NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY
... Background radiation • Background radiation: a constant level of radioactivity that results from natural sources and from sources related to human activity. o You can’t completely eliminate background radiation it’s essentially everywhere: soil, water, food, rocks, etc… o Currently, 500 mrem (mill ...
... Background radiation • Background radiation: a constant level of radioactivity that results from natural sources and from sources related to human activity. o You can’t completely eliminate background radiation it’s essentially everywhere: soil, water, food, rocks, etc… o Currently, 500 mrem (mill ...
3 Background radiation
... A high energy electron given off by a radioactive atom Radioactive tracers are used to investigate a patient's body without the need for surgery. Gamma emitters and sometimes beta emitters are used. This is because gamma rays and beta particles can pass through skin, whereas alpha particles cannot. ...
... A high energy electron given off by a radioactive atom Radioactive tracers are used to investigate a patient's body without the need for surgery. Gamma emitters and sometimes beta emitters are used. This is because gamma rays and beta particles can pass through skin, whereas alpha particles cannot. ...
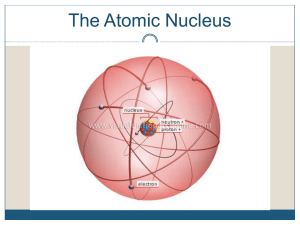
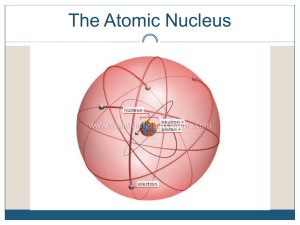
1 The Nucleus Total number of nucleons: mass number Number of
... 25 – 50 rem slight temp. decrease of white blood cell 100 – 200 rem nausea, marked decrease of white blood cell 500 rem death within 30 D for ½ exposed population ...
... 25 – 50 rem slight temp. decrease of white blood cell 100 – 200 rem nausea, marked decrease of white blood cell 500 rem death within 30 D for ½ exposed population ...
cps ch 10 notes
... • Radon is a naturally occurring radioactive element that is formed in the decay chain of uranium-238. • Radon gas is produced underground as the uranium in rocks and soil decays. • As the radon seeps up through the ground, it can get into buildings by passing through cracks or holes in their found ...
... • Radon is a naturally occurring radioactive element that is formed in the decay chain of uranium-238. • Radon gas is produced underground as the uranium in rocks and soil decays. • As the radon seeps up through the ground, it can get into buildings by passing through cracks or holes in their found ...
Revision of Atomic Structure and Nuclide Notations Nuclide
... Since every radioisotope has a unique and constant half-life that fact can be used to find out how old an object containing that substance is. The radioactive element Carbon-14 is found in any object made of once living things. Carbon-14 is made in the upper atmosphere at a constant rate due to a ty ...
... Since every radioisotope has a unique and constant half-life that fact can be used to find out how old an object containing that substance is. The radioactive element Carbon-14 is found in any object made of once living things. Carbon-14 is made in the upper atmosphere at a constant rate due to a ty ...
Electromagnetic Spectrum
... You actually know more about it than you may think! The electromagnetic spectrum is just a name that scientists give a bunch of types of radiation when they want to talk about them as a group. Radiation is energy that travels and spreads out as it goes– visible light that comes from a lamp in your ...
... You actually know more about it than you may think! The electromagnetic spectrum is just a name that scientists give a bunch of types of radiation when they want to talk about them as a group. Radiation is energy that travels and spreads out as it goes– visible light that comes from a lamp in your ...
Average Atomic Mass
... • The third common type of radiation is gamma radiation or gamma rays. • Gamma rays are high-energy radiation that possess no mass and have no charge. • Gamma rays are denoted by the symbol 00γ. • Gamma rays usually accompany alpha and beta radiation and account for most of the energy lost during th ...
... • The third common type of radiation is gamma radiation or gamma rays. • Gamma rays are high-energy radiation that possess no mass and have no charge. • Gamma rays are denoted by the symbol 00γ. • Gamma rays usually accompany alpha and beta radiation and account for most of the energy lost during th ...
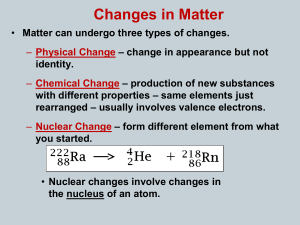
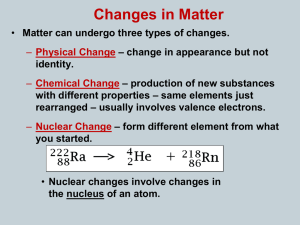
Chemistry: Matter and Change
... Types of Radiation (cont.) • Gamma rays are high-energy electromagnetic radiation. • Gamma rays (short wavelength) are photons, which are high-energy • Gamma rays have no mass or charge so the emission of gamma rays does not change the atomic number or mass number of a nucleus. • Gamma rays almost ...
... Types of Radiation (cont.) • Gamma rays are high-energy electromagnetic radiation. • Gamma rays (short wavelength) are photons, which are high-energy • Gamma rays have no mass or charge so the emission of gamma rays does not change the atomic number or mass number of a nucleus. • Gamma rays almost ...
NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY
... normally strong enough to hold the protons and neutrons together. However, sometimes the force of repulsion due to the protons having the same charge overcomes the strong nuclear force and the atom breaks apart. ...
... normally strong enough to hold the protons and neutrons together. However, sometimes the force of repulsion due to the protons having the same charge overcomes the strong nuclear force and the atom breaks apart. ...
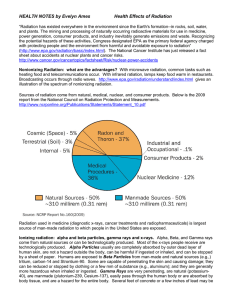
Health Effects of Radiation
... required to stop energetic gamma rays. X-Rays essentially have the same properties as Gamma rays but differ in origin; are generally lower in energy, therefore less penetrating than Gamma rays; and a few mm of lead can stop penetration of medical x-rays. How can alpha particles affect people’s heal ...
... required to stop energetic gamma rays. X-Rays essentially have the same properties as Gamma rays but differ in origin; are generally lower in energy, therefore less penetrating than Gamma rays; and a few mm of lead can stop penetration of medical x-rays. How can alpha particles affect people’s heal ...
Radioisotopes
... (Nuclides) of the same chemical element, each having a different atomic mass (mass number) • Isotopes of an element have nuclei with the same number of protons (the same atomic number) but different numbers of neutrons. • Therefore, isotopes have different mass numbers, which give the total number o ...
... (Nuclides) of the same chemical element, each having a different atomic mass (mass number) • Isotopes of an element have nuclei with the same number of protons (the same atomic number) but different numbers of neutrons. • Therefore, isotopes have different mass numbers, which give the total number o ...
Background radiation

Background radiation is the ubiquitous ionizing radiation that people on the planet Earth are exposed to, including natural and artificial sources.Both natural and artificial background radiation varies depending on location and altitude.