Mechanisms for the Radiation of Electromagnetic Waves
... Electromagnetic energy is not released in the form of an electromagnetic “wave” but rather is released in the form of an electromagnetic “particle” called a photon. The energy of motion of this photon is not the usual kinetic energy, but the energy of the photon is given by ...
... Electromagnetic energy is not released in the form of an electromagnetic “wave” but rather is released in the form of an electromagnetic “particle” called a photon. The energy of motion of this photon is not the usual kinetic energy, but the energy of the photon is given by ...
Phys 209BH
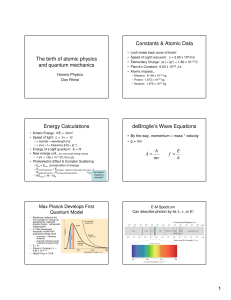
... The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons released from a metal surface when exposed to 492 nm light is 9.9 10-20 J. Energy drops to 3.8 10-20 J if the wavelength is changed to 579 nm. Use this data to calculate plank’s constant h and work function . ...
... The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons released from a metal surface when exposed to 492 nm light is 9.9 10-20 J. Energy drops to 3.8 10-20 J if the wavelength is changed to 579 nm. Use this data to calculate plank’s constant h and work function . ...
一 - 國立嘉義大學
... forming a conducting loop with the rod as the top member. The plane of the rails makes an angle with ...
... forming a conducting loop with the rod as the top member. The plane of the rails makes an angle with ...
Notes - Photons, the Photoelectric Effect and the Compton Effect (ppt)
... • Classical physics predicts that any frequency of light can eject electrons as long as the intensity is high enough. • Experimental data shows there is a minimum (cutoff frequency) that the light must have. • Classical physics predicts that the kinetic energy of the ejected electrons should increas ...
... • Classical physics predicts that any frequency of light can eject electrons as long as the intensity is high enough. • Experimental data shows there is a minimum (cutoff frequency) that the light must have. • Classical physics predicts that the kinetic energy of the ejected electrons should increas ...
03 Homework File
... 2. It is proposed to use the LHC to collide 7 TeV protons with 50 GeV electrons, in the so-called LHeC. Calculate the centre of mass energy of this system. ...
... 2. It is proposed to use the LHC to collide 7 TeV protons with 50 GeV electrons, in the so-called LHeC. Calculate the centre of mass energy of this system. ...
B E , 2012
... film and find the condition of maxima and minima. b) Describe and explain the formation of Newton’s rings in reflected monochromatic light. Prove that in reflected light, diameters of bright rings are proportional to the square-roots of odd numbers. ...
... film and find the condition of maxima and minima. b) Describe and explain the formation of Newton’s rings in reflected monochromatic light. Prove that in reflected light, diameters of bright rings are proportional to the square-roots of odd numbers. ...
IntroQuantumNuclearp..
... Built on deBroglie and Heisenberg’s ideas...developed more complex wavefunction equation (ψ) model Predicted behavior of e- in space and time – think of it as predicting where and when an e- based on probability* If you map out these likely locations over time, you would see a “cloud” of possible lo ...
... Built on deBroglie and Heisenberg’s ideas...developed more complex wavefunction equation (ψ) model Predicted behavior of e- in space and time – think of it as predicting where and when an e- based on probability* If you map out these likely locations over time, you would see a “cloud” of possible lo ...
No Slide Title
... that we can never simultaneously know the position (radius) and momentum (energy) of an electron, as defined in the Bohr model of the atom. ...
... that we can never simultaneously know the position (radius) and momentum (energy) of an electron, as defined in the Bohr model of the atom. ...
Laser Physics I
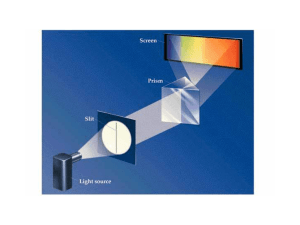
... Light and Electromagnetic Waves Light is one form of electromagnetic radiation. Electromagnetic radiation, which transports energy from point to point at the velocity of light, can be described in terms of both wave and particle "pictures" or "models." This is the famous "wave-particle" duality ...
... Light and Electromagnetic Waves Light is one form of electromagnetic radiation. Electromagnetic radiation, which transports energy from point to point at the velocity of light, can be described in terms of both wave and particle "pictures" or "models." This is the famous "wave-particle" duality ...
Chapter 4
... • Light and electrons both behave quantum mechanically. – Waves • Waves are an oscillation that moves outward from a disturbance (ripples moving away from a pebble dropped into a pond) ...
... • Light and electrons both behave quantum mechanically. – Waves • Waves are an oscillation that moves outward from a disturbance (ripples moving away from a pebble dropped into a pond) ...
The Zeeman Effect
... moments of several coupled electrons. When an atom has L≠0 and S≠0, these net magnetic moments are simply additive. Spin-orbit coupling (itself a magnetic effect) is usually large enough that the total electronic angular momentum, J, and its projection, MJ, are better overall labels for the atomic s ...
... moments of several coupled electrons. When an atom has L≠0 and S≠0, these net magnetic moments are simply additive. Spin-orbit coupling (itself a magnetic effect) is usually large enough that the total electronic angular momentum, J, and its projection, MJ, are better overall labels for the atomic s ...
Electron Configuration - Warren County Public Schools
... particle nature. • Light has wave-like properties but can also be thought of as a stream of particles. • Each particle of light carries a quantum of energy. • He called these particles photons. • A photon is a particle of electromagnetic radiation having zero mass and carrying a quantum of energy. ...
... particle nature. • Light has wave-like properties but can also be thought of as a stream of particles. • Each particle of light carries a quantum of energy. • He called these particles photons. • A photon is a particle of electromagnetic radiation having zero mass and carrying a quantum of energy. ...
Electron Configuration and New Atomic Model
... particle nature. • Light has wave-like properties but can also be thought of as a stream of particles. • Each particle of light carries a quantum of energy. • He called these particles photons. • A photon is a particle of electromagnetic radiation having zero mass and carrying a quantum of energ ...
... particle nature. • Light has wave-like properties but can also be thought of as a stream of particles. • Each particle of light carries a quantum of energy. • He called these particles photons. • A photon is a particle of electromagnetic radiation having zero mass and carrying a quantum of energ ...