PHQ-9 AND GAD-7: Measuring Vital Signs in Mental Health
... (Kessing LV, Hansen MG, Andersen PK, Angst J. (2004) The predictive effect of episodes on the risk of recurrence in depressive and bipolar disorders - a life-long perspective. Acta Psychiatr Scand.109:339–44) Richard M, (2004) The early warning symptom intervention for patients with bipolar affectiv ...
... (Kessing LV, Hansen MG, Andersen PK, Angst J. (2004) The predictive effect of episodes on the risk of recurrence in depressive and bipolar disorders - a life-long perspective. Acta Psychiatr Scand.109:339–44) Richard M, (2004) The early warning symptom intervention for patients with bipolar affectiv ...
NS330 Quiz 3 - WordPress.com
... -postpartum onset (w/in 4 wks postpartum)- severe anxiety, possible psychotic features -seasonal features- generally occurring in fall or winter & remitting in spring; tx w/ light therapy -atypical features- appetite changes, wt gain, hypersomnia, extreme sensitivity to perceived interpersonal rejec ...
... -postpartum onset (w/in 4 wks postpartum)- severe anxiety, possible psychotic features -seasonal features- generally occurring in fall or winter & remitting in spring; tx w/ light therapy -atypical features- appetite changes, wt gain, hypersomnia, extreme sensitivity to perceived interpersonal rejec ...
File - Sarah M. Brothwell
... energy, lasting at least 4 consecutive days B. During the mood disturbance 3 (or more) of the following symptoms have persisted 1. more talkative than usual or pressure to keep taking 2. increased in goal-directed activity 3. excessive involvement in activities that have high potential for painful c ...
... energy, lasting at least 4 consecutive days B. During the mood disturbance 3 (or more) of the following symptoms have persisted 1. more talkative than usual or pressure to keep taking 2. increased in goal-directed activity 3. excessive involvement in activities that have high potential for painful c ...
Peripapillary Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness in Bipolar Disorder
... There are only few studies on OCT in psychiatric disorders that was exclusive to schizophrenia and none on bipolar disorder but they are compatible with our result showing decreasing of RNFLT (5, 7) this is in line with studies on gray matter deficit in bipolar disorder [10,15]. We also observed sta ...
... There are only few studies on OCT in psychiatric disorders that was exclusive to schizophrenia and none on bipolar disorder but they are compatible with our result showing decreasing of RNFLT (5, 7) this is in line with studies on gray matter deficit in bipolar disorder [10,15]. We also observed sta ...
Depressive Disorders
... A distinct period of abnormally and persistently elevated, expansive, or irritable mood Mood disturbance plus three of the following symptoms (four if the mood is only irritable): Inflated self esteem or grandiosity Decreased need for sleep More talkative than usual or pressure to keep talking Fligh ...
... A distinct period of abnormally and persistently elevated, expansive, or irritable mood Mood disturbance plus three of the following symptoms (four if the mood is only irritable): Inflated self esteem or grandiosity Decreased need for sleep More talkative than usual or pressure to keep talking Fligh ...
Bipolar Disorder: A Review - International Journal of Research in
... clinical picture of major depression (lower pole), the manic or hypomanic phase (upper pole), and euthymia, or the asymptomatic phase. Manic and hypomanic episodes are characterized by grandiosity, inflated self-esteem, diminished need for sleep, increased goal-directed activity, and talkativeness. ...
... clinical picture of major depression (lower pole), the manic or hypomanic phase (upper pole), and euthymia, or the asymptomatic phase. Manic and hypomanic episodes are characterized by grandiosity, inflated self-esteem, diminished need for sleep, increased goal-directed activity, and talkativeness. ...
All You Wanted to Know About Medications But Were Afraid
... • Significant functional impairment • Bipolar I people go through cycles of major depression and mania • Bipolar II similar to Bipolar I except that people have hypomanic episodes, a milder form of mania • Rapid cyclers ...
... • Significant functional impairment • Bipolar I people go through cycles of major depression and mania • Bipolar II similar to Bipolar I except that people have hypomanic episodes, a milder form of mania • Rapid cyclers ...
Friday, October 29
... (psychoanalytic theory, biological theory, social-cognitive theory ((ex. attributional theory)), humanistic) ...
... (psychoanalytic theory, biological theory, social-cognitive theory ((ex. attributional theory)), humanistic) ...
Mood Disorders DSM V Handout
... mood is only irritable) are present to a significant degree and represent a noticeable change from usual behavior: 1. Inflated self-esteem or grandiosity. 2. Decreased need for sleep (e.g., feels rested after only 3 hours of sleep). 3. More talkative than usual or pressure to keep talking. 4. Flight ...
... mood is only irritable) are present to a significant degree and represent a noticeable change from usual behavior: 1. Inflated self-esteem or grandiosity. 2. Decreased need for sleep (e.g., feels rested after only 3 hours of sleep). 3. More talkative than usual or pressure to keep talking. 4. Flight ...
DSM-IV
... – 4 to 8 weeks to produce effect – SSRI’s (Prozac, Zoloft, Celexa) – Dopamine specific reuptake inhibitors (Wellbutrin) ...
... – 4 to 8 weeks to produce effect – SSRI’s (Prozac, Zoloft, Celexa) – Dopamine specific reuptake inhibitors (Wellbutrin) ...
Psychosis - Santa Barbara Therapist
... • Can function in the community • May have depression after psychotic episode and this is the most dangerous time for suicide • Decreased sleep, energy and mood tend to precipitate a psychotic break • Recovery is NOT related to severity of psychosis ...
... • Can function in the community • May have depression after psychotic episode and this is the most dangerous time for suicide • Decreased sleep, energy and mood tend to precipitate a psychotic break • Recovery is NOT related to severity of psychosis ...
Mental Health 101
... Symptoms of mania or manic episodes include: Mood Changes A long period of feeling “high”, or an overly happy or outgoing mood Extremely irritable mood, agitation, feeling “jumpy” or “wired.” Behavioural Changes Talking very fast, jumping from one idea to another, having racing thoughts Being easily ...
... Symptoms of mania or manic episodes include: Mood Changes A long period of feeling “high”, or an overly happy or outgoing mood Extremely irritable mood, agitation, feeling “jumpy” or “wired.” Behavioural Changes Talking very fast, jumping from one idea to another, having racing thoughts Being easily ...
Adjustment and Breakdown
... Conversion Disorder- a somatoform disorder characterized cy changing emotional difficulties into a loss of a specific voluntary body function Bipolar Disorder- a disorder in which a person’s mood inappropriately alternates between feelings of mania and depression Schizophrenia- a group of severe psy ...
... Conversion Disorder- a somatoform disorder characterized cy changing emotional difficulties into a loss of a specific voluntary body function Bipolar Disorder- a disorder in which a person’s mood inappropriately alternates between feelings of mania and depression Schizophrenia- a group of severe psy ...
Abnormal test review -Know which collections of symptoms are
... Students may be asked about one of the classifications, for example: Describe the Personality Disorder category and describe two disorders in this category. Or Mood, Anxiety etc. Describe the difference between depression and bipolar and to identify their classification. Identify the major symptoms ...
... Students may be asked about one of the classifications, for example: Describe the Personality Disorder category and describe two disorders in this category. Or Mood, Anxiety etc. Describe the difference between depression and bipolar and to identify their classification. Identify the major symptoms ...
DSM-5 And Mood disorders - Institut universitaire en santé mentale
... G. The symptoms are not attributable to the physiological effects of a substance (e.g., a drug of abuse, a medication) or another medical condition (e.g., hypothyroidism) H. The symptoms cause a clinical significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of function ...
... G. The symptoms are not attributable to the physiological effects of a substance (e.g., a drug of abuse, a medication) or another medical condition (e.g., hypothyroidism) H. The symptoms cause a clinical significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of function ...
Treatment of Acute Mania in Pediatric Bipolar Disorder
... risperidone in combination Records indicate she has missed her last three appointments, and her medication supply should have been exhausted two months ago ...
... risperidone in combination Records indicate she has missed her last three appointments, and her medication supply should have been exhausted two months ago ...
Psych 451 -2 - Western Washington University
... Good in short term, bad in long term activation ...
... Good in short term, bad in long term activation ...
View Full Page PDF - The Royal College of Psychiatrists
... alterations in mood, volition and thought that could occur during an episode of mood disorder. Further, it has the potential to stratify research to identify more homogeneous subgroups of individuals, to develop more personalised treatment. This approach has already proven useful: lurasidone, an aty ...
... alterations in mood, volition and thought that could occur during an episode of mood disorder. Further, it has the potential to stratify research to identify more homogeneous subgroups of individuals, to develop more personalised treatment. This approach has already proven useful: lurasidone, an aty ...
Bipolar Disorder
... Psychotherapy - the aim here is to alleviate core symptoms, to help the patient identify and recognize the key triggers, minimize negativity in relationships, recognize the first symptoms that indicate onset of a full-blown episode (prodromal symptoms), and work on the factors that help maintain the ...
... Psychotherapy - the aim here is to alleviate core symptoms, to help the patient identify and recognize the key triggers, minimize negativity in relationships, recognize the first symptoms that indicate onset of a full-blown episode (prodromal symptoms), and work on the factors that help maintain the ...
Mood Disorders in Children & Adolescents
... • Rates in females increase at age 13-14; greater than 2:1 when compared with males at late adolescence. • 1 in 4 adolescents have experienced a depressive episode by age 18. Wichstrom, 1999; Kessler et al., 1996 ...
... • Rates in females increase at age 13-14; greater than 2:1 when compared with males at late adolescence. • 1 in 4 adolescents have experienced a depressive episode by age 18. Wichstrom, 1999; Kessler et al., 1996 ...
Kleptomania
... Kleptomania Kleptomania involves a failure to resist impulses to steal items that are not needed or sought for personal use or monetary value. Kleptomania should be distinguished from shoplifting, in which the action is usually well-planned and motivated by need or monetary gain. Some clinicians vie ...
... Kleptomania Kleptomania involves a failure to resist impulses to steal items that are not needed or sought for personal use or monetary value. Kleptomania should be distinguished from shoplifting, in which the action is usually well-planned and motivated by need or monetary gain. Some clinicians vie ...
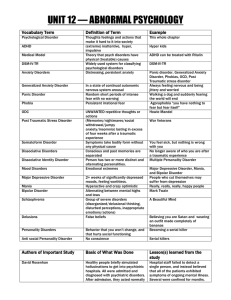
unit 12 — abnormal psychology
... (disorganized/delusional thinking, disturbed perceptions, inappropriate emotions/actions) False beliefs ...
... (disorganized/delusional thinking, disturbed perceptions, inappropriate emotions/actions) False beliefs ...
Family History of Mental Illness - Emory University Department of
... adult population) have a mood disorder. The median age of onset for mood disorders is 30 years. • Depression: Major depressive disorder is the leading cause of disability in the U.S. for ages 15-44. While major depressive disorder can occur at any age, the median age of onset is 32 years. Major depr ...
... adult population) have a mood disorder. The median age of onset for mood disorders is 30 years. • Depression: Major depressive disorder is the leading cause of disability in the U.S. for ages 15-44. While major depressive disorder can occur at any age, the median age of onset is 32 years. Major depr ...
Document
... Rapid-cycling bipolar disorder is characterized by four or more mood episodes that occur within a 12-month period. Some people experience multiple episodes within a single week, or even within a single day. Rapid cycling tends to develop later in the course of illness. Women are more likely than m ...
... Rapid-cycling bipolar disorder is characterized by four or more mood episodes that occur within a 12-month period. Some people experience multiple episodes within a single week, or even within a single day. Rapid cycling tends to develop later in the course of illness. Women are more likely than m ...