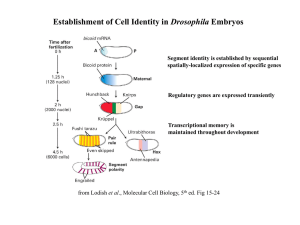
Establishment of Cell Identity in Drosophila Embryos
... Polycomb and Trithorax Complexes Prevents changes in cell identity by preserving transcription patterns Chromatin is altered in a heritable manner ...
... Polycomb and Trithorax Complexes Prevents changes in cell identity by preserving transcription patterns Chromatin is altered in a heritable manner ...
Document
... 1. Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) lies within the matrix, it appears in highly condensed structure called nucleoids. The mtDNA of most cells does not reside in a single location. 2. The number of mitochondria, nucleoids, and mtDNA molecules are variable. The mechanisms are not yet understood. 3. Mitochon ...
... 1. Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) lies within the matrix, it appears in highly condensed structure called nucleoids. The mtDNA of most cells does not reside in a single location. 2. The number of mitochondria, nucleoids, and mtDNA molecules are variable. The mechanisms are not yet understood. 3. Mitochon ...
File
... A. New Techniques Developed to Manipulate DNA B. Techniques Can Be Applied to Alter an Organism's Genes II. Plasmids and the New Genetics A. First Human Gene Inserted into Bacteria 1. Interferon a. Increases to viral infection b. Rare, purification of small quantities is very expensive 2. Bacterial ...
... A. New Techniques Developed to Manipulate DNA B. Techniques Can Be Applied to Alter an Organism's Genes II. Plasmids and the New Genetics A. First Human Gene Inserted into Bacteria 1. Interferon a. Increases to viral infection b. Rare, purification of small quantities is very expensive 2. Bacterial ...
Lecture 3b - Organelles, mitosis, central dogma
... ÆtRNA is like the translator Each tRNA has an anticodon that matches and binds to the codon on the mRNA 1 mRNA codon translates to 1 amino acid Enzymes in the ribosome join amino acids with peptide bonds Resulting protein has specific sequence of amino acids (Why important?) ...
... ÆtRNA is like the translator Each tRNA has an anticodon that matches and binds to the codon on the mRNA 1 mRNA codon translates to 1 amino acid Enzymes in the ribosome join amino acids with peptide bonds Resulting protein has specific sequence of amino acids (Why important?) ...
Reading GuideBacterialGenetics(CH8)
... focus on sections 8.1-8.5 for now. We will finish the last sections, 8.6-8.9, after talking about viruses. So let’s begin with a look at some key terms and the different types of mutations that can occur in bacterial cells. Bacterial cells are good models to use for genetic research since they are h ...
... focus on sections 8.1-8.5 for now. We will finish the last sections, 8.6-8.9, after talking about viruses. So let’s begin with a look at some key terms and the different types of mutations that can occur in bacterial cells. Bacterial cells are good models to use for genetic research since they are h ...
DNA Replication, Transcript
... composed of more than one polypeptide and it was proposed that each polypeptide required a separate gene. • Researchers in the last few years have discovered that at least some genes are not that straightforward. One gene may lead to a single mRNA molecule, but the mRNA molecule may then be modified ...
... composed of more than one polypeptide and it was proposed that each polypeptide required a separate gene. • Researchers in the last few years have discovered that at least some genes are not that straightforward. One gene may lead to a single mRNA molecule, but the mRNA molecule may then be modified ...
D - Cloudfront.net
... 12. After performing amniocentesis, which analysis is most often used to determine the chromosomal condition of a developing fetus? a. blood type b. DNA sequence c. genetic marker d. karyotype ...
... 12. After performing amniocentesis, which analysis is most often used to determine the chromosomal condition of a developing fetus? a. blood type b. DNA sequence c. genetic marker d. karyotype ...
Biology I Formative Assessment #7
... B. DNA replication is important for regulating the expression of genes during protein synthesis. C. DNA replication is important for ensuring that organisms have common ancestry. D. DNA replication is important for transmitting and conserving genetic information. SC.912.L.16.3 2. As a cell prepares ...
... B. DNA replication is important for regulating the expression of genes during protein synthesis. C. DNA replication is important for ensuring that organisms have common ancestry. D. DNA replication is important for transmitting and conserving genetic information. SC.912.L.16.3 2. As a cell prepares ...
Lecture 3b - Organelles, mitosis, central dogma
... RNA stores genetic information in sets of three nucleotides called codons. Each codon specifies a particular amino acid (3 nucleic acid bases = 1 amino acid) There are 64 codons and only 20 amino acids An adapter molecule allows mRNA codons to be read and the proper amino acids to be put int ...
... RNA stores genetic information in sets of three nucleotides called codons. Each codon specifies a particular amino acid (3 nucleic acid bases = 1 amino acid) There are 64 codons and only 20 amino acids An adapter molecule allows mRNA codons to be read and the proper amino acids to be put int ...
Gene!
... argued that acridines such aa pro5vin act as mutagens because they add or dslsts a base or bases. The most striking evidence in favour of this is that mutants produced by a&dines are seldom ‘leaky’ ; they are almost always completely Since our note lacking in the function of the gene. was published, ...
... argued that acridines such aa pro5vin act as mutagens because they add or dslsts a base or bases. The most striking evidence in favour of this is that mutants produced by a&dines are seldom ‘leaky’ ; they are almost always completely Since our note lacking in the function of the gene. was published, ...
Beyond the double helix
... because it was identified in test-tube conditions, the left-handed Z-DNA wasn’t considered a significant player in cellular life. Only recently have researchers found evidence that Z-DNA might be vital in controlling gene activity. In 2001, a team led by Keji Zhao of the National Heart, Lung, and Bl ...
... because it was identified in test-tube conditions, the left-handed Z-DNA wasn’t considered a significant player in cellular life. Only recently have researchers found evidence that Z-DNA might be vital in controlling gene activity. In 2001, a team led by Keji Zhao of the National Heart, Lung, and Bl ...
EOC Review 2 - Wayne County Public Schools
... The combination of genetic material from 2 or more organisms is called ________. • recombinant DNA - rDNA ...
... The combination of genetic material from 2 or more organisms is called ________. • recombinant DNA - rDNA ...
BIOL 221-GENETICS
... C. Mutagenesis of E. coli V. Molecular Genetics (2-3 exercises, usually from among the following) A. DNA isolation B. DNA sequencing videotapes C. Plasmid transformation of E. coli and DNA electrophoresis VI. Genes in Populations (1-3 exercises, usually from among the following) A. Allele competitio ...
... C. Mutagenesis of E. coli V. Molecular Genetics (2-3 exercises, usually from among the following) A. DNA isolation B. DNA sequencing videotapes C. Plasmid transformation of E. coli and DNA electrophoresis VI. Genes in Populations (1-3 exercises, usually from among the following) A. Allele competitio ...
Deoxyribonucleic acid from calf thymus (D4522)
... The Activated Calf Thymus DNA is prepared by modification of a published method using calf thymus DNA (Product No. D 1501) and DNase I (Product No. ...
... The Activated Calf Thymus DNA is prepared by modification of a published method using calf thymus DNA (Product No. D 1501) and DNase I (Product No. ...
DNA Discovery
... • The individual grains are purple with white streaks or mottling. This mottling effect defies Mendel's basic principles of genetics because individual grains may be multicolored rather than a single color. • In the pigmented layer of corn grains, the position of transposons may inhibit or block pig ...
... • The individual grains are purple with white streaks or mottling. This mottling effect defies Mendel's basic principles of genetics because individual grains may be multicolored rather than a single color. • In the pigmented layer of corn grains, the position of transposons may inhibit or block pig ...
Biology 3 Questions 1. Which is found in prokaryotic cell? (Cell)
... c) In non-competitive inhibitor, the inhibitor binds to a site other than the active site d) Addition of more substrate can overcome a competitive inhibitor e) all true 72. Protein molecules may be modified by addition of sulfate, carbohydrate or lipid group to the side chains of certain amino acids ...
... c) In non-competitive inhibitor, the inhibitor binds to a site other than the active site d) Addition of more substrate can overcome a competitive inhibitor e) all true 72. Protein molecules may be modified by addition of sulfate, carbohydrate or lipid group to the side chains of certain amino acids ...
Leukaemia Section t(20;21)(q13;q22) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... Mathew S, Shurtleff SA, Raimondi SC. Novel cryptic, complex rearrangements involving ETV6-CBFA2 (TEL-AML1) genes identified by fluorescence in situ hybridization in pediatric patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2001 Oct;32(2):188-93 This article should be referenced ...
... Mathew S, Shurtleff SA, Raimondi SC. Novel cryptic, complex rearrangements involving ETV6-CBFA2 (TEL-AML1) genes identified by fluorescence in situ hybridization in pediatric patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2001 Oct;32(2):188-93 This article should be referenced ...
Biotechnology
... In addition to the nucleoid, many bacteria often contain small nonchromosomal DNA molecules called plasmids. Plasmids usually contain between 5 and 100 genes. Plasmids are not essential for normal bacterial growth and bacteria may lose or gain them without harm Transposons (transposable elements or ...
... In addition to the nucleoid, many bacteria often contain small nonchromosomal DNA molecules called plasmids. Plasmids usually contain between 5 and 100 genes. Plasmids are not essential for normal bacterial growth and bacteria may lose or gain them without harm Transposons (transposable elements or ...
Primary transcript

A primary transcript is the single-stranded ribonucleic acid (RNA) product synthesized by transcription of DNA, and processed to yield various mature RNA products such as mRNAs, tRNAs, and rRNAs. The primary transcripts designated to be mRNAs are modified in preparation for translation. For example, a precursor messenger RNA (pre-mRNA) is a type of primary transcript that becomes a messenger RNA (mRNA) after processing.There are several steps contributing to the production of primary transcripts. All these steps involve a series of interactions to initiate and complete the transcription of DNA in the nucleus of eukaryotes. Certain factors play key roles in the activation and inhibition of transcription, where they regulate primary transcript production. Transcription produces primary transcripts that are further modified by several processes. These processes include the 5' cap, 3'-polyadenylation, and alternative splicing. In particular, alternative splicing directly contributes to the diversity of mRNA found in cells. The modifications of primary transcripts have been further studied in research seeking greater knowledge of the role and significance of these transcripts. Experimental studies based on molecular changes to primary transcripts the processes before and after transcription have led to greater understanding of diseases involving primary transcripts.