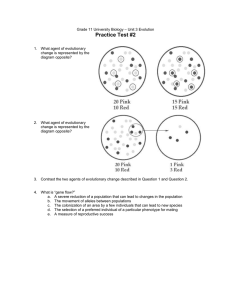
mutation-selection balance.
... deleterious rare alleles are hard to eliminate from a gene pool because they hide from selection as heterozygotes. ...
... deleterious rare alleles are hard to eliminate from a gene pool because they hide from selection as heterozygotes. ...
Gene Linkage PPT
... Discovered by American Geneticist Thomas Hunt Morgan in the early 1900s studying fruit flies Normally, fruit flies have red eyes, but Morgan discovered that some mutant flies had white eyes (most of which ...
... Discovered by American Geneticist Thomas Hunt Morgan in the early 1900s studying fruit flies Normally, fruit flies have red eyes, but Morgan discovered that some mutant flies had white eyes (most of which ...
Broad-Sense Heritability Index
... By demonstrating loci within populations that do not evolve, we can use the H-W law to identify forces that cause populations to evolve by examining loci that do show changes in allele frequencies over ...
... By demonstrating loci within populations that do not evolve, we can use the H-W law to identify forces that cause populations to evolve by examining loci that do show changes in allele frequencies over ...
Broad-Sense Heritability Index
... By demonstrating loci within populations that do not evolve, we can use the H-W law to identify forces that cause populations to evolve by examining loci that do show changes in allele frequencies over ...
... By demonstrating loci within populations that do not evolve, we can use the H-W law to identify forces that cause populations to evolve by examining loci that do show changes in allele frequencies over ...
Science Starter 1. Evolution is as much a fact as the fact
... ! Traveling individuals can introduce new genes 3. Genetic Drift ! Some just do better just by chance 4. Natural Selection ! A gene increases survival ...
... ! Traveling individuals can introduce new genes 3. Genetic Drift ! Some just do better just by chance 4. Natural Selection ! A gene increases survival ...
is p = 1
... gametes will not be random and the HardyWeinberg equilibrium does not occur. (5) No natural selection. If there is differential survival or mating success among genotypes, then the frequencies of alleles in the next variation will deviate from the frequencies predicted by the HardyWeinberg equation. ...
... gametes will not be random and the HardyWeinberg equilibrium does not occur. (5) No natural selection. If there is differential survival or mating success among genotypes, then the frequencies of alleles in the next variation will deviate from the frequencies predicted by the HardyWeinberg equation. ...
YEAR 10 REVISION – SEMESTER II EXAM
... 4. The following list has the steps in natural selection jumbled. Un-jumble them into the correct order. i. The environment changes which causes some vi. Variation in the gene pool individuals to die vii. The individuals that are benefited by ii. A greater proportion of the population their benefici ...
... 4. The following list has the steps in natural selection jumbled. Un-jumble them into the correct order. i. The environment changes which causes some vi. Variation in the gene pool individuals to die vii. The individuals that are benefited by ii. A greater proportion of the population their benefici ...
Chapter 15 Reading Guide - Student
... 37. There are formulas to calculate the rate that a mutations occur in populations and the rate that they get fixed in populations. Because this rate is relatively constant over time, it can be used as a sort of __________________________________ to calculate the evolutionary divergence times betwe ...
... 37. There are formulas to calculate the rate that a mutations occur in populations and the rate that they get fixed in populations. Because this rate is relatively constant over time, it can be used as a sort of __________________________________ to calculate the evolutionary divergence times betwe ...
design a baby face
... Genotype: the DNA = the genes. Phenotype: how the genes are expressed (what the trait looks like). Allele: form of a gene. Dominant Allele: the allele that is seen in hybrid phenotypes. Recessive Allele: the allele that is not seen in hybrid phenotypes. Incomplete Dominance: hybrid alleles blend to ...
... Genotype: the DNA = the genes. Phenotype: how the genes are expressed (what the trait looks like). Allele: form of a gene. Dominant Allele: the allele that is seen in hybrid phenotypes. Recessive Allele: the allele that is not seen in hybrid phenotypes. Incomplete Dominance: hybrid alleles blend to ...
Genetics PowerPoint Notes
... DNA: The ____________________________ that carries information about an organism that is passed on from _____________________ to _____________________. Chromosome: A collection of ____________. Human DNA has ____ chromosomes. Genes: A segments of your DNA on a _________________ that code for specifi ...
... DNA: The ____________________________ that carries information about an organism that is passed on from _____________________ to _____________________. Chromosome: A collection of ____________. Human DNA has ____ chromosomes. Genes: A segments of your DNA on a _________________ that code for specifi ...
Population
... • Birth and Death Rates also remove or add genes from individuals to a population. ...
... • Birth and Death Rates also remove or add genes from individuals to a population. ...
Chapter 23: Evolution of Populations - Biology E
... Directional selection occurs when conditions favor individuals exhibiting one extreme of a phenotype, thereby shifting a population’s frequency curve for the phenotypic character in one direction or the other. Directional selection is common when a population’s environment changes or when members of ...
... Directional selection occurs when conditions favor individuals exhibiting one extreme of a phenotype, thereby shifting a population’s frequency curve for the phenotypic character in one direction or the other. Directional selection is common when a population’s environment changes or when members of ...
AP Biology Notes Outline Enduring Understanding
... mating, the absence of migration, and a net lack of mutations can lead to loss of genetic diversity. Human-directed processes such as genetic engineering can also result in new genes and combinations of alleles that confer new phenotypes. Focusing on evolutionary change in populations, we can define ...
... mating, the absence of migration, and a net lack of mutations can lead to loss of genetic diversity. Human-directed processes such as genetic engineering can also result in new genes and combinations of alleles that confer new phenotypes. Focusing on evolutionary change in populations, we can define ...
AP Biology Notes Outline Enduring Understanding 1.A Big Idea 1
... mating, the absence of migration, and a net lack of mutations can lead to loss of genetic diversity. Human-directed processes such as genetic engineering can also result in new genes and combinations of alleles that confer new phenotypes. Focusing on evolutionary change in populations, we can define ...
... mating, the absence of migration, and a net lack of mutations can lead to loss of genetic diversity. Human-directed processes such as genetic engineering can also result in new genes and combinations of alleles that confer new phenotypes. Focusing on evolutionary change in populations, we can define ...
Evolution - BEHS Science
... What does that mean? • It means that over time, the genes found in groups of living organisms have changed ▫ Alleles – the DNA sequences that are directly responsible for traits ▫ Frequency – the amount of times they appear in a population ...
... What does that mean? • It means that over time, the genes found in groups of living organisms have changed ▫ Alleles – the DNA sequences that are directly responsible for traits ▫ Frequency – the amount of times they appear in a population ...
Chapter 15 - Clayton State University
... Five conditions must be met for a population to be in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium: 1. No mutation introducing new alleles into the population 2. No natural selection favoring some alleles over others 3. An infinitely large population size (and therefore no genetic drift) 4. No influx of alleles from ...
... Five conditions must be met for a population to be in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium: 1. No mutation introducing new alleles into the population 2. No natural selection favoring some alleles over others 3. An infinitely large population size (and therefore no genetic drift) 4. No influx of alleles from ...
Evolution Concept List 2 1. Use each of the following terms in a
... 2. For each pair of terms, explain how the meanings of the terms differ. a. allele frequency and phenotype frequency b. stabilizing selection and disruptive selection c. immigration and emigration d. geo ...
... 2. For each pair of terms, explain how the meanings of the terms differ. a. allele frequency and phenotype frequency b. stabilizing selection and disruptive selection c. immigration and emigration d. geo ...
The Spandrels of San Marco
... adapted through design toward a purpose • Lamarck: adaptation through increased complexity and influence of circumstances • Darwin and Wallace: adaptation is ‘good enough’ outcome of natural selection ...
... adapted through design toward a purpose • Lamarck: adaptation through increased complexity and influence of circumstances • Darwin and Wallace: adaptation is ‘good enough’ outcome of natural selection ...
Genetic drift

Genetic drift (or allelic drift) is the change in the frequency of a gene variant (allele) in a population due to random sampling of organisms.The alleles in the offspring are a sample of those in the parents, and chance has a role in determining whether a given individual survives and reproduces. A population's allele frequency is the fraction of the copies of one gene that share a particular form. Genetic drift may cause gene variants to disappear completely and thereby reduce genetic variation.When there are few copies of an allele, the effect of genetic drift is larger, and when there are many copies the effect is smaller. In the early twentieth century vigorous debates occurred over the relative importance of natural selection versus neutral processes, including genetic drift. Ronald Fisher, who explained natural selection using Mendelian genetics, held the view that genetic drift plays at the most a minor role in evolution, and this remained the dominant view for several decades. In 1968, Motoo Kimura rekindled the debate with his neutral theory of molecular evolution, which claims that most instances where a genetic change spreads across a population (although not necessarily changes in phenotypes) are caused by genetic drift. There is currently a scientific debate about how much of evolution has been caused by natural selection, and how much by genetic drift.