File
... • Mutations and genetic variation occur through the recombining and sorting of meiosis • What cell does a mutation need to occur in, in order to be passed on to its offspring? ...
... • Mutations and genetic variation occur through the recombining and sorting of meiosis • What cell does a mutation need to occur in, in order to be passed on to its offspring? ...
How natural selection changes allele frequencies
... How natural selection changes allele frequencies Drift changes allele frequencies randomly (up or down) and slowly (proportional to 1/N). Selection biases the direction of allele-frequency change, and increases its speed. Alleles change frequency at speeds proportional to their difference in average ...
... How natural selection changes allele frequencies Drift changes allele frequencies randomly (up or down) and slowly (proportional to 1/N). Selection biases the direction of allele-frequency change, and increases its speed. Alleles change frequency at speeds proportional to their difference in average ...
Mechanisms of Evolution
... specific variation of traits do not have to be inherited together Independent Assortment – homologous chromosomes from each parent do not have to all line up on one side of metaphase plate; ensures that parental DNA is shuffled in offspring creating genetic variability Random Fertilization – eac ...
... specific variation of traits do not have to be inherited together Independent Assortment – homologous chromosomes from each parent do not have to all line up on one side of metaphase plate; ensures that parental DNA is shuffled in offspring creating genetic variability Random Fertilization – eac ...
Genetics Vocabulary
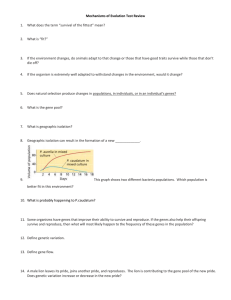
... The chemical factors in your DNA that determine your traits Genes for things give us codons which we use to make proteins and proteins help us express those traits! ...
... The chemical factors in your DNA that determine your traits Genes for things give us codons which we use to make proteins and proteins help us express those traits! ...
Evolution The Change of Populations over Time
... A population bottleneck sometimes causes destruction of genetic variation, leading to an even bigger decrease in the population as the lack of variation allows many of the same species to die to a single event. ...
... A population bottleneck sometimes causes destruction of genetic variation, leading to an even bigger decrease in the population as the lack of variation allows many of the same species to die to a single event. ...
Population
... Formation of New Alleles • Mutation can cause a change in an allele • Only mutations in cells that produce gametes can be passed to offspring ...
... Formation of New Alleles • Mutation can cause a change in an allele • Only mutations in cells that produce gametes can be passed to offspring ...
Lesson Overview Evolution and Ecology
... Differential success of individuals within the population that results from their interaction with the environment. - Reproduction and survival of different genotypes. - The result of natural selection is evolution. ...
... Differential success of individuals within the population that results from their interaction with the environment. - Reproduction and survival of different genotypes. - The result of natural selection is evolution. ...
The origin of genetic variation
... between species reflects genetic differences between species = genetic variation across species What is the origin of genetic variation?? Ultimate:MUTATION!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! II. What is a mutation??? -new variant of DNA that is different from both parents -deleterious alleles in population ...
... between species reflects genetic differences between species = genetic variation across species What is the origin of genetic variation?? Ultimate:MUTATION!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! II. What is a mutation??? -new variant of DNA that is different from both parents -deleterious alleles in population ...
4.2 Test Review File - Northwest ISD Moodle
... If the organism is extremely well adapted to withstand changes in the environment, would it change? ...
... If the organism is extremely well adapted to withstand changes in the environment, would it change? ...
BIOL 502 Population Genetics Spring 2017
... Populations descended from a small founder group may have low genetic variation or by chance have a high or low frequency of particular alleles. ...
... Populations descended from a small founder group may have low genetic variation or by chance have a high or low frequency of particular alleles. ...
Causes of microevolution
... Describes a nonevolving population. It states that the frequencies of alleles and genotypes in a population’s gene pool remain constant over the generations unless acted upon by agents other than sexual recombination. So sexual shuffling of alleles due to meiosis and random fertilization have no eff ...
... Describes a nonevolving population. It states that the frequencies of alleles and genotypes in a population’s gene pool remain constant over the generations unless acted upon by agents other than sexual recombination. So sexual shuffling of alleles due to meiosis and random fertilization have no eff ...
File
... An adaptation is a genetic variation that is favored by selection and is manifested as a trait that provides an advantage to an organism in a particular environment. ...
... An adaptation is a genetic variation that is favored by selection and is manifested as a trait that provides an advantage to an organism in a particular environment. ...
ModelsOfChange23_2
... How mutation and sexual reproduction each produce genetic variation. How natural selection, genetic drift, and gene flow contribute to changing allele frequencies. ...
... How mutation and sexual reproduction each produce genetic variation. How natural selection, genetic drift, and gene flow contribute to changing allele frequencies. ...
Gene Pool
... • Most individuals breed with others of the ____________________________ that share the same ecosystem increased inbreeding. • Limits the frequency of the expression of certain alleles. 4) Mutations • Increase the frequency and type of allele changes within population. • DNA can _____________ and ...
... • Most individuals breed with others of the ____________________________ that share the same ecosystem increased inbreeding. • Limits the frequency of the expression of certain alleles. 4) Mutations • Increase the frequency and type of allele changes within population. • DNA can _____________ and ...
Evolution
... Higher organisms are more closely related to the archaebacteria than to the eubacteria. ...
... Higher organisms are more closely related to the archaebacteria than to the eubacteria. ...
Bottlenecks and Founder Effects
... 1. Count out the numbers of each phenotype in your large population (bag received from the teacher). Determine your phenotypic (trait= “color”) ratio (depict your ratios of each phenotype as percentages). 2. Randomly take a sample from the population (roughly 40-50). 3. Determine the ratio in the sa ...
... 1. Count out the numbers of each phenotype in your large population (bag received from the teacher). Determine your phenotypic (trait= “color”) ratio (depict your ratios of each phenotype as percentages). 2. Randomly take a sample from the population (roughly 40-50). 3. Determine the ratio in the sa ...
ch 4 notes
... environments for mosquitoes carrying malaria Genetic Drift: Genetic Change Due to Chance Random change in allele frequency over time Can lead to one allele being lost and the other fixed in a population May occur in a group that is endogamous (reproducing only within the group) Gene Flow: Spread of ...
... environments for mosquitoes carrying malaria Genetic Drift: Genetic Change Due to Chance Random change in allele frequency over time Can lead to one allele being lost and the other fixed in a population May occur in a group that is endogamous (reproducing only within the group) Gene Flow: Spread of ...
CHAPTER 24 LECTURE SLIDES Prepared by Brenda Leady
... Genetic drift Changes allelic frequency due to random chance Random events unrelated to fitness Favors either loss or fixation of an allele ...
... Genetic drift Changes allelic frequency due to random chance Random events unrelated to fitness Favors either loss or fixation of an allele ...
The Evolution of Populations CHAPTER 23 Microevolution Change
... In the pea plant, red individuals may be either homozygous (R1R1) or heterozygous (R1R2), whereas white flowers are homozygous (R2R2). In a sample of plants, there are 35 red flowers and 65 white flowers. Assume that the population is not evolving. What are the allele frequencies? What proportion ...
... In the pea plant, red individuals may be either homozygous (R1R1) or heterozygous (R1R2), whereas white flowers are homozygous (R2R2). In a sample of plants, there are 35 red flowers and 65 white flowers. Assume that the population is not evolving. What are the allele frequencies? What proportion ...
Evolution of Populations
... Evolutionary fitness can be viewed as an organism’s success in passing genes to the next generation. Evolutionary adaptation can be viewed as any genetically controlled trait that increases an individual’s ability to pass along its genes. ...
... Evolutionary fitness can be viewed as an organism’s success in passing genes to the next generation. Evolutionary adaptation can be viewed as any genetically controlled trait that increases an individual’s ability to pass along its genes. ...
mutations - Université d`Ottawa
... 1. Relatively high rate of amino acid sequence evolution - variable among proteins, but in many cases about 0.5 – 1.5 x 10-9 changes per non-synonymous (ie. amino acid-altering) site per year (Table 4.1) 2. Relatively constant rate of evolution for given protein over time - based on pairwise compari ...
... 1. Relatively high rate of amino acid sequence evolution - variable among proteins, but in many cases about 0.5 – 1.5 x 10-9 changes per non-synonymous (ie. amino acid-altering) site per year (Table 4.1) 2. Relatively constant rate of evolution for given protein over time - based on pairwise compari ...
Genetic drift

Genetic drift (or allelic drift) is the change in the frequency of a gene variant (allele) in a population due to random sampling of organisms.The alleles in the offspring are a sample of those in the parents, and chance has a role in determining whether a given individual survives and reproduces. A population's allele frequency is the fraction of the copies of one gene that share a particular form. Genetic drift may cause gene variants to disappear completely and thereby reduce genetic variation.When there are few copies of an allele, the effect of genetic drift is larger, and when there are many copies the effect is smaller. In the early twentieth century vigorous debates occurred over the relative importance of natural selection versus neutral processes, including genetic drift. Ronald Fisher, who explained natural selection using Mendelian genetics, held the view that genetic drift plays at the most a minor role in evolution, and this remained the dominant view for several decades. In 1968, Motoo Kimura rekindled the debate with his neutral theory of molecular evolution, which claims that most instances where a genetic change spreads across a population (although not necessarily changes in phenotypes) are caused by genetic drift. There is currently a scientific debate about how much of evolution has been caused by natural selection, and how much by genetic drift.