Microbial Metabolism Notes
... B. Enzymes 1. proteins that facilitate chemical reactions A) reactant (substrate) binds to a specific binding site (active site) on the enzyme resulting in a lowering of the reaction’s activation energy 1) amount of energy required to initiate a chemical reaction 2. often require specific cofactors ...
... B. Enzymes 1. proteins that facilitate chemical reactions A) reactant (substrate) binds to a specific binding site (active site) on the enzyme resulting in a lowering of the reaction’s activation energy 1) amount of energy required to initiate a chemical reaction 2. often require specific cofactors ...
Chem of life
... Carbon (C), nitrogen (N), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O) and sometimes (S) Parts of the cell membrane Parts of organelles Muscles have lots of protein ...
... Carbon (C), nitrogen (N), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O) and sometimes (S) Parts of the cell membrane Parts of organelles Muscles have lots of protein ...
1 - contentextra
... create an mRNA molecule in a process called transcription. Second, this mRNA molecule with the help of a ribosome, tRNA and amino acids synthesizes the actual protein in a process called translation. 12 The genetic code is written in sequences of three bases along the DNA molecule. Each sequence of ...
... create an mRNA molecule in a process called transcription. Second, this mRNA molecule with the help of a ribosome, tRNA and amino acids synthesizes the actual protein in a process called translation. 12 The genetic code is written in sequences of three bases along the DNA molecule. Each sequence of ...
1 - contentextra
... help of a ribosome, tRNA and amino acids synthesizes the actual protein in a process called translation. 12 The genetic code is written in sequences of three bases along the DNA molecule. Each sequence of three bases is called a triplet. 13 Some proteins act as organic catalysts within cells and are ...
... help of a ribosome, tRNA and amino acids synthesizes the actual protein in a process called translation. 12 The genetic code is written in sequences of three bases along the DNA molecule. Each sequence of three bases is called a triplet. 13 Some proteins act as organic catalysts within cells and are ...
Nattokinase - Dr. Fred Hui
... The enzyme was discovered by Dr Hiroyuki Sumi who tested around 200 natural foods for their ability to dissolve the clot or thrombus. When Natto was dropped onto a thrombus, the thrombus dissolved completely in about 18 hours. The enzyme was named as "Nattokinase", which means "enzyme in Natto". Wha ...
... The enzyme was discovered by Dr Hiroyuki Sumi who tested around 200 natural foods for their ability to dissolve the clot or thrombus. When Natto was dropped onto a thrombus, the thrombus dissolved completely in about 18 hours. The enzyme was named as "Nattokinase", which means "enzyme in Natto". Wha ...
Chapter 3 Chemistry of Life Modern Biology Textbook Holt
... • Waxes: A wax is made of one long fatty acid chain joined to one long alcohol. Protect animal ears and plant leaves. • Steroids: A steroid is a lipid composed of four fused carbon rings that help regulate body functions-testerone and estrogen Cholesterol is a steroid found in cell membranes that co ...
... • Waxes: A wax is made of one long fatty acid chain joined to one long alcohol. Protect animal ears and plant leaves. • Steroids: A steroid is a lipid composed of four fused carbon rings that help regulate body functions-testerone and estrogen Cholesterol is a steroid found in cell membranes that co ...
Biochemistry_Short_Course
... the properties of water and biological molecules such as proteins • Allows blood (mostly H2O) to absorb and transport a large amount of nutrients • DNA’s alpha helix shape is due to hydrogen bonds between strands ...
... the properties of water and biological molecules such as proteins • Allows blood (mostly H2O) to absorb and transport a large amount of nutrients • DNA’s alpha helix shape is due to hydrogen bonds between strands ...
Exam 2 Review Answer Key
... If the above reactions are coupled they will have a net ΔG of: a. +4kcal/mol endergonic b. -4kcal/mol exergonic c. +4kcal/mol exergonic d. -4kcal/mol endergonic 4. T/F competitive inhibitors bind the active site of an enzyme while noncompetitive inhibitors bind an allosteric site Ch. 7.1-7.2: Respir ...
... If the above reactions are coupled they will have a net ΔG of: a. +4kcal/mol endergonic b. -4kcal/mol exergonic c. +4kcal/mol exergonic d. -4kcal/mol endergonic 4. T/F competitive inhibitors bind the active site of an enzyme while noncompetitive inhibitors bind an allosteric site Ch. 7.1-7.2: Respir ...
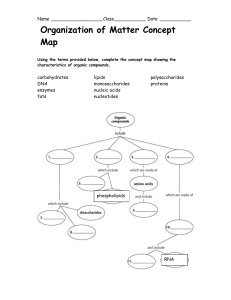
Polymers vs. monomers wkst. and concept map
... 8-18. Complete the chart below. Remember mono means one and poly means many. ...
... 8-18. Complete the chart below. Remember mono means one and poly means many. ...
An overview of biochemistry for bioCHEM480
... molecules). Other types of enzyme activity 'fine' regulation are allosterism and hormone-controlled covalent modification by phosphorylation (requiring ‘kinases’) and dephosphorylation (requiring ‘phosphatases’).These enzymes can be regulated as well in ‘enzyme cascades’. Flux in biochemical pathway ...
... molecules). Other types of enzyme activity 'fine' regulation are allosterism and hormone-controlled covalent modification by phosphorylation (requiring ‘kinases’) and dephosphorylation (requiring ‘phosphatases’).These enzymes can be regulated as well in ‘enzyme cascades’. Flux in biochemical pathway ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Nerve activates contraction
... • All complex sugars MUST be broken down into MONOSACCHARIDES for the body to utilize in glycolysis and cellular respiration ...
... • All complex sugars MUST be broken down into MONOSACCHARIDES for the body to utilize in glycolysis and cellular respiration ...
Biochemistry WebQuest
... C) folds on itself (bends) D) More than one chain joins together E) all of these Enzymes Go to http://science.howstuffworks.com/cell2.htm Read the text and answer the following questions 1. What is the purpose of enzymes? 2. What type of organic molecules (carbohydrate, lipid, protein, nucleic acid) ...
... C) folds on itself (bends) D) More than one chain joins together E) all of these Enzymes Go to http://science.howstuffworks.com/cell2.htm Read the text and answer the following questions 1. What is the purpose of enzymes? 2. What type of organic molecules (carbohydrate, lipid, protein, nucleic acid) ...
Histology Cell Organelles By Dr. Nand Lal Dhomeja
... Most important disease is Zellweger Syndrome. There is absence of functional peroxisomes. This leads to the accumulation of long chain fatty acids in the brain, decreased formation of plasmalogens, and defects of bile acid formation. ...
... Most important disease is Zellweger Syndrome. There is absence of functional peroxisomes. This leads to the accumulation of long chain fatty acids in the brain, decreased formation of plasmalogens, and defects of bile acid formation. ...
ANPS 019 Black 09-02
... At equilibrium the rates of two opposing reactions are in balance: anabolism = catabolism ENZYMES Most enzymes are proteins: organic molecules Reactants (substrate interact to yield a product by binding to the active site of the enzyme Enzymes are catalysts that promote chemical reactions Active sit ...
... At equilibrium the rates of two opposing reactions are in balance: anabolism = catabolism ENZYMES Most enzymes are proteins: organic molecules Reactants (substrate interact to yield a product by binding to the active site of the enzyme Enzymes are catalysts that promote chemical reactions Active sit ...
Lecture #1 ~ Date_________
... Factors affecting enzyme function • pH – changes in pH • adds or remove H+ • disrupts bonds, disrupts 3D shape – disrupts attractions between charged amino acids – affect 2° & 3° structure – denatures protein ...
... Factors affecting enzyme function • pH – changes in pH • adds or remove H+ • disrupts bonds, disrupts 3D shape – disrupts attractions between charged amino acids – affect 2° & 3° structure – denatures protein ...
Higher Human Biology unit 1 section 5 ENZYMES
... Tips - This is a quantitative experiment and requires great accuracy • Weigh out sodium phosphate to the nearest 0.01g • Rinse the boat with an eye wash bottle after adding beaker with 80ml of distilled water • Dissolve thoroughly and add 80ml to 100ml volumetric flask ...
... Tips - This is a quantitative experiment and requires great accuracy • Weigh out sodium phosphate to the nearest 0.01g • Rinse the boat with an eye wash bottle after adding beaker with 80ml of distilled water • Dissolve thoroughly and add 80ml to 100ml volumetric flask ...
Lecture 6
... Enzymes fall into classes based on function • There are 6 major classes of enzymes: 1.Oxidoreductases which are involved in oxidation, reduction, and electron or proton transfer reactions; 2.Transferases, catalysing reactions in which groups are transferred; 3.Hydrolases which cleave various covale ...
... Enzymes fall into classes based on function • There are 6 major classes of enzymes: 1.Oxidoreductases which are involved in oxidation, reduction, and electron or proton transfer reactions; 2.Transferases, catalysing reactions in which groups are transferred; 3.Hydrolases which cleave various covale ...
Metabolism & Enzymes - T.R. Robinson High School
... permanently binds to allosteric site permanently changes shape of enzyme ...
... permanently binds to allosteric site permanently changes shape of enzyme ...
Today`s Plan: 1/5/09
... Allosteric regulation=similar to noncompetitive inhibition but not permanent and either causes activation by stabilizing the protein shape, or can cause inhibition by destabilizing the protein shape (usually at the junction of the polypeptide chains of the enzyme) Cooperativity=remember that since m ...
... Allosteric regulation=similar to noncompetitive inhibition but not permanent and either causes activation by stabilizing the protein shape, or can cause inhibition by destabilizing the protein shape (usually at the junction of the polypeptide chains of the enzyme) Cooperativity=remember that since m ...
a very large molecule, Protein, carbohydrate, Lipid, Nucleic Acid
... Proteins to Enzymes A protein sometimes works as an enzyme An enzyme speeds up chemical reactions in our bodies An enzyme speeds up a reaction by making it easier. This is done by lowering the activation energy ...
... Proteins to Enzymes A protein sometimes works as an enzyme An enzyme speeds up chemical reactions in our bodies An enzyme speeds up a reaction by making it easier. This is done by lowering the activation energy ...
Document
... • molecules (mostly protein) that accelerate or catalyze chemical reactions (A--->B) in cells by breaking old covalent bonds and forming new covalent bonds ...
... • molecules (mostly protein) that accelerate or catalyze chemical reactions (A--->B) in cells by breaking old covalent bonds and forming new covalent bonds ...
Enzyme

Enzymes /ˈɛnzaɪmz/ are macromolecular biological catalysts. Enzymes accelerate, or catalyze, chemical reactions. The molecules at the beginning of the process are called substrates and the enzyme converts these into different molecules, called products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. The set of enzymes made in a cell determines which metabolic pathways occur in that cell. The study of enzymes is called enzymology.Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Most enzymes are proteins, although a few are catalytic RNA molecules. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures.Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the rate of a reaction by lowering its activation energy. Some enzymes can make their conversion of substrate to product occur many millions of times faster. An extreme example is orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase, which allows a reaction that would otherwise take millions of years to occur in milliseconds. Chemically, enzymes are like any catalyst and are not consumed in chemical reactions, nor do they alter the equilibrium of a reaction. Enzymes differ from most other catalysts by being much more specific. Enzyme activity can be affected by other molecules: inhibitors are molecules that decrease enzyme activity, and activators are molecules that increase activity. Many drugs and poisons are enzyme inhibitors. An enzyme's activity decreases markedly outside its optimal temperature and pH.Some enzymes are used commercially, for example, in the synthesis of antibiotics. Some household products use enzymes to speed up chemical reactions: enzymes in biological washing powders break down protein, starch or fat stains on clothes, and enzymes in meat tenderizer break down proteins into smaller molecules, making the meat easier to chew.