Review L14 Gene to Protein L15 Gene Reg
... 13. What happens to the polypeptide chain after it is synthesized? 14. How do proteins that should be made in the ER get to the ER? 15. Make a list of all the different types of RNA and their functions. 16. What is a mutation? 17. What is a point mutation? 18. Distinguish between the following types ...
... 13. What happens to the polypeptide chain after it is synthesized? 14. How do proteins that should be made in the ER get to the ER? 15. Make a list of all the different types of RNA and their functions. 16. What is a mutation? 17. What is a point mutation? 18. Distinguish between the following types ...
Comparing Different Linear Expression Systems
... A promoter for any of these genes is put next to the gene for rtTA; transcription of the gene rtTA is activated. rtTA makes a tetracycline activator, but with a twist: it only works when doxycycline is present. Then, dox and the tet activator form a complex, and they bind to a special promoter, cons ...
... A promoter for any of these genes is put next to the gene for rtTA; transcription of the gene rtTA is activated. rtTA makes a tetracycline activator, but with a twist: it only works when doxycycline is present. Then, dox and the tet activator form a complex, and they bind to a special promoter, cons ...
Reverse Engineering of Metazoan Gene Regulatory
... Gene regulatory networks play a vital role in metazoan development and function. The protein-DNA interactions (PDIs) that form the basis of these networks have however been poorly characterized. The recent availability of the human genome sequence, as well as genomic resources for other organisms, h ...
... Gene regulatory networks play a vital role in metazoan development and function. The protein-DNA interactions (PDIs) that form the basis of these networks have however been poorly characterized. The recent availability of the human genome sequence, as well as genomic resources for other organisms, h ...
Fragile Sites and Cancer Powerpoint
... • Staining of metaphase chromosomes, one area failed to stain giving the appearance of a gap. • Gaps were susceptible to chromosome breakage. • Cause of fragility is unknown. ...
... • Staining of metaphase chromosomes, one area failed to stain giving the appearance of a gap. • Gaps were susceptible to chromosome breakage. • Cause of fragility is unknown. ...
Biotechnoloy :Guides for Exam 2
... B. 70-80% C. 60-70% D. 80-90% 2. Hemophilia A is due to A. absence of clotting factor VIII B. absence of clotting factor IX C. defective protein defective beta globin D. defective muscle protein. 3. Sickle-cell disease is due to a defective beta globin. A. True. B. False. 4. In US any clinical trial ...
... B. 70-80% C. 60-70% D. 80-90% 2. Hemophilia A is due to A. absence of clotting factor VIII B. absence of clotting factor IX C. defective protein defective beta globin D. defective muscle protein. 3. Sickle-cell disease is due to a defective beta globin. A. True. B. False. 4. In US any clinical trial ...
Genes Section RHOH (ras homolog gene family, member H)
... RHOH (4p13) - Courtesy Mariano Rocchi, Resources for Molecular Cytogenetics. Laboratories willing to validate the probes are welcome: contact [email protected]. ...
... RHOH (4p13) - Courtesy Mariano Rocchi, Resources for Molecular Cytogenetics. Laboratories willing to validate the probes are welcome: contact [email protected]. ...
Modeling Multiple-Allele Genes in NetLogo
... Modeling Multiple-Allele Genes in NetLogo By Max Harmony and Haven Mills Jim Lyons, mentor ...
... Modeling Multiple-Allele Genes in NetLogo By Max Harmony and Haven Mills Jim Lyons, mentor ...
PPT
... Perspective: Historically, the conclusions of genetic experiments were based on the results of selected matings; In other words, we didn’t know what was happening inside the cell, but we could make conclusions based on the phenotypic results (e.g. ratios) of the offspring. It was only recently that ...
... Perspective: Historically, the conclusions of genetic experiments were based on the results of selected matings; In other words, we didn’t know what was happening inside the cell, but we could make conclusions based on the phenotypic results (e.g. ratios) of the offspring. It was only recently that ...
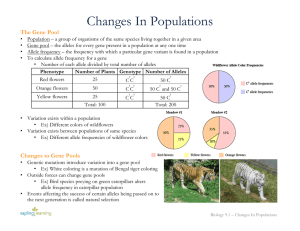
Changes In Populations
... Changes to Gene Pools • Genetic mutations introduce variation into a gene pool • Ex) White coloring is a mutation of Bengal tiger coloring • Outside forces can change gene pools • Ex) Bird species preying on green caterpillars alters allele frequency in caterpillar population • Events affecting the ...
... Changes to Gene Pools • Genetic mutations introduce variation into a gene pool • Ex) White coloring is a mutation of Bengal tiger coloring • Outside forces can change gene pools • Ex) Bird species preying on green caterpillars alters allele frequency in caterpillar population • Events affecting the ...
Student Cancer Notes
... 1. Translocation → Cancer cells are frequently found to contain chromosomes that have broken and rejoined incorrectly → _____________________________________________________________ If a translocated proto-oncogene ends up near an especially active promoter (or other control element), its transcript ...
... 1. Translocation → Cancer cells are frequently found to contain chromosomes that have broken and rejoined incorrectly → _____________________________________________________________ If a translocated proto-oncogene ends up near an especially active promoter (or other control element), its transcript ...
C-13 Part II Non-Mendelian inheritance
... Continuous variation • When multiple genes act together to produce a physical (phenotypic) character, a gradation or range of differences occur. • Examples: height, weight in humans • Referred to as polygenic traits ...
... Continuous variation • When multiple genes act together to produce a physical (phenotypic) character, a gradation or range of differences occur. • Examples: height, weight in humans • Referred to as polygenic traits ...
Genetics and Heredity heredity is the passing of traits from one
... flower position, and stem length used pea plants because they were able to be cross pollinated ...
... flower position, and stem length used pea plants because they were able to be cross pollinated ...
The expression of motility functions in the soil bacterium Bacillus
... fascinating. I am particularly interested in transcription initiation and how a gene that was previously not expressed gets “turned on”. My research interests have focused on the regulation of gene expression by alternate sigma factors in the soil bacterium Bacillus subtilis. Recently, I have also b ...
... fascinating. I am particularly interested in transcription initiation and how a gene that was previously not expressed gets “turned on”. My research interests have focused on the regulation of gene expression by alternate sigma factors in the soil bacterium Bacillus subtilis. Recently, I have also b ...
Chapter 16
... Evolution of the toe • Toes are short, which make humans great long distance runners • Short toes are great for push off during running (toes are for balance too) • The pinky toes – are not used for running…so it may be possible that people may start being born without them… ...
... Evolution of the toe • Toes are short, which make humans great long distance runners • Short toes are great for push off during running (toes are for balance too) • The pinky toes – are not used for running…so it may be possible that people may start being born without them… ...
Jasmonic acid (JA) is a plant hormone that plays an important role in
... stress hormone ethylene. ORA59, belonging to the plant‐specific class of AP2‐domain transcription factors, is the main regulator of JA/ethylene‐ responsive defense gene expression in the model plant species Arabidopsis thaliana. The aim of the research described in this thesis was to study how th ...
... stress hormone ethylene. ORA59, belonging to the plant‐specific class of AP2‐domain transcription factors, is the main regulator of JA/ethylene‐ responsive defense gene expression in the model plant species Arabidopsis thaliana. The aim of the research described in this thesis was to study how th ...
Chapter 18 – 17 pts total - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... 8. Explain why identical twins become less “identical” as they age. 9. Imagine that a check of your DNA reveals that the chromosome area for the protein p53 has somehow been duplicated on one of your chromosomes, giving you 4 copies of the gene. Speculate on what this mutation might mean in terms of ...
... 8. Explain why identical twins become less “identical” as they age. 9. Imagine that a check of your DNA reveals that the chromosome area for the protein p53 has somehow been duplicated on one of your chromosomes, giving you 4 copies of the gene. Speculate on what this mutation might mean in terms of ...
Gene Section WHSC1L1 (Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome candidate 1 like gene 1)
... A hybrid gene involving WHSC1L1/NSD3 was found in a rare leukemia subtype (see below); amplification of a region containing WHSC1L1/NSD3 was found in a subset of breast cancers (but it remains to be determined which gene, within an amplicon, is the critical gene). ...
... A hybrid gene involving WHSC1L1/NSD3 was found in a rare leukemia subtype (see below); amplification of a region containing WHSC1L1/NSD3 was found in a subset of breast cancers (but it remains to be determined which gene, within an amplicon, is the critical gene). ...
Set 5
... 5. You believe that the product of your antenna gene turns on other genes in the antenna. How would you test this idea? What materials would you need? What parts of the regulated genes must you identify? How would you verify a direct interaction in vitro and in vivo, between the protein and candidat ...
... 5. You believe that the product of your antenna gene turns on other genes in the antenna. How would you test this idea? What materials would you need? What parts of the regulated genes must you identify? How would you verify a direct interaction in vitro and in vivo, between the protein and candidat ...
Genetics and Heredity heredity is the passing of traits from one
... seed shape, seed colour, pod shape, pod colour, flower colour flower position, and stem length used pea plants because they were able to be cross pollinated ...
... seed shape, seed colour, pod shape, pod colour, flower colour flower position, and stem length used pea plants because they were able to be cross pollinated ...
Transgenic Sheep and Goats
... • Sheep fibroblasts (connective tissue cells) growing in tissue culture were treated with a vector that contained these segments of DNA: • 2 regions homologous to the sheep COL1A1 gene. This gene encodes Type 1 collagen. (Its absence in humans causes the inherited disease osteogenesis imperfecta.) ...
... • Sheep fibroblasts (connective tissue cells) growing in tissue culture were treated with a vector that contained these segments of DNA: • 2 regions homologous to the sheep COL1A1 gene. This gene encodes Type 1 collagen. (Its absence in humans causes the inherited disease osteogenesis imperfecta.) ...
X-Linked, Epistasis and Multifactorial Problems File
... gene is found on the X chromosome. Cross a woman who is homozygous normal with a hemophiliac man. 4. Height in a plant called spike weed is a multifactorial trait. Three gene pairs are involved, each adding an additional 5 cm to the base plant height. (i.e. they are quantitative characters.) The sma ...
... gene is found on the X chromosome. Cross a woman who is homozygous normal with a hemophiliac man. 4. Height in a plant called spike weed is a multifactorial trait. Three gene pairs are involved, each adding an additional 5 cm to the base plant height. (i.e. they are quantitative characters.) The sma ...