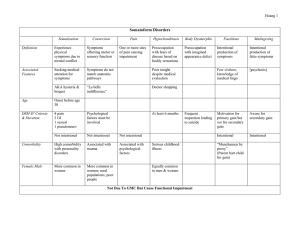
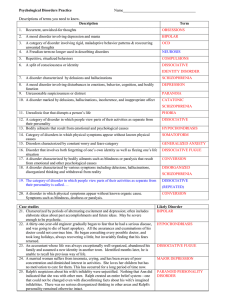
Depressive Disorders
... symptoms have persisted (4 if the mood is only irritable): Inflated self esteem decreased need for sleep distractibility flight of ideas more talkative than usual increase in goal-directed activity or psychomotor agitation. excessive involvement in pleasurable activities that have a hi ...
... symptoms have persisted (4 if the mood is only irritable): Inflated self esteem decreased need for sleep distractibility flight of ideas more talkative than usual increase in goal-directed activity or psychomotor agitation. excessive involvement in pleasurable activities that have a hi ...
8-AFFECTIVE DISORDERS
... - Delusions = Grandiose, Paranoid, - Inflated self-esteem. - Perception: - Hallucination may be present. ...
... - Delusions = Grandiose, Paranoid, - Inflated self-esteem. - Perception: - Hallucination may be present. ...
Behavioral Supports for Students: Addressing Mental Health Needs
... 7. Feelings of worthlessness or excessive or inappropriate guilt (which may be delusional) nearly every day. 8. Diminished ability to think or concentrate, or indecisiveness, nearly every day. 9. Recurrent thoughts of death (not just fear of dying), recurrent suicidal ideation without a specific pla ...
... 7. Feelings of worthlessness or excessive or inappropriate guilt (which may be delusional) nearly every day. 8. Diminished ability to think or concentrate, or indecisiveness, nearly every day. 9. Recurrent thoughts of death (not just fear of dying), recurrent suicidal ideation without a specific pla ...
Mental Health Unit 30-2
... Agitation- inappropriate verbal, vocal, or motor activity due to other causes other than disorientation or real need. Includes behavior such as: pacing, cursing, biting, demanding attention,etc. (p.498) Contributing factors include: Noise, loneliness, depression, etc. (p.499) ...
... Agitation- inappropriate verbal, vocal, or motor activity due to other causes other than disorientation or real need. Includes behavior such as: pacing, cursing, biting, demanding attention,etc. (p.498) Contributing factors include: Noise, loneliness, depression, etc. (p.499) ...
What is Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
... Postnatal psychosis (PP) presents dangers to mum and child 70-fold, increase in maternal suicide risk Leading cause of maternal death in first year after birth Homicidal behaviour is rare But 28%–35% PP mums described delusions about infants Only 9% had thoughts of harming the infant A ...
... Postnatal psychosis (PP) presents dangers to mum and child 70-fold, increase in maternal suicide risk Leading cause of maternal death in first year after birth Homicidal behaviour is rare But 28%–35% PP mums described delusions about infants Only 9% had thoughts of harming the infant A ...
An Update On Depressive Disorders
... S - insomnia/hypersomnia I - interest decreased G – guilt or self blame E – energy loss or fatigue C – concentration problems A – change in appetite/weight P – psychomotor retardation/agitation S – suicidal thoughts ...
... S - insomnia/hypersomnia I - interest decreased G – guilt or self blame E – energy loss or fatigue C – concentration problems A – change in appetite/weight P – psychomotor retardation/agitation S – suicidal thoughts ...
Major Depressive Disorder The Mood Disorders section includes
... (Criterion A4). Individuals typically have middle insomnia (i.e., waking up during the night and having difficulty returning to sleep) or terminal insomnia (i.e., waking too early and being unable to return to sleep). Initial insomnia (i.e., difficulty falling asleep) may also occur. Less frequently ...
... (Criterion A4). Individuals typically have middle insomnia (i.e., waking up during the night and having difficulty returning to sleep) or terminal insomnia (i.e., waking too early and being unable to return to sleep). Initial insomnia (i.e., difficulty falling asleep) may also occur. Less frequently ...
- bYTEBoss
... Women have a higher propensity to develop PTSD after exposure to traume than men (Kessler, et al, 1995) Rate of PTSD secondary to birth trauma ranges from 1.5% to 5.6% (Beck, ...
... Women have a higher propensity to develop PTSD after exposure to traume than men (Kessler, et al, 1995) Rate of PTSD secondary to birth trauma ranges from 1.5% to 5.6% (Beck, ...
Slide 1
... outcome goals is done. The efficacy of the treatment can be judged by: – assessment of presence or absence of suicidal ideas, negative thoughts (worthlessness, hopelessness and of helplessness), self-care deficits, sleep and appetite changes and social interactions. – If the indictors have not been ...
... outcome goals is done. The efficacy of the treatment can be judged by: – assessment of presence or absence of suicidal ideas, negative thoughts (worthlessness, hopelessness and of helplessness), self-care deficits, sleep and appetite changes and social interactions. – If the indictors have not been ...
Hypochondriasis - Cloudfront.net
... The belief or fear of illness must not be of delusional intensity. Delusional health fears are more likely to be bizarre in nature— for instance, the belief that one's skin emits a foul odor or that food is rotting in one's intestines. The preoccupations must not be limited to a concern about appear ...
... The belief or fear of illness must not be of delusional intensity. Delusional health fears are more likely to be bizarre in nature— for instance, the belief that one's skin emits a foul odor or that food is rotting in one's intestines. The preoccupations must not be limited to a concern about appear ...
1 - Psychology
... 16. The best evidence for the effectiveness of the psychodynamic approach comes from: A) work with seriously depressed people. B) case study reports.* C) large-scale research projects conducted by the APA. D) situations when the childhood loss is less obvious. 17. The effectiveness of psychodynamic ...
... 16. The best evidence for the effectiveness of the psychodynamic approach comes from: A) work with seriously depressed people. B) case study reports.* C) large-scale research projects conducted by the APA. D) situations when the childhood loss is less obvious. 17. The effectiveness of psychodynamic ...
Mood Disorders09
... compulsions are rituals or behavior that is performed to try to prevent or reduce the obsessive thoughts. Disorder that affects men and women equally, 1 in 50 often show up in teens, early adulthood. Obsessions-uncontrollable thoughts or impulses occur repeatedly Compulsions-performed behaviors or r ...
... compulsions are rituals or behavior that is performed to try to prevent or reduce the obsessive thoughts. Disorder that affects men and women equally, 1 in 50 often show up in teens, early adulthood. Obsessions-uncontrollable thoughts or impulses occur repeatedly Compulsions-performed behaviors or r ...
Psyc 213: Abnormal Psychology
... rapid cycling cognitive therapy tricyclics ECS altruistic suicide contagious suicide ...
... rapid cycling cognitive therapy tricyclics ECS altruistic suicide contagious suicide ...
Griggs Chapter 10: Abnormal Psychology
... ◦ Dramatic changes in eating and sleeping behavior ◦ Inability to concentrate ◦ Greatly diminished interest in family, friends, and activities for a period of two weeks or more ◦ Thoughts of suicide ...
... ◦ Dramatic changes in eating and sleeping behavior ◦ Inability to concentrate ◦ Greatly diminished interest in family, friends, and activities for a period of two weeks or more ◦ Thoughts of suicide ...
Development of Diagnostic Variables
... A. Five (or more) of the following symptoms have been present during the same 2-week period and represent a change from previous functioning; at least one of the symptoms is either (1) depressed mood or (2) loss of interest or pleasure. Note: Do not include symptoms that are clearly due to a general ...
... A. Five (or more) of the following symptoms have been present during the same 2-week period and represent a change from previous functioning; at least one of the symptoms is either (1) depressed mood or (2) loss of interest or pleasure. Note: Do not include symptoms that are clearly due to a general ...
Mood Disorders - Psychology for you and me
... or decrease or increase appetite nearly everyday. Note: in children, consider failure to make expected weight gains. (4) Insomnia or hypersomnia nearly every day. (5) Psychomotor agitation or retardation nearly every day (observable by others, not merely subjective feelings of restlessness or being ...
... or decrease or increase appetite nearly everyday. Note: in children, consider failure to make expected weight gains. (4) Insomnia or hypersomnia nearly every day. (5) Psychomotor agitation or retardation nearly every day (observable by others, not merely subjective feelings of restlessness or being ...
File
... • Community support programs This support should include information; accommodation; help with finding suitable work; training and education; psychosocial rehabilitation and mutual support groups. Under-standing and acceptance by the community is also very important. ...
... • Community support programs This support should include information; accommodation; help with finding suitable work; training and education; psychosocial rehabilitation and mutual support groups. Under-standing and acceptance by the community is also very important. ...
Mood disorders handout
... mania. Delusions are usually mood congruent e.g. delusions of grandeur in mania. Delusions of poverty or guilt in depression. Hallucinations are usually auditory and in the second person. "Neurotic" Symptoms - Most commonly anxiety symptoms but prominent obsessive compulsive or hypochondriacal sympt ...
... mania. Delusions are usually mood congruent e.g. delusions of grandeur in mania. Delusions of poverty or guilt in depression. Hallucinations are usually auditory and in the second person. "Neurotic" Symptoms - Most commonly anxiety symptoms but prominent obsessive compulsive or hypochondriacal sympt ...
psychiatric problems
... the teenage years, although it is usually diagnosed in adult life. The illness can affect anyone. However, if one or both parents have Bipolar Disorder, the chances are greater that their children may develop the disorder. Family history of drug or alcohol abuse also may be associated with greater ...
... the teenage years, although it is usually diagnosed in adult life. The illness can affect anyone. However, if one or both parents have Bipolar Disorder, the chances are greater that their children may develop the disorder. Family history of drug or alcohol abuse also may be associated with greater ...
Check your answers - Grand Haven Area Public Schools
... boy or a girl. Do you think I will ever get married and have a baby?' And she would say, 'You are staying young and I am growing old.'" 55. During an interview, the 50 year-old female patient expressed beliefs covering almost the entire range of delusions. She felt that her niece was in on a plot wi ...
... boy or a girl. Do you think I will ever get married and have a baby?' And she would say, 'You are staying young and I am growing old.'" 55. During an interview, the 50 year-old female patient expressed beliefs covering almost the entire range of delusions. She felt that her niece was in on a plot wi ...
Atypical Antipsychotic Drug Use in Children and Adolescents
... Fritz, G. First do no harm: prescribing new antipsychotic medications to children. 2006; The Brown Univ Child and Adolescent Behavior Letter 22(10): 8. Gogtay, N., Sporn, A. et al. Comparison of progressive cortical gray matter loss in childhood-onset schizophrenia with that in childhood-onset atypi ...
... Fritz, G. First do no harm: prescribing new antipsychotic medications to children. 2006; The Brown Univ Child and Adolescent Behavior Letter 22(10): 8. Gogtay, N., Sporn, A. et al. Comparison of progressive cortical gray matter loss in childhood-onset schizophrenia with that in childhood-onset atypi ...