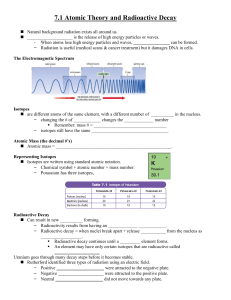
Name
... 9. The conversion of an atomic nucleus of one element into an atomic nucleus of another element through a loss or gain in the number of protons. 10. High-energy radiation emitted by the nuclei of radioactive atoms. 11. Nuclear fusion produced by high temperature. Down 2. The force of interaction bet ...
... 9. The conversion of an atomic nucleus of one element into an atomic nucleus of another element through a loss or gain in the number of protons. 10. High-energy radiation emitted by the nuclei of radioactive atoms. 11. Nuclear fusion produced by high temperature. Down 2. The force of interaction bet ...
radioisotopes and radiotherapy - video
... therefore give off more or less radiation, producing a dark or light area on the image. 10. The time taken for the decay of one-half of the original sample of atoms is called the half-life of a radioactive material. 99mTc’s radiation is reduced by half with every 6-hour period. 11. High activity and ...
... therefore give off more or less radiation, producing a dark or light area on the image. 10. The time taken for the decay of one-half of the original sample of atoms is called the half-life of a radioactive material. 99mTc’s radiation is reduced by half with every 6-hour period. 11. High activity and ...
Nuclear Chemistry - Northwest ISD Moodle
... • PROTONS give the atom its identity • Held together by a very strong nuclear force o One of the four fundamental forces in our universe o Incredibly powerful o Releasing nuclear force results in a nuclear reaction ...
... • PROTONS give the atom its identity • Held together by a very strong nuclear force o One of the four fundamental forces in our universe o Incredibly powerful o Releasing nuclear force results in a nuclear reaction ...
Radioactivity and man
... Since his appearance on Earth, man has been exposed to natural radiation to which he has adapted perfectly. The dose of natural radiation to which each living organism is exposed every year is about 2.4 mSv. This natural radiation comes from two sources: the Earth, deriving from radionuclides presen ...
... Since his appearance on Earth, man has been exposed to natural radiation to which he has adapted perfectly. The dose of natural radiation to which each living organism is exposed every year is about 2.4 mSv. This natural radiation comes from two sources: the Earth, deriving from radionuclides presen ...
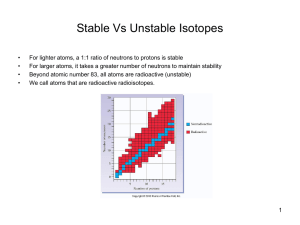
Stable Vs Unstable Isotopes
... For lighter atoms, a 1:1 ratio of neutrons to protons is stable For larger atoms, it takes a greater number of neutrons to maintain stability Beyond atomic number 83, all atoms are radioactive (unstable) We call atoms that are radioactive radioisotopes. ...
... For lighter atoms, a 1:1 ratio of neutrons to protons is stable For larger atoms, it takes a greater number of neutrons to maintain stability Beyond atomic number 83, all atoms are radioactive (unstable) We call atoms that are radioactive radioisotopes. ...
Word - chemmybear.com
... number of protons. Scientists knew that the nucleus consisted of protons and neutrons in _______ [1730 1830 1930] The number of ________ determines the identity of atoms. Isotopes have different numbers of ____________. Hydrogen has three isotopes: hydrogen-1, hydrogen-2, and hydrogen-3. How many ne ...
... number of protons. Scientists knew that the nucleus consisted of protons and neutrons in _______ [1730 1830 1930] The number of ________ determines the identity of atoms. Isotopes have different numbers of ____________. Hydrogen has three isotopes: hydrogen-1, hydrogen-2, and hydrogen-3. How many ne ...
ICRP Guidelines: `the effective dose equivalent from all sources
... ICRP Guidelines: ‘the effective dose equivalent from all sources, excluding background radiation and medical procedures, to representative members of a critical group, should not exceed 1 mSv in any one year; effective dose equivalents of up to 5 mSv are permissible in some years provided that the t ...
... ICRP Guidelines: ‘the effective dose equivalent from all sources, excluding background radiation and medical procedures, to representative members of a critical group, should not exceed 1 mSv in any one year; effective dose equivalents of up to 5 mSv are permissible in some years provided that the t ...
Background radiation

Background radiation is the ubiquitous ionizing radiation that people on the planet Earth are exposed to, including natural and artificial sources.Both natural and artificial background radiation varies depending on location and altitude.