Egypt Web Quest
... Despite all of the benefits of the Nile, it’s flooding is also capable of killing crops and taking human lives Overflow too much—destroyed Crops; Killed people Overflow too little—Crops could not grow; Overcome this problem and able to survive by using surplus of food and resources ...
... Despite all of the benefits of the Nile, it’s flooding is also capable of killing crops and taking human lives Overflow too much—destroyed Crops; Killed people Overflow too little—Crops could not grow; Overcome this problem and able to survive by using surplus of food and resources ...
PowerPoint Presentation - No Slide Title
... King Tutankhamun was a married boy King of 19 years when he died Tutankhamun was in his teens when he married his half sister Keeping property, wealth and power closely within the family was thought to safeguard the continuance of the dynasty. Many of the ancient Egyptian names end in 'amun” or “ama ...
... King Tutankhamun was a married boy King of 19 years when he died Tutankhamun was in his teens when he married his half sister Keeping property, wealth and power closely within the family was thought to safeguard the continuance of the dynasty. Many of the ancient Egyptian names end in 'amun” or “ama ...
Chapter 2, Section 2 Egypt`s Old Kingdom Vocabulary
... • Deities controlled every human activity & all natural forces. ...
... • Deities controlled every human activity & all natural forces. ...
Egypt`s Early Rulers - Mater Academy Lakes High School
... • Two of the most crucial gods were the sun god Re and the river god Hapi . • Another important god was Osiris . According to legend, Osiris was an early pharaoh who gave the Egyptian people laws and taught them farming. • Isis represented the faithful wife and mother. • Osiris and Isis together rul ...
... • Two of the most crucial gods were the sun god Re and the river god Hapi . • Another important god was Osiris . According to legend, Osiris was an early pharaoh who gave the Egyptian people laws and taught them farming. • Isis represented the faithful wife and mother. • Osiris and Isis together rul ...
Kingdoms of Egypt
... The first ritual was to remove all the organs. The first organ was the Brain which was removed from the nose. They believed the brain was not important. Then they took out the liver, intestines, lungs and stomach were placed in conopic jars. The heart was left in the body. The heads on the jars were ...
... The first ritual was to remove all the organs. The first organ was the Brain which was removed from the nose. They believed the brain was not important. Then they took out the liver, intestines, lungs and stomach were placed in conopic jars. The heart was left in the body. The heads on the jars were ...
Egypt - Allenwood BNS
... and sell goods. Instead they battered [exchanged goods] with other traders. Merchants visted the countries bordering the Mediterranean sea as well as those lands to the south. The Egyptians offered goods such as gold a kind of paper called papyruus and cattle ...
... and sell goods. Instead they battered [exchanged goods] with other traders. Merchants visted the countries bordering the Mediterranean sea as well as those lands to the south. The Egyptians offered goods such as gold a kind of paper called papyruus and cattle ...
Study Guide Chapter 3 Test Social Studies
... Middle Kingdom was known for a new class system (added slaves), trade and hieroglyphics. Lower Egypt is found at a lower ELEVATION than Upper Egypt. ...
... Middle Kingdom was known for a new class system (added slaves), trade and hieroglyphics. Lower Egypt is found at a lower ELEVATION than Upper Egypt. ...
ancient of egypt
... ISIS: wife of Osiris; wings,horns or hieroglyphics on head. SET(SETH): evil bother of Osaris; head of unknown animal, a crocodile, a hippopotamus or a black pig. HORUS: sky god and son of Osiris/ Isis who revenged the death of his father ANUBIS: guide of dead and god of embalming; dog or jackal head ...
... ISIS: wife of Osiris; wings,horns or hieroglyphics on head. SET(SETH): evil bother of Osaris; head of unknown animal, a crocodile, a hippopotamus or a black pig. HORUS: sky god and son of Osiris/ Isis who revenged the death of his father ANUBIS: guide of dead and god of embalming; dog or jackal head ...
Chapter 4: Egypt
... polytheistic- believed in many gods Hapi- river god: brought them water and fertile soil Re- sun god: helped their crops grow Osiris: god of the harvest and afterlife Isis: wife of Osiris; helped rule over dead Book of the Dead: magic spells ...
... polytheistic- believed in many gods Hapi- river god: brought them water and fertile soil Re- sun god: helped their crops grow Osiris: god of the harvest and afterlife Isis: wife of Osiris; helped rule over dead Book of the Dead: magic spells ...
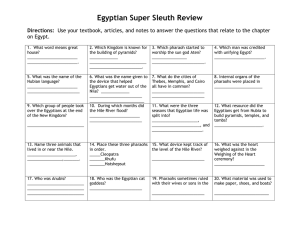
Egyptian Super Sleuth Review Directions
... 6. What was the name given to the device that helped Egyptians get water out of the Nile? _____________ ________________________ _________________________ 10. During which months did the Nile River flood? _______________________ ________________________ ...
... 6. What was the name given to the device that helped Egyptians get water out of the Nile? _____________ ________________________ _________________________ 10. During which months did the Nile River flood? _______________________ ________________________ ...
ANCIENT EGYPTIAN RELIGION General Remarks Most people
... their dead in reasonably lifelike form. It is believed that this belief probably originated from the observation of the natural preservative effects of burials in shallow sand-filled graves in the desert, a practice the earliest Egyptians used. Some must have been uncovered by jackals or pharaoh dog ...
... their dead in reasonably lifelike form. It is believed that this belief probably originated from the observation of the natural preservative effects of burials in shallow sand-filled graves in the desert, a practice the earliest Egyptians used. Some must have been uncovered by jackals or pharaoh dog ...
What was daily life like in ancient Egypt?
... different kinds of oils that were used as make-up – found in Egyptian tombs and coffins bears testament to their interest in beauty. Wigs were also very popular and could be found in a variety of colors such as blue, green, yellow and gold. Moreover, in spite of their dark skin, many Egyptian women ...
... different kinds of oils that were used as make-up – found in Egyptian tombs and coffins bears testament to their interest in beauty. Wigs were also very popular and could be found in a variety of colors such as blue, green, yellow and gold. Moreover, in spite of their dark skin, many Egyptian women ...
The Field Museum Public Relations Department
... informative displays help visitors understand ancient Egyptian religious beliefs and give context to the elaborate preparations for death and the afterlife. The religious life of ancient Egyptians continues through the exhibition at the shrine of the cat-goddess Bastet. Visitors to Inside Ancient Eg ...
... informative displays help visitors understand ancient Egyptian religious beliefs and give context to the elaborate preparations for death and the afterlife. The religious life of ancient Egyptians continues through the exhibition at the shrine of the cat-goddess Bastet. Visitors to Inside Ancient Eg ...
Why was the body not preserved? - 6th-d
... In addition to a recognizable body, the ka also needed food to survive. When Egyptians left food and water at the tomb, they were leaving it for the ka. The akh was represented by a type of bird called a crested ibis. At death, the akh flew to the stars to spend eternity in the heavens. ...
... In addition to a recognizable body, the ka also needed food to survive. When Egyptians left food and water at the tomb, they were leaving it for the ka. The akh was represented by a type of bird called a crested ibis. At death, the akh flew to the stars to spend eternity in the heavens. ...
Ancient Egypt Test Study Guide Answers
... Vocabulary • Afterlife – life after death, much of Egyptian religion focused on the afterlife • Mummies – a specially treated body wrapped in cloth for preservation • Sarcophagus – a case which contained the preserved mummy-like a casket today • Ka – Ancient Egyptians believed that ka was a person’ ...
... Vocabulary • Afterlife – life after death, much of Egyptian religion focused on the afterlife • Mummies – a specially treated body wrapped in cloth for preservation • Sarcophagus – a case which contained the preserved mummy-like a casket today • Ka – Ancient Egyptians believed that ka was a person’ ...
Chapter 4 Section 1-‐ Egypt Under the Pharaohs Titles Notes QCIPL
... -‐Osiris! god of Underworld or the dead—his myth plays major role in the reason for mummification -‐Isis! his wife and mother goddess of Egypt represented love, caring, and protection -‐Horus! the ...
... -‐Osiris! god of Underworld or the dead—his myth plays major role in the reason for mummification -‐Isis! his wife and mother goddess of Egypt represented love, caring, and protection -‐Horus! the ...
discovery - Art Gallery of Western Australia
... Immortal: everlasting and not subject to death. Ka: often shown as a pair of raised arms, the ka was the part of the dead person’s life force that stayed in the tomb. Lapis lazuli: blue mineral with golden flecks. Mummification: process of preserving the remains of the deceased. Mummy: preserved bod ...
... Immortal: everlasting and not subject to death. Ka: often shown as a pair of raised arms, the ka was the part of the dead person’s life force that stayed in the tomb. Lapis lazuli: blue mineral with golden flecks. Mummification: process of preserving the remains of the deceased. Mummy: preserved bod ...
Social Studies Review Chapter 4 (pgs. 86
... Began building them because the Egyptians believed that burial sites were very important, so they built spectacular monuments to honor their rulers Burial in a pyramid demonstrated a pharaohs importance and the shape, pointing to the sky, symbolized the pharaohs journey to the afterlife and if the s ...
... Began building them because the Egyptians believed that burial sites were very important, so they built spectacular monuments to honor their rulers Burial in a pyramid demonstrated a pharaohs importance and the shape, pointing to the sky, symbolized the pharaohs journey to the afterlife and if the s ...
Early Civilizations: Nile, Eastern Mediterranean
... where the religious leader and political leader is the same Since the Egyptians believed the pharoah was a god, it was necessary to preserve the body and built an elaborate tomb mummification – the preservation of dead bodies by embalming and wrapping them in cloth Pyramids were built as tombs ...
... where the religious leader and political leader is the same Since the Egyptians believed the pharoah was a god, it was necessary to preserve the body and built an elaborate tomb mummification – the preservation of dead bodies by embalming and wrapping them in cloth Pyramids were built as tombs ...
Animal mummy
.jpg?width=300)
Animal mummification originated in Egypt. They mummified various animals. It was an enormous part of Egyptian culture, not only in their role as food and pets, but also for religious reasons. They were typically mummified for four main purposes — to allow beloved pets to go on to the afterlife, to provide food in the afterlife, to act as offerings to a particular god, and because some were seen as physical manifestations of specific gods that the Egyptians worshipped. Bast, the cat goddess is an example of one such deity.In 1888, an Egyptian farmer digging in the sand near Istabl Antar discovered a mass grave of felines, ancient cats that were mummified and buried in pits at great numbers.