Module 36 Chapter 110 Essentials of Understanding
... Antisocial (Sociopath) – lacks feelings of guilt or remorse (make a good con artists) Borderline – Difficulty developing sense of self – ...
... Antisocial (Sociopath) – lacks feelings of guilt or remorse (make a good con artists) Borderline – Difficulty developing sense of self – ...
Psychological Disorders Review
... According to Abraham Maslow, this is the process of striving toward ideal functioning. The problem is, it is difficult to tell if a person is doing a good job of this or not. ...
... According to Abraham Maslow, this is the process of striving toward ideal functioning. The problem is, it is difficult to tell if a person is doing a good job of this or not. ...
(1) sex (men vs women), (2)
... 1) depressed mood most of the day, nearly every day, as indicated by either subjective report (e.g., feels sad or empty) or observation made by others (e.g., appears tearful). Note: In children and adolescents, can be irritable mood. 2) markedly diminished interest or pleasure in all, or almost all, ...
... 1) depressed mood most of the day, nearly every day, as indicated by either subjective report (e.g., feels sad or empty) or observation made by others (e.g., appears tearful). Note: In children and adolescents, can be irritable mood. 2) markedly diminished interest or pleasure in all, or almost all, ...
Emotional and Behavioral Disorders
... • An inability to learn that cannot be explained by intellectual, sensory, or health factors An inability to build or maintain satisfactory interpersonal relationships with peers and teachers Inappropriate types of behavior or feelings under normal circumstances A general pervasive mood of unha ...
... • An inability to learn that cannot be explained by intellectual, sensory, or health factors An inability to build or maintain satisfactory interpersonal relationships with peers and teachers Inappropriate types of behavior or feelings under normal circumstances A general pervasive mood of unha ...
Moderate depressive episode
... to severe depression, and now presents with a mild depressive episode When the patient is experiencing ongoing stressors that may perpetuate or worsen the depression ...
... to severe depression, and now presents with a mild depressive episode When the patient is experiencing ongoing stressors that may perpetuate or worsen the depression ...
Bill Sari Mood slides 01 - University of Illinois Archives
... came for psychiatric evaluation because, “I think there is something wrong with me”. She had a 6 month history of problems including: difficulty falling asleep, trouble staying asleep, early morning awakening, a feeling of no energy, decreased concentration, crying spells, irritability, social withd ...
... came for psychiatric evaluation because, “I think there is something wrong with me”. She had a 6 month history of problems including: difficulty falling asleep, trouble staying asleep, early morning awakening, a feeling of no energy, decreased concentration, crying spells, irritability, social withd ...
Abnormal Psychology
... Dissociative Identity Disorder • Used to be known as Multiple Personality Disorder. • A person has several rather than one integrated personality. • People with DID commonly have a history of childhood abuse or trauma. ...
... Dissociative Identity Disorder • Used to be known as Multiple Personality Disorder. • A person has several rather than one integrated personality. • People with DID commonly have a history of childhood abuse or trauma. ...
ISSUES SURROUNDING CLASSIFICATION AND DIAGNOSIS OF
... 1. Identify three issues that surround the classification and diagnosis of depression. 5. Depression is a very common disorder and can be quite mild. It is self limiting in that the symptoms usually disappear even if not treated (although they tend to recur at a later point). If this is the case ...
... 1. Identify three issues that surround the classification and diagnosis of depression. 5. Depression is a very common disorder and can be quite mild. It is self limiting in that the symptoms usually disappear even if not treated (although they tend to recur at a later point). If this is the case ...
Mood disorders Mood disorders: A category of mental disorders in
... • About 90% of those with the disorder have recurrences, and about 50% experience another episode within a year of recovering from the previous episode. • 70-80% of the patients return to a state of emotional stability, but mild cognitive deficits such as difficulties in planning, persist in many pa ...
... • About 90% of those with the disorder have recurrences, and about 50% experience another episode within a year of recovering from the previous episode. • 70-80% of the patients return to a state of emotional stability, but mild cognitive deficits such as difficulties in planning, persist in many pa ...
MOOD DISORDERS LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the clinical
... Sleep decreased (e.g., feels rested after only 3 hours of sleep) Talking increased from usual or pressure to keep talking Flight of ideas or subjective experience that thoughts are racing Distractibility (i.e., attention too easily drawn to unimportant or irrelevant external stimuli) Activity increa ...
... Sleep decreased (e.g., feels rested after only 3 hours of sleep) Talking increased from usual or pressure to keep talking Flight of ideas or subjective experience that thoughts are racing Distractibility (i.e., attention too easily drawn to unimportant or irrelevant external stimuli) Activity increa ...
Bipolar Disorder and Substance Use Disorders
... Depressed mood most of the day, every day Loss of interest or pleasure in most all activities, every day Significant weight loss w/o dieting Insomnia / hypersomnia every day Psychomotor agitation / retardation every day Fatigue or energy loss every day Worthlessness or inappropriate guilt feelings n ...
... Depressed mood most of the day, every day Loss of interest or pleasure in most all activities, every day Significant weight loss w/o dieting Insomnia / hypersomnia every day Psychomotor agitation / retardation every day Fatigue or energy loss every day Worthlessness or inappropriate guilt feelings n ...
Geriatric Depression
... At least 5 of 9 symptoms, present nearly every day for 2 or more weeks: 1. Depressed mood or irritable most of the day** 2. Decreased interest or pleasure in most activities (anhedonia)** 3. Significant weight change (5%) or change in appetite 4. Change in sleep: Insomnia or hypersomnia 5. Change in ...
... At least 5 of 9 symptoms, present nearly every day for 2 or more weeks: 1. Depressed mood or irritable most of the day** 2. Decreased interest or pleasure in most activities (anhedonia)** 3. Significant weight change (5%) or change in appetite 4. Change in sleep: Insomnia or hypersomnia 5. Change in ...
An Overview of Mood Disorders/Depression
... conditions bring to daily living. Children with autism spectrum disorder are at higher risk for major mood disorders. Serious medical conditions such as heart problems and cancer can also contribute to depression, partly because of the physical weakness and stress they bring on. People who have had ...
... conditions bring to daily living. Children with autism spectrum disorder are at higher risk for major mood disorders. Serious medical conditions such as heart problems and cancer can also contribute to depression, partly because of the physical weakness and stress they bring on. People who have had ...
Depression and Anxiety Disorder
... cardiovascular disease, and substance abuse. Risk is highest early in the course of the disorder or within 2 years of a hospitalization. Mood disorders are divided into Unipolar (depression) and Bipolar Disorders (manic depressive). Dysthymia is chronic low-grade depression that does not meet the cr ...
... cardiovascular disease, and substance abuse. Risk is highest early in the course of the disorder or within 2 years of a hospitalization. Mood disorders are divided into Unipolar (depression) and Bipolar Disorders (manic depressive). Dysthymia is chronic low-grade depression that does not meet the cr ...
Mood Disorders
... 2-Markedly diminished interest or pleasure in all or almost all activities most of the day, nearly every day. 3-Significant weight loss when not dieting or weight gain ,or decrease or increase in appetite. ...
... 2-Markedly diminished interest or pleasure in all or almost all activities most of the day, nearly every day. 3-Significant weight loss when not dieting or weight gain ,or decrease or increase in appetite. ...
WHAT'S REALLY NEW IN BIPOLAR DISORDER, OCTOBER 2005
... Family history of Bipolar Disorder (BD) Bipolar like age of onset (teens and 20’s) High episode frequency (every 18-24 mo) Represents 25-35% of unipolar cases May convert to BD, but many don’t, unless receiving antidepressants without mood stabilizer Patients respond to Li better than imipramine No ...
... Family history of Bipolar Disorder (BD) Bipolar like age of onset (teens and 20’s) High episode frequency (every 18-24 mo) Represents 25-35% of unipolar cases May convert to BD, but many don’t, unless receiving antidepressants without mood stabilizer Patients respond to Li better than imipramine No ...
Psychopathology and Treatment abbreviated
... Set of symptoms that vary together Must meet minimum threshold (e.g., 4 or more symptoms out of 9), to have the disorder ...
... Set of symptoms that vary together Must meet minimum threshold (e.g., 4 or more symptoms out of 9), to have the disorder ...
Integrating Interpersonal Social Rhythm Therapy and Eye Movement
... personal, but it may provide encouragement to speak out and receive support for his or her illness. Additional elements of advocacy, such as supporting legislation or writing senators and congressman to support a broadening of mental health services are steps that can be utilized to increase access ...
... personal, but it may provide encouragement to speak out and receive support for his or her illness. Additional elements of advocacy, such as supporting legislation or writing senators and congressman to support a broadening of mental health services are steps that can be utilized to increase access ...
Chapter 1 - Redlands Community College
... • Cyclic disorder (manic-depressive disorder) • Mood levels swing from severe depression to extreme euphoria (mania) • No regular relationship to time of year (SAD) • Must have at least one manic episode – Supreme self-confidence – Grandiose ideas and movements – Flight of ideas ...
... • Cyclic disorder (manic-depressive disorder) • Mood levels swing from severe depression to extreme euphoria (mania) • No regular relationship to time of year (SAD) • Must have at least one manic episode – Supreme self-confidence – Grandiose ideas and movements – Flight of ideas ...
Uncovering Major Depressive Disorder
... depressive mood and 4 or more of the following characteristics: • Significant weight loss or gain ...
... depressive mood and 4 or more of the following characteristics: • Significant weight loss or gain ...
MOOD DISORDERS THEME A (final copy) (prof. alhamad).
... Huda is a 25 yr-old single female teacher. She had an episode –of at least 2 weeks duration- low mood associated with loss of interest, isolation, crying spells, excessive guilt feelings, death wishes, suicidal ideation and reduction in libido. Her mother has history of bipolar disorder and one of h ...
... Huda is a 25 yr-old single female teacher. She had an episode –of at least 2 weeks duration- low mood associated with loss of interest, isolation, crying spells, excessive guilt feelings, death wishes, suicidal ideation and reduction in libido. Her mother has history of bipolar disorder and one of h ...
644.3 Bipolar Disorder
... Flat affect – lack of facial expression or visible emotion. Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) – an anxiety disorder in which the individual suffers from excessive worry during a majority of the days over at least a six month period; this anxiety tends to revolve around a variety of events rather th ...
... Flat affect – lack of facial expression or visible emotion. Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) – an anxiety disorder in which the individual suffers from excessive worry during a majority of the days over at least a six month period; this anxiety tends to revolve around a variety of events rather th ...
hi low
... Loss of interest (anhedonia) Significant weight loss or gain Insomnia or hypersomnia Psychomotor agitation or retardation Fatigue or loss of energy Worthlessness or guilt Diminished ability to concentrate, indecisiveness ...
... Loss of interest (anhedonia) Significant weight loss or gain Insomnia or hypersomnia Psychomotor agitation or retardation Fatigue or loss of energy Worthlessness or guilt Diminished ability to concentrate, indecisiveness ...
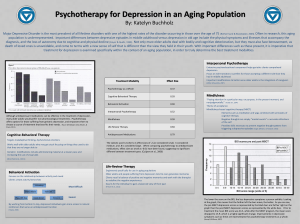
Psychotherapy for Depression in an Aging Population
... Major Depressive Disorder is the most prevalent of all lifetime disorders with one of the highest rates of the disorder occurring in those over the age of 75 (Rothermund & Brandstater, 2003). Often in research, this aging population is underrepresented. Important differences between depressive episo ...
... Major Depressive Disorder is the most prevalent of all lifetime disorders with one of the highest rates of the disorder occurring in those over the age of 75 (Rothermund & Brandstater, 2003). Often in research, this aging population is underrepresented. Important differences between depressive episo ...