Biochemistry - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... Enzymes special proteins that are biological catalyst lock & key fit with enzyme & substrate substrate – is the substance that binds to enzyme substrate changes enzyme does not ...
... Enzymes special proteins that are biological catalyst lock & key fit with enzyme & substrate substrate – is the substance that binds to enzyme substrate changes enzyme does not ...
Macromolecules: Building blocks of life
... Living organisms must have water for life processes, because molecules and ions must be free to move and interact, which only happens when they are dissolved in water. Water also transports materials in living organisms, such as in blood or sap. ...
... Living organisms must have water for life processes, because molecules and ions must be free to move and interact, which only happens when they are dissolved in water. Water also transports materials in living organisms, such as in blood or sap. ...
Studying Enzyme Kinetics by Means of Progress - Beilstein
... The conventional method used to set up enzyme-kinetic models is to isolate the respective enzyme from the cell and to determine its kinetic properties monitoring the reaction kinetics under well-controlled in vitro conditions. This procedure usually ends up in the formulation of a rate law represent ...
... The conventional method used to set up enzyme-kinetic models is to isolate the respective enzyme from the cell and to determine its kinetic properties monitoring the reaction kinetics under well-controlled in vitro conditions. This procedure usually ends up in the formulation of a rate law represent ...
Section 5: Enzymes, Equilibrium, Energy and the
... Metabolic reactions/energy production Molecular binding specificity Mechanism of action of metabolic inhibitors ...
... Metabolic reactions/energy production Molecular binding specificity Mechanism of action of metabolic inhibitors ...
Catalysis
... 4. Enzyme catalysed reactions are much more sensitive to catalytic poisons such as HCN, H2S, CS2 etc. The inhibitors interact with the active functional groups present on the enzyme surface and often reduce or completely destroy the catalytic activity of the enzymes 5. The activity of certain enzym ...
... 4. Enzyme catalysed reactions are much more sensitive to catalytic poisons such as HCN, H2S, CS2 etc. The inhibitors interact with the active functional groups present on the enzyme surface and often reduce or completely destroy the catalytic activity of the enzymes 5. The activity of certain enzym ...
Practice Exam III answers
... e). Separating opposing metabolic pathways alters the committed steps of the opposing pathways. : (d), separating opposing metabolic pathways avoids the creation of a futile cycle. 13). Which of the following is a characteristic of a phosphoanhydride bond? a). Has more resonance stabilization than ...
... e). Separating opposing metabolic pathways alters the committed steps of the opposing pathways. : (d), separating opposing metabolic pathways avoids the creation of a futile cycle. 13). Which of the following is a characteristic of a phosphoanhydride bond? a). Has more resonance stabilization than ...
Document
... List the three mechanisms that can be used to regulate the function of a protein (e.g., an enzyme) and briefly (1-2 sentences) describe their key features. Key: Mechanism 1: Covalent modification – no change in the abundance of a protein. Here, preexisting protein is made active or inactive by coval ...
... List the three mechanisms that can be used to regulate the function of a protein (e.g., an enzyme) and briefly (1-2 sentences) describe their key features. Key: Mechanism 1: Covalent modification – no change in the abundance of a protein. Here, preexisting protein is made active or inactive by coval ...
study guide section 3-1 carbon compounds
... a. the R groups of the amino acids they contain. b. the amino groups of the amino acids they contain. c. the carboxyl groups of the amino acids they contain. d. whether or not they contain any amino acids. 3. ______ Most enzymes a. are changed by the reactions they catalyze. b. increase that activat ...
... a. the R groups of the amino acids they contain. b. the amino groups of the amino acids they contain. c. the carboxyl groups of the amino acids they contain. d. whether or not they contain any amino acids. 3. ______ Most enzymes a. are changed by the reactions they catalyze. b. increase that activat ...
supporting information file s1
... a favorable energy environment (S5). Similar results were obtained from the graphical plot of the GROMOS empirical force field energy (S6).The modeled CoaE structure was further verified and validated by several different programs. The What Check Structure Assessment tool which helps in protein stru ...
... a favorable energy environment (S5). Similar results were obtained from the graphical plot of the GROMOS empirical force field energy (S6).The modeled CoaE structure was further verified and validated by several different programs. The What Check Structure Assessment tool which helps in protein stru ...
reactants -> products. - University of San Diego Home Pages
... – Group complementation -‐ the ability to recognize specific regions of the substrate to align reactants with catalytic site. – Based on non-‐covalent molecular interactions. – Lock and key vs. induced fit -‐ ...
... – Group complementation -‐ the ability to recognize specific regions of the substrate to align reactants with catalytic site. – Based on non-‐covalent molecular interactions. – Lock and key vs. induced fit -‐ ...
Topic 2: Molecular biology (21 hours)
... denaturation experiments. • Students should know that most organisms use the same 20 amino acids in the same genetic code although there are some exceptions. Specific examples could be used for illustration. ...
... denaturation experiments. • Students should know that most organisms use the same 20 amino acids in the same genetic code although there are some exceptions. Specific examples could be used for illustration. ...
6.3 Reading guide macromolecule
... Draw the number of bars needed to show a double bond between the following two carbon atoms. C C Draw the number of bars needed to show a single bond between the following two carbon atoms. C C Draw the number of bars needed to show a triple bond between the following two carbon atoms. C C What thre ...
... Draw the number of bars needed to show a double bond between the following two carbon atoms. C C Draw the number of bars needed to show a single bond between the following two carbon atoms. C C Draw the number of bars needed to show a triple bond between the following two carbon atoms. C C What thre ...
Session 1 Worksheet - Iowa State University
... Odd Man Out: Choose the word in each group that does not belong. If not already given, indicate what the words have in common. Alimentary Canal Mouth Esophagus Stomach Liver ...
... Odd Man Out: Choose the word in each group that does not belong. If not already given, indicate what the words have in common. Alimentary Canal Mouth Esophagus Stomach Liver ...
An overview of biochemistry for bioCHEM480
... which these ‘R’ groups will be involved. This HbA Glu will be solvated by water whereas in HbS, the Val has a non-‐polar hydrophobic ‘R’ group . To ‘avoid’ this exposure of the isopropyl gro ...
... which these ‘R’ groups will be involved. This HbA Glu will be solvated by water whereas in HbS, the Val has a non-‐polar hydrophobic ‘R’ group . To ‘avoid’ this exposure of the isopropyl gro ...
Protein Function
... • This carbon atom is then attacked by the –COO- from aspartic acid (Asp52), forming a (temporary) covalent bond between the sugar and the enzyme. ...
... • This carbon atom is then attacked by the –COO- from aspartic acid (Asp52), forming a (temporary) covalent bond between the sugar and the enzyme. ...
Ch. 5 Molecules of Life – Test Study Guide Carbohydrates, Fats
... -What are the monomers of each? How does the molecule progress to become a polymer? -How does dehydration synthesis work to the build a polymer of each group? -What kind of bond / elements are involved with each type of bond to make a polymer? -How does hydrolysis work to break down the polymer of e ...
... -What are the monomers of each? How does the molecule progress to become a polymer? -How does dehydration synthesis work to the build a polymer of each group? -What kind of bond / elements are involved with each type of bond to make a polymer? -How does hydrolysis work to break down the polymer of e ...
Topic 2 Molecular Biology
... illustrate the functions of proteins is not needed. • Egg white or albumin solutions can be used in denaturation experiments. • Students should know that most organisms use the same 20 amino acids in the same genetic code although there are some exceptions. Specific examples could be used for illust ...
... illustrate the functions of proteins is not needed. • Egg white or albumin solutions can be used in denaturation experiments. • Students should know that most organisms use the same 20 amino acids in the same genetic code although there are some exceptions. Specific examples could be used for illust ...
APDC Unit IV Biochem
... enormous variety of biological molecules. For reasons- compounds containing C is said to be an organic compound, and compounds associated with life contain H atoms in addition to C atoms. ...
... enormous variety of biological molecules. For reasons- compounds containing C is said to be an organic compound, and compounds associated with life contain H atoms in addition to C atoms. ...
Macromolecules Part 2
... Proteins (A. K.A. Polypeptides) and Enzymes (Enzymes are a TYPE of protein.) A. These macromolecules make up greater than 50% of an organisms dry weight, called biomass. B. Names usually end with the suffix “lin” (i.e. Insulin) for proteins and “ase” for enzymes (i.e. Sucrase) C. The monomer “buildi ...
... Proteins (A. K.A. Polypeptides) and Enzymes (Enzymes are a TYPE of protein.) A. These macromolecules make up greater than 50% of an organisms dry weight, called biomass. B. Names usually end with the suffix “lin” (i.e. Insulin) for proteins and “ase” for enzymes (i.e. Sucrase) C. The monomer “buildi ...
Enzyme

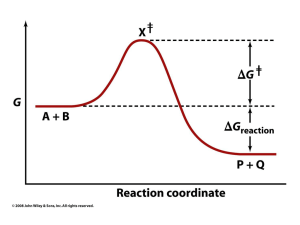
Enzymes /ˈɛnzaɪmz/ are macromolecular biological catalysts. Enzymes accelerate, or catalyze, chemical reactions. The molecules at the beginning of the process are called substrates and the enzyme converts these into different molecules, called products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. The set of enzymes made in a cell determines which metabolic pathways occur in that cell. The study of enzymes is called enzymology.Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Most enzymes are proteins, although a few are catalytic RNA molecules. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures.Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the rate of a reaction by lowering its activation energy. Some enzymes can make their conversion of substrate to product occur many millions of times faster. An extreme example is orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase, which allows a reaction that would otherwise take millions of years to occur in milliseconds. Chemically, enzymes are like any catalyst and are not consumed in chemical reactions, nor do they alter the equilibrium of a reaction. Enzymes differ from most other catalysts by being much more specific. Enzyme activity can be affected by other molecules: inhibitors are molecules that decrease enzyme activity, and activators are molecules that increase activity. Many drugs and poisons are enzyme inhibitors. An enzyme's activity decreases markedly outside its optimal temperature and pH.Some enzymes are used commercially, for example, in the synthesis of antibiotics. Some household products use enzymes to speed up chemical reactions: enzymes in biological washing powders break down protein, starch or fat stains on clothes, and enzymes in meat tenderizer break down proteins into smaller molecules, making the meat easier to chew.