of variability, motivation of the need for statistical analysis Introduction to programming and data analysis using R and Bioconductor. Basics of probability theory (random events, probability, random variables, probability distrib ...
Overview of Articles for the literature talks Nr PMID Titel Date
... Recent studies of genome-wide nucleosomal organization suggest that the DNA sequence is one of the major determinants of nucleosome positioning. Although the search for underlying patterns encoded in nucleosomal DNA has been going on for about 30 years, our knowledge of these patterns still remains ...
... Recent studies of genome-wide nucleosomal organization suggest that the DNA sequence is one of the major determinants of nucleosome positioning. Although the search for underlying patterns encoded in nucleosomal DNA has been going on for about 30 years, our knowledge of these patterns still remains ...
Gene Section TFE3 (transcription factor E3) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... Transcription factor; member of the basic helix-loophelix family (b-HLH) of transcription factors primarily found to bind to the immunoglobulin enhancer muE3 motif, Ig K enhancers and Ig H variable regions promotors; the helix-loop-helix-leucine zipper region is implicated in DNA binding and dimeriz ...
... Transcription factor; member of the basic helix-loophelix family (b-HLH) of transcription factors primarily found to bind to the immunoglobulin enhancer muE3 motif, Ig K enhancers and Ig H variable regions promotors; the helix-loop-helix-leucine zipper region is implicated in DNA binding and dimeriz ...
Name
... 33-37. Label where you would find each of the following. If it’s both inside and outside the nucleus, show an arrow coming out of the nucleus. □ DNA □ ribosomes □ mRNA □ tRNA □ amino acids ...
... 33-37. Label where you would find each of the following. If it’s both inside and outside the nucleus, show an arrow coming out of the nucleus. □ DNA □ ribosomes □ mRNA □ tRNA □ amino acids ...
Answer Key
... Epigenetics is the study of other factors besides the DNA sequence that influence whether or not a gene is transcribed into mRNA and then translated (conversion of mRNA sequence into amino acids) into a protein. An individual’s environment, even in the womb, can influence these factors and permanent ...
... Epigenetics is the study of other factors besides the DNA sequence that influence whether or not a gene is transcribed into mRNA and then translated (conversion of mRNA sequence into amino acids) into a protein. An individual’s environment, even in the womb, can influence these factors and permanent ...
Introduction to DNA Function and transcription
... • How does the information stored in DNA determine which proteins can be made in a cell? • How is protein made in a cell? • How does the environment influence which proteins are made in cell? ...
... • How does the information stored in DNA determine which proteins can be made in a cell? • How is protein made in a cell? • How does the environment influence which proteins are made in cell? ...
Imaging in CRISPR/Cas9 Applications
... The CRISPR/Cas9 system is an exciting methodology for genetic modification. Aubrey, Kelly et al. have advanced this technology by developing an inducible lentiviral system. This platform facilitates efficient gene targeting and utilizes an imagingbased tool for phenotypic assessment following deleti ...
... The CRISPR/Cas9 system is an exciting methodology for genetic modification. Aubrey, Kelly et al. have advanced this technology by developing an inducible lentiviral system. This platform facilitates efficient gene targeting and utilizes an imagingbased tool for phenotypic assessment following deleti ...
Lecture 20 DNA Repair and Genetic Recombination
... Modulators of the L1 lifecycle. The L1 amplification cycle can be divided into several steps. (a) Transcription. L1 amplification initiates with transcription, and regulation of L1 at this step can be modified by epigenetic modifications, DNA methylation, and recruitment of transcription factors. (b ...
... Modulators of the L1 lifecycle. The L1 amplification cycle can be divided into several steps. (a) Transcription. L1 amplification initiates with transcription, and regulation of L1 at this step can be modified by epigenetic modifications, DNA methylation, and recruitment of transcription factors. (b ...
Let` review answers as a class.
... 2. Match up the vocabulary words with the definition and the picture that best represents each word. 3. Work with your neighbor to discuss answers and then copy the ...
... 2. Match up the vocabulary words with the definition and the picture that best represents each word. 3. Work with your neighbor to discuss answers and then copy the ...
Making Copies of DNA
... from an adult female sheep. Next, they transferred the nucleus from that cell to an egg cell from which the nucleus had been removed. After a couple of chemical tweaks, the egg cell, with its new nucleus, was behaving just like a freshly fertilized zygote. It developed into an embryo, which was impl ...
... from an adult female sheep. Next, they transferred the nucleus from that cell to an egg cell from which the nucleus had been removed. After a couple of chemical tweaks, the egg cell, with its new nucleus, was behaving just like a freshly fertilized zygote. It developed into an embryo, which was impl ...
Father of Modern Genetics
... DNA (genes) and “unzips” the hydrogen bonds The RNA polymerase also begins the building of the RNA by adding RNA nucleotides in accordance with the DNA base sequence ...
... DNA (genes) and “unzips” the hydrogen bonds The RNA polymerase also begins the building of the RNA by adding RNA nucleotides in accordance with the DNA base sequence ...
ACADEMIC BIOLOGY MIDTERM REVIEW GUIDE
... 10. What are sex-linked traits? 11. Who shows more sex linked traits? 12. What is a carrier? Can a male be a carrier? 13. Be able to solve sex-linked punnett squares and give genotypic and phenotypic ratio of offspring. 14. Name two sex linked traits 15. What can be learned by looking at a karyotype ...
... 10. What are sex-linked traits? 11. Who shows more sex linked traits? 12. What is a carrier? Can a male be a carrier? 13. Be able to solve sex-linked punnett squares and give genotypic and phenotypic ratio of offspring. 14. Name two sex linked traits 15. What can be learned by looking at a karyotype ...
PowerPoint-Präsentation
... selectable marker flanked by homologous sequences. The chromosomal segment is replaced by this URA3 containing fragment after integration by homologous recombination. (B) The URA3 marker introduced in the YFG1 locus, can be excised if URA3 is also flanked by direct repeats of DNA, preferably not ori ...
... selectable marker flanked by homologous sequences. The chromosomal segment is replaced by this URA3 containing fragment after integration by homologous recombination. (B) The URA3 marker introduced in the YFG1 locus, can be excised if URA3 is also flanked by direct repeats of DNA, preferably not ori ...
Primary transcript

A primary transcript is the single-stranded ribonucleic acid (RNA) product synthesized by transcription of DNA, and processed to yield various mature RNA products such as mRNAs, tRNAs, and rRNAs. The primary transcripts designated to be mRNAs are modified in preparation for translation. For example, a precursor messenger RNA (pre-mRNA) is a type of primary transcript that becomes a messenger RNA (mRNA) after processing.There are several steps contributing to the production of primary transcripts. All these steps involve a series of interactions to initiate and complete the transcription of DNA in the nucleus of eukaryotes. Certain factors play key roles in the activation and inhibition of transcription, where they regulate primary transcript production. Transcription produces primary transcripts that are further modified by several processes. These processes include the 5' cap, 3'-polyadenylation, and alternative splicing. In particular, alternative splicing directly contributes to the diversity of mRNA found in cells. The modifications of primary transcripts have been further studied in research seeking greater knowledge of the role and significance of these transcripts. Experimental studies based on molecular changes to primary transcripts the processes before and after transcription have led to greater understanding of diseases involving primary transcripts.