`background radiation`.
... 2.What types of radiation cause ionization? Only Alpha and Beta. 3.What is an isotope? Atoms of the same element with a different Mass number (i.e. different numbers of neutrons). 4.What is a radioisotope? An isotope/s of an element which emits nuclear radiation ...
... 2.What types of radiation cause ionization? Only Alpha and Beta. 3.What is an isotope? Atoms of the same element with a different Mass number (i.e. different numbers of neutrons). 4.What is a radioisotope? An isotope/s of an element which emits nuclear radiation ...
SIMPLE RADIATION TRANSFER FOR SPHERICAL STARS
... We obtained only one half of the radiation energy density expected under LTE conditions for the temperature T , because radiation was coming from one hemisphere only. The radiative energy flux may be calculated for our case: ...
... We obtained only one half of the radiation energy density expected under LTE conditions for the temperature T , because radiation was coming from one hemisphere only. The radiative energy flux may be calculated for our case: ...
Chapter 4
... Radioactivity ■ In the late 1890’s Scientists noticed some substances spontaneously emitted radiation in a process called radioactivity. This is because their nuclei is unstable ■ Rays and particles emitted are called radiation ■ Radioactive atoms undergo changes that alters their identity and allo ...
... Radioactivity ■ In the late 1890’s Scientists noticed some substances spontaneously emitted radiation in a process called radioactivity. This is because their nuclei is unstable ■ Rays and particles emitted are called radiation ■ Radioactive atoms undergo changes that alters their identity and allo ...
Nuclear - PEO Scarborough Chapter
... the centre of the atom is a very small region called a nucleus. The nucleus houses protons and neutrons. The electrons form a cloud around the nucleus. The neutrons hold mass containing particles (protons) together in the nucleus. When an atom has too much energy, it dissipates energy through emissi ...
... the centre of the atom is a very small region called a nucleus. The nucleus houses protons and neutrons. The electrons form a cloud around the nucleus. The neutrons hold mass containing particles (protons) together in the nucleus. When an atom has too much energy, it dissipates energy through emissi ...
Chapter 3 Nuclear Radiation
... Learning Check A typical intravenous dose of I-125 for a thyroid diagnostic test is 100 Ci. What is this dosage in megabecquerels (MBq)? (3.7 x 1010 Bq = 1 Ci) ...
... Learning Check A typical intravenous dose of I-125 for a thyroid diagnostic test is 100 Ci. What is this dosage in megabecquerels (MBq)? (3.7 x 1010 Bq = 1 Ci) ...
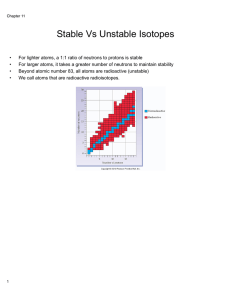
Stable Vs Unstable Isotopes
... When an atom loses an alpha particle: its atomic number decreases by 2 units and its mass number decreases by 4 units neither its atomic number nor its mass number changes its mass number decreases by 1 unit but its atomic number remains unchanged its atomic number increases by 1 unit but its mass n ...
... When an atom loses an alpha particle: its atomic number decreases by 2 units and its mass number decreases by 4 units neither its atomic number nor its mass number changes its mass number decreases by 1 unit but its atomic number remains unchanged its atomic number increases by 1 unit but its mass n ...
radioactive decay - Aurora City Schools
... • An element with a different number of neutrons • Because has same number of protons, still that element and has all chem/phys properties • Write isotopes using atomic # & mass # ...
... • An element with a different number of neutrons • Because has same number of protons, still that element and has all chem/phys properties • Write isotopes using atomic # & mass # ...
isotope - Aurora City Schools
... • An element with a different number of neutrons • Because has same number of protons, still that element and has all chem/phys properties • Write isotopes using atomic # & mass # ...
... • An element with a different number of neutrons • Because has same number of protons, still that element and has all chem/phys properties • Write isotopes using atomic # & mass # ...
Independent Study: Nuclear Chemistry
... 21. The symbol represents tritium. 22. Gamma rays can be stopped by an aluminum sheet. 23. The change of an atom into a new element is called a chemical change. 24. The first artificial transmutation was performed by Albert Einstein. 25. The rate at which a radioactive element decays is known as the ...
... 21. The symbol represents tritium. 22. Gamma rays can be stopped by an aluminum sheet. 23. The change of an atom into a new element is called a chemical change. 24. The first artificial transmutation was performed by Albert Einstein. 25. The rate at which a radioactive element decays is known as the ...
Background radiation

Background radiation is the ubiquitous ionizing radiation that people on the planet Earth are exposed to, including natural and artificial sources.Both natural and artificial background radiation varies depending on location and altitude.