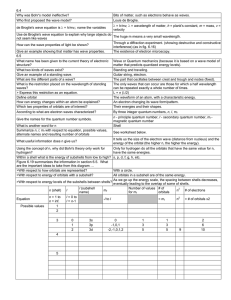
D - sris-physics
... V. The charge on the drop must be A. mgd/V B. mgV/d C. V/mgd D. d/mgV §D. In Rutherford’s scattering experiment, a stream of alpha particles is fired at a thin gold foil. Most of the alpha particles A. are scattered randomly B. rebound C. are scattered uniformly D. go though the foil §B. A piece of ...
... V. The charge on the drop must be A. mgd/V B. mgV/d C. V/mgd D. d/mgV §D. In Rutherford’s scattering experiment, a stream of alpha particles is fired at a thin gold foil. Most of the alpha particles A. are scattered randomly B. rebound C. are scattered uniformly D. go though the foil §B. A piece of ...
Session 26 - Iowa State University
... 2) An electromagnetic plane wave in vacuum is moving in the + y direction. At time t = 0 and at position (x,y,z) = (0,0,0), the electric field is pointing in the + z direction. At that time and position, the magnetic field in the wave is pointed in the ____ direction. a) +x b) +y c) +z ...
... 2) An electromagnetic plane wave in vacuum is moving in the + y direction. At time t = 0 and at position (x,y,z) = (0,0,0), the electric field is pointing in the + z direction. At that time and position, the magnetic field in the wave is pointed in the ____ direction. a) +x b) +y c) +z ...
lecture 15 (zipped power point) (update: 2 Jan 03)
... Notification of “ Constructive WebBased Learning” Please be notified that the “computer-based test” as mentioned earlier on is now ready Each student taking the course ZCT 104/3E please fill up your name in the registration lists that have been put up outside the “Makmal Kumputer Fizik Gunaa” in ...
... Notification of “ Constructive WebBased Learning” Please be notified that the “computer-based test” as mentioned earlier on is now ready Each student taking the course ZCT 104/3E please fill up your name in the registration lists that have been put up outside the “Makmal Kumputer Fizik Gunaa” in ...
4. Energy, Power, and Photons
... we shine light on a piece of metal in a vacuum: 1. The light can cause electrons to be ejected from the metal surface (that’s not so unusual) 2. The energy of these electrons (i.e., their velocity once they leave the metal) does not depend on the light intensity, although the total number of ...
... we shine light on a piece of metal in a vacuum: 1. The light can cause electrons to be ejected from the metal surface (that’s not so unusual) 2. The energy of these electrons (i.e., their velocity once they leave the metal) does not depend on the light intensity, although the total number of ...
Quantum Physics 3 - FSU Physics Department
... Compton effect Light exhibits diffraction and interference phenomena that are only explicable in terms of wave properties Light is always detected as packets (photons); we never observe half a photon Number of photons proportional to energy density (i.e. to square of electromagnetic field stre ...
... Compton effect Light exhibits diffraction and interference phenomena that are only explicable in terms of wave properties Light is always detected as packets (photons); we never observe half a photon Number of photons proportional to energy density (i.e. to square of electromagnetic field stre ...
Historic Development by Mihai
... Einstein came up with the hypothesis of the corpuscular nature of light explaining the photoelectric effect. Einstein theory was verified by Millikan experiments (1916) ,he received Nobel price for that. Careful investigations toward the end of the nineteenth century proved that the photoelectric ef ...
... Einstein came up with the hypothesis of the corpuscular nature of light explaining the photoelectric effect. Einstein theory was verified by Millikan experiments (1916) ,he received Nobel price for that. Careful investigations toward the end of the nineteenth century proved that the photoelectric ef ...
Quantum Theory Historical Reference
... wave properties under certain circumstances. His doctoral thesis (1925) proposed that a particle of mass (m) and velocity (v) should have a wavelength associated with it. Ultimately explains the quantized energy of electrons. de Broglie = h/(mv) h = Plank’s constant: 6.63 x 10-34 J.s In order ...
... wave properties under certain circumstances. His doctoral thesis (1925) proposed that a particle of mass (m) and velocity (v) should have a wavelength associated with it. Ultimately explains the quantized energy of electrons. de Broglie = h/(mv) h = Plank’s constant: 6.63 x 10-34 J.s In order ...
Slide 1
... The attractive Coulomb force between the positive nucleus and the orbiting electron could provide the attractive force which keeps the electron in it’s orbit, much as the planets orbit the sun with gravity providing the centripetal force. ...
... The attractive Coulomb force between the positive nucleus and the orbiting electron could provide the attractive force which keeps the electron in it’s orbit, much as the planets orbit the sun with gravity providing the centripetal force. ...
Exam sample
... 7. “No two electrons in the same atom may have the same values for all four quantum numbers” is a statement of: a. Hund’s Rule. b. deBroglie’s Hypothesis. c. the Pauli Exclusion Principle. d. the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle. 8. All s orbitals are: a. shaped like four-leaf clovers. b. dumbbell- ...
... 7. “No two electrons in the same atom may have the same values for all four quantum numbers” is a statement of: a. Hund’s Rule. b. deBroglie’s Hypothesis. c. the Pauli Exclusion Principle. d. the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle. 8. All s orbitals are: a. shaped like four-leaf clovers. b. dumbbell- ...
Lecture 16
... Completely solving the problem is simply a matter of equating the wave function and first derivative of the wave function at the potential boundary. More interesting is comparing the probability for a wave to exist as a right moving, transmitted wave, or left moving, reflected, wave after encounteri ...
... Completely solving the problem is simply a matter of equating the wave function and first derivative of the wave function at the potential boundary. More interesting is comparing the probability for a wave to exist as a right moving, transmitted wave, or left moving, reflected, wave after encounteri ...
Thirteenth quantum mechanics sheet
... From b) it follows that it is possible to form joint Eigenvectors of J~2 , J3 , L these Eigenvectors |j, mj ; l, si with J~2 |j, mj ; l, si = h̄2 j(j + 1)|j, mj ; l, si J3 |j, mj ; l, si = h̄mj |j, mj ; l, si ~ 2 |j, mj ; l, si = h̄2 l(l + 1)|j, mj ; l, si L ~ 2 |j, mj ; l, si = h̄2 s(s + 1)|j, mj ; ...
... From b) it follows that it is possible to form joint Eigenvectors of J~2 , J3 , L these Eigenvectors |j, mj ; l, si with J~2 |j, mj ; l, si = h̄2 j(j + 1)|j, mj ; l, si J3 |j, mj ; l, si = h̄mj |j, mj ; l, si ~ 2 |j, mj ; l, si = h̄2 l(l + 1)|j, mj ; l, si L ~ 2 |j, mj ; l, si = h̄2 s(s + 1)|j, mj ; ...
operators
... Expectation Values •Suppose we know the wave function (x) and we measure x. What answer will we get? •We only know probability of getting different values •Let’s find the average value you get •Recall |(x)|2 tells you the probability density that it is at x •We want an expectation value x P x ...
... Expectation Values •Suppose we know the wave function (x) and we measure x. What answer will we get? •We only know probability of getting different values •Let’s find the average value you get •Recall |(x)|2 tells you the probability density that it is at x •We want an expectation value x P x ...
Quantum Theory
... Hot objects emit light and other forms of electromagnetic radiation, but not continuously, as expected Instead, it is emitted in small, specific amounts called quanta. E=hv H=6.626 x 10 -34 J*s This number is called Planck’s constant ...
... Hot objects emit light and other forms of electromagnetic radiation, but not continuously, as expected Instead, it is emitted in small, specific amounts called quanta. E=hv H=6.626 x 10 -34 J*s This number is called Planck’s constant ...
AtomLightEmissQuantum
... Think-The mass of a gold ring is the mass of a single gold atom multiplied by the number of atoms in the ring. ...
... Think-The mass of a gold ring is the mass of a single gold atom multiplied by the number of atoms in the ring. ...