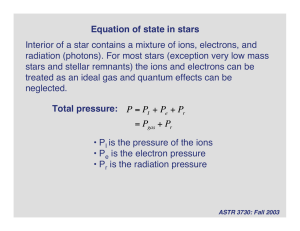
Equation of state in stars Interior of a star contains a mixture of ions
... A detailed model of the Sun gives core conditions of: • T = 1.6 x 107 K • r = 150 g cm-3 • X = 0.34, Y = 0.64, Z = 0.02 (note: hydrogen is almost half gone compared to initial or surface composition!) ...
... A detailed model of the Sun gives core conditions of: • T = 1.6 x 107 K • r = 150 g cm-3 • X = 0.34, Y = 0.64, Z = 0.02 (note: hydrogen is almost half gone compared to initial or surface composition!) ...
Atomic and Nuclear Physics
... with a neutron to produce 2 daughter nuclei and a small number of neutrons (3) • This process releases energy in the form of kinetic energy (= thermal energy) of the 2 nuclei (fission products) • The neutrons produced by one fission can strike other U-235 nuclei creating a chain reaction ...
... with a neutron to produce 2 daughter nuclei and a small number of neutrons (3) • This process releases energy in the form of kinetic energy (= thermal energy) of the 2 nuclei (fission products) • The neutrons produced by one fission can strike other U-235 nuclei creating a chain reaction ...
Unit 3 Study Guide: Atomic Structure and Nuclear
... alpha, beta, or gamma radiation. _______________ 4. The first induced nuclear transmutation was carried out by Marie and Pierre Curie in 1897. _______________ 5. Most induced transmutation reactions are produced in high-energy particle accelerators. _______________ 6. Neptunium and plutonium were th ...
... alpha, beta, or gamma radiation. _______________ 4. The first induced nuclear transmutation was carried out by Marie and Pierre Curie in 1897. _______________ 5. Most induced transmutation reactions are produced in high-energy particle accelerators. _______________ 6. Neptunium and plutonium were th ...
7.2 - Moodle
... • There exists ground state and excited states (*). • Whenever a nucleus makes a transition from a higher to a lower energy state, it emits a photon whose energy is equal to the energy difference between the initial and final energy states of the nucleus. • This is why a gamma radiation has specific ...
... • There exists ground state and excited states (*). • Whenever a nucleus makes a transition from a higher to a lower energy state, it emits a photon whose energy is equal to the energy difference between the initial and final energy states of the nucleus. • This is why a gamma radiation has specific ...
Lab 77 Nuclear Radiation Detection
... As nuclear radiation travels away from its source, its strength decreases. This weakening is inversely related to the square of the distance from the radiation source. This is known as the inverse square law. All forms of radiation follow this law. Therefore, unless you know where a radiation source ...
... As nuclear radiation travels away from its source, its strength decreases. This weakening is inversely related to the square of the distance from the radiation source. This is known as the inverse square law. All forms of radiation follow this law. Therefore, unless you know where a radiation source ...
Nuclear Radiation1516
... fragments is less than the original mass. This 'missing' mass (about 0.1 percent of the original mass) has been converted into energy according to Einstein's equation. Fission can occur when a nucleus of a heavy atom captures a neutron, or it can happen spontaneously. ...
... fragments is less than the original mass. This 'missing' mass (about 0.1 percent of the original mass) has been converted into energy according to Einstein's equation. Fission can occur when a nucleus of a heavy atom captures a neutron, or it can happen spontaneously. ...
Nuclear Reactions - Manasquan Public Schools
... Because of their large mass and charge, alpha particles do not travel very far and are not very penetrating. • A sheet of paper or the surface of your skin can stop them. – But radioisotopes that emit alpha particles can cause harm when ingested. – Once inside the body, the particles don’t have to t ...
... Because of their large mass and charge, alpha particles do not travel very far and are not very penetrating. • A sheet of paper or the surface of your skin can stop them. – But radioisotopes that emit alpha particles can cause harm when ingested. – Once inside the body, the particles don’t have to t ...
Background radiation

Background radiation is the ubiquitous ionizing radiation that people on the planet Earth are exposed to, including natural and artificial sources.Both natural and artificial background radiation varies depending on location and altitude.