* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 4: Egypt
Plagues of Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Animal mummy wikipedia , lookup
Index of Egypt-related articles wikipedia , lookup
Thebes, Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Middle Kingdom of Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian funerary practices wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian race controversy wikipedia , lookup
Prehistoric Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Women in ancient Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian medicine wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian religion wikipedia , lookup
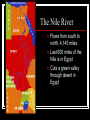
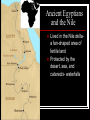
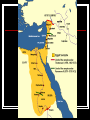
Chapter 4: Ancient Egypt-Land of Abundance 3100 BC - 671 BC Section 1: The Nile The Nile River Flows from south to north, 4,145 miles Last 600 miles of the Nile is in Egypt Cuts a green valley through desert in Egypt Ancient Egyptians and the Nile Lived in the Nile deltaa fan-shaped area of fertile land Protected by the desert, sea, and cataracts- waterfalls The Nile would flood every July and leave rich soil good for growing crops Used shadoofs to lift water to their fields Section 2: The Old Kingdom Made up of two kingdoms: Upper Egypt (white) in the south Lower Egypt (red) in the north Menes united both kingdoms Called “Wearer of Both Crowns” Created capital at Memphis Daily Life in the Old Kingdom 2600 BC - 2100 BC Cities were centers for government and religion Most lived among the banks of the Nile Rich lived in brick and wood houses surrounded by gardens and pools Poor lived in villages on the estates of the rich in one room houses The Pharaoh Ruler, priest, and king the center of Egyptian life owned all of the land built granaries to store grains chose all government officials his actions decided their fate The Pyramids tombs for the pharaohs “Houses of Eternity” placed pharaoh’s personal belongings inside for a happy afterlife Worked on by pharaohs during the summer months when their fields were flooded Made out of granite and limestone Egyptian Gods and Goddesses polytheistic- believed in many gods Hapi- river god: brought them water and fertile soil Re- sun god: helped their crops grow Osiris: god of the harvest and afterlife Isis: wife of Osiris; helped rule over dead Book of the Dead: magic spells Pharaoh Afterlife Used embalming to preserve the body and protect the soul of the dead believed soul could not live without the body Mummification 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Took 70 days Remove the organs Organs dried out with natron, a chemical Organs preserved in jars for afterlife Remove brain Wash body in wine and spices: natron Wrapped in strips of linen Section 3: The Middle Kingdom 2300 BC - 1786 BC Government officials took power from pharaohs 1786 BC- Hyksos, from western Asia, invaded using chariots and bronze and iron weapons 1550 BC- Ahmose, an Egyptian prince, used the Hyksos weapons and drove them out of Egypt Section 4: The New Kingdom 1570 BC- 1070 BC Hatshepsut- Powerful Leader Interested in trade and building temples traded metal tools and weapons for ivory, ebony, monkeys, incense, hunting dogs Never seen before items Thutmose III Succeeds Hatshepsut and Erases Her Name Warrior-pharaoh army of 20,000 archers, throwers, charioteers conquered Syria and Palestine spear- Religion Began to worship new god – Amon Amon was god of Thebes Thebes became capital and main god became Amon-Re Most powerful god of all to Egyptians Temples built Work to sculptors and artisans Also served as schools Hieroglyphics Egyptian picture writing One of three types of Egyptian writing Used on monuments Decline of Egypt 1370 B.C. Amenhotep IV came to power – didn’t agree with power of the priests Closed temples of Amon-Re Set up new religion Worshiped Aton – changed Amenhotep’s name to Akhenaton (“Spirit of Aton”) Not accepted by Egyptians Decline of Egypt (continued) Tutankhamen took over after his death (only 9 years old) By 1150 B.C. Egypt’s empire was gone Taken over by the Assyrians in 671 B.C. Section 5: Contributions Papyrus- used for paper, baskets, sandals Mathematics number system based on 10 geometry- to survey (measure) land Calendar based off Nile three seasons of 120 days five feast days First specialists in medicine first to use bandages and splints used castor oil for indigestion