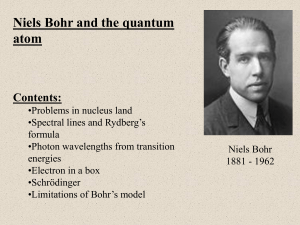
Learning Goals
... Be able to describe a physical situation that would correspond to simple potential energy curves. Given a simple physical system, be able to draw the relevant potential energy curve needed to model dynamical behaviour. Explain why models are useful in physics. 2. Light as a Particle- why believe ide ...
... Be able to describe a physical situation that would correspond to simple potential energy curves. Given a simple physical system, be able to draw the relevant potential energy curve needed to model dynamical behaviour. Explain why models are useful in physics. 2. Light as a Particle- why believe ide ...
Wave Particle Duality File
... • Waves interfere with each other, they can reinforce each other or cancel each other out ...
... • Waves interfere with each other, they can reinforce each other or cancel each other out ...
Chapter 8 - Fayetteville State University
... electrons are emitted from the metal it is shining upon. C. A bright light causes more electrons to be emitted than a faint light. D. Higher frequency light emits electrons with higher kinetic energies. 3. Max Planck A. proposed that light consists of photons. B. developed a theory to explain the ab ...
... electrons are emitted from the metal it is shining upon. C. A bright light causes more electrons to be emitted than a faint light. D. Higher frequency light emits electrons with higher kinetic energies. 3. Max Planck A. proposed that light consists of photons. B. developed a theory to explain the ab ...
wave-particle duality
... • Diffraction and interference Evidence for particle-nature of light • Photoelectric effect • Compton effect •Light exhibits diffraction and interference phenomena that are only explicable in terms of wave properties •Light is always detected as packets (photons); if we look, we never observe half a ...
... • Diffraction and interference Evidence for particle-nature of light • Photoelectric effect • Compton effect •Light exhibits diffraction and interference phenomena that are only explicable in terms of wave properties •Light is always detected as packets (photons); if we look, we never observe half a ...
WAVE-PARTICLE DUALITY
... • Diffraction and interference Evidence for particle-nature of light • Photoelectric effect • Compton effect •Light exhibits diffraction and interference phenomena that are only explicable in terms of wave properties •Light is always detected as packets (photons); if we look, we never observe half a ...
... • Diffraction and interference Evidence for particle-nature of light • Photoelectric effect • Compton effect •Light exhibits diffraction and interference phenomena that are only explicable in terms of wave properties •Light is always detected as packets (photons); if we look, we never observe half a ...
Postulate 1 of Quantum Mechanics (wave function)
... • Wikipedia (http://en.wikipedia.org): Search for Wave function Measurement in quantum mechanics Schrodinger equation ...
... • Wikipedia (http://en.wikipedia.org): Search for Wave function Measurement in quantum mechanics Schrodinger equation ...
Questions and Answers - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... experiment when detectors are used to determine which slit an electron is passing through? How do researchers explain this? 2. When the electrons are observed, what interpretations do researchers suggest causes the electrons to travel the way they do? Which interpretation do you think is true and wh ...
... experiment when detectors are used to determine which slit an electron is passing through? How do researchers explain this? 2. When the electrons are observed, what interpretations do researchers suggest causes the electrons to travel the way they do? Which interpretation do you think is true and wh ...
T3 F2013 9 30
... 6. At time t, r = 2t2i – 3t3j +k gives the position of a 2.0 kg particle relative to the origin of an xy coordinate system ( is in meters and t is in seconds). I. Find an expression as a function of time for a) the velocity b) the linear momentum c) the acceleration d) the force, of the particle re ...
... 6. At time t, r = 2t2i – 3t3j +k gives the position of a 2.0 kg particle relative to the origin of an xy coordinate system ( is in meters and t is in seconds). I. Find an expression as a function of time for a) the velocity b) the linear momentum c) the acceleration d) the force, of the particle re ...
hw08_assingnment
... 3. If the magnetic field in a traveling EM wave has a peak magnitude of 17.5 nT at a given point, what is the peak magnitude of the electric field? ...
... 3. If the magnetic field in a traveling EM wave has a peak magnitude of 17.5 nT at a given point, what is the peak magnitude of the electric field? ...
Introduction
... • Light behaves simultaneously as a wave and a flux of particles • The wave enables calculation of particle-related probabilities; e. g., when the photon is emitted, the probability of its striking the screen is proportional to light intensity, which in turn is proportional to the square of the fiel ...
... • Light behaves simultaneously as a wave and a flux of particles • The wave enables calculation of particle-related probabilities; e. g., when the photon is emitted, the probability of its striking the screen is proportional to light intensity, which in turn is proportional to the square of the fiel ...
Chapter 8 - Bakersfield College
... C. Lasers use materials whose atoms have metastable states, which are excited states with relatively long lifetimes. 1. Ruby lasers use xenon-filled flash lamps to excite chromium ions in ruby rods. 2. Helium-neon lasers use an electric discharge to bring the atoms of the gas mixture to metastable l ...
... C. Lasers use materials whose atoms have metastable states, which are excited states with relatively long lifetimes. 1. Ruby lasers use xenon-filled flash lamps to excite chromium ions in ruby rods. 2. Helium-neon lasers use an electric discharge to bring the atoms of the gas mixture to metastable l ...
Linear Circuit Analysis with Reactive Components
... Solving the Schrödinger Equation on a 2D Lattice in Quantum Wave Interference (QWI) PhET Sam Reid Quantum Wave Interference allows the user to visualize the propagation of a wavefunction in the presence of potential barriers and detectors. We implement a 2D Richardson algorithm[1], a local propagati ...
... Solving the Schrödinger Equation on a 2D Lattice in Quantum Wave Interference (QWI) PhET Sam Reid Quantum Wave Interference allows the user to visualize the propagation of a wavefunction in the presence of potential barriers and detectors. We implement a 2D Richardson algorithm[1], a local propagati ...
lect3
... Consider a flux of particles, momentum ħk, energy E= ħ2k2/2m approaching a barrier, height V0 (V0 > E), width a. ...
... Consider a flux of particles, momentum ħk, energy E= ħ2k2/2m approaching a barrier, height V0 (V0 > E), width a. ...