Radioactivity
... • When a radium source (held in tongs, and well away from the face) is held close to the cap, without touching it, the leaf is seen to collapse. This is due to the ionization of the air produced by the radiation emitted by the radium, which produces positive ions and negative electrons. If the cap i ...
... • When a radium source (held in tongs, and well away from the face) is held close to the cap, without touching it, the leaf is seen to collapse. This is due to the ionization of the air produced by the radiation emitted by the radium, which produces positive ions and negative electrons. If the cap i ...
Appendix A Glossary of Nuclear Terms
... accompanied by the emission of radiation. radioisotope: A radioactive isotope. A common term for a radionuclide. radionuclide: A radioactive nuclide. An unstable isotope of an element that decays or disintegrates spontaneously, emitting radiation. rem (röntgen equivalent, man): A measure of dose dep ...
... accompanied by the emission of radiation. radioisotope: A radioactive isotope. A common term for a radionuclide. radionuclide: A radioactive nuclide. An unstable isotope of an element that decays or disintegrates spontaneously, emitting radiation. rem (röntgen equivalent, man): A measure of dose dep ...
Nuc Chem PP - Liberty Union High School District
... • They will undergo decay • The type of decay depends on the reason for the instability ...
... • They will undergo decay • The type of decay depends on the reason for the instability ...
Chapter 4.3: How Atoms Differ
... Number of ____________ identifies an _______ as part of a particular ___________. Referred to as ___________ ______________. ...
... Number of ____________ identifies an _______ as part of a particular ___________. Referred to as ___________ ______________. ...
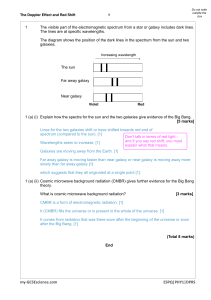
Question Answer What device uses light from the sun to produce
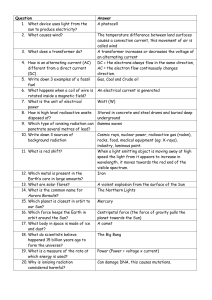
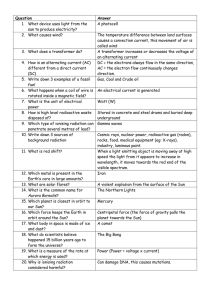
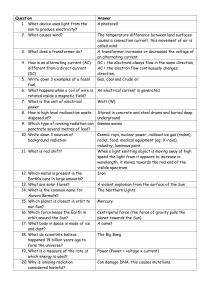
... 8. How is high level radioactive waste disposed of? 9. Which type of ionising radiation can penetrate several metres of lead? 10. Write down 3 sources of background radiation 11. What is red shift? 12. Which metal is present in the Earth’s core in large amounts? 13. What are solar flares? 14. What i ...
... 8. How is high level radioactive waste disposed of? 9. Which type of ionising radiation can penetrate several metres of lead? 10. Write down 3 sources of background radiation 11. What is red shift? 12. Which metal is present in the Earth’s core in large amounts? 13. What are solar flares? 14. What i ...
Nuclear Chemistry
... • Example: Beta decay process is the decay of iodine- 131 into xenon131 by beta-particle emission • The mass number of the product nucleus is the same as that of the original nucleus ( they are both 131), but its atomic number has increased by 1 (54 instead of 53). This changed in atomic number, and ...
... • Example: Beta decay process is the decay of iodine- 131 into xenon131 by beta-particle emission • The mass number of the product nucleus is the same as that of the original nucleus ( they are both 131), but its atomic number has increased by 1 (54 instead of 53). This changed in atomic number, and ...
Background radiation

Background radiation is the ubiquitous ionizing radiation that people on the planet Earth are exposed to, including natural and artificial sources.Both natural and artificial background radiation varies depending on location and altitude.