notes File - selu moodle
... glucose in the blood. Can be broken down later into glucose and used as energy. Keeps blood glucose levels stable. 2)starch – energy storage in plants Glycogen and starch are easily degraded and can be used when necessary for energy. 3) chitin – structural storage in animals (ex. shrimp shells, cock ...
... glucose in the blood. Can be broken down later into glucose and used as energy. Keeps blood glucose levels stable. 2)starch – energy storage in plants Glycogen and starch are easily degraded and can be used when necessary for energy. 3) chitin – structural storage in animals (ex. shrimp shells, cock ...
Higher Human Biology HW 3
... Suggest how cyanide is able to do this. ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ...
... Suggest how cyanide is able to do this. ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ...
Cell Metabolism - Cathkin High School
... Suggest how cyanide is able to do this. ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ...
... Suggest how cyanide is able to do this. ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ...
The activity reaction core and plasticity of metabolic networks
... The core enzymes may prove effective antibiotic targets. Currently used antibiotics: Fosfomycin and cycloserine inhibit cell-wall peptidoglycan. Sulfonamides and trimethoprim inhibit tetrahydrofolte biosynthesis. Both pathways are present in H. pylori and E. coli. ...
... The core enzymes may prove effective antibiotic targets. Currently used antibiotics: Fosfomycin and cycloserine inhibit cell-wall peptidoglycan. Sulfonamides and trimethoprim inhibit tetrahydrofolte biosynthesis. Both pathways are present in H. pylori and E. coli. ...
Physiology is an Integrated Science
... many AA to protein many glucose to glycogen many nucleotides to DNA ATP synthesis reactions that require energy anabolic reactions are endergonic ...
... many AA to protein many glucose to glycogen many nucleotides to DNA ATP synthesis reactions that require energy anabolic reactions are endergonic ...
Chemistry of Life Vocabulary
... substance present at the initiation of the reaction. Product - A substance resulting from a chemical reaction. Activation energy –minimum amount of energy required for a chemical reaction to happen. Substrate - a molecule which is acted upon by an enzyme Catalyst - A substance, usually used in small ...
... substance present at the initiation of the reaction. Product - A substance resulting from a chemical reaction. Activation energy –minimum amount of energy required for a chemical reaction to happen. Substrate - a molecule which is acted upon by an enzyme Catalyst - A substance, usually used in small ...
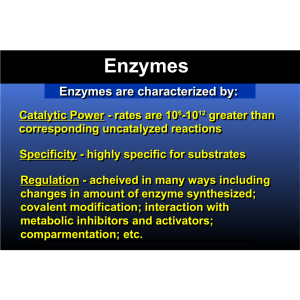
Enzymes Enzymes are characterized by
... enzyme synthesized; synthesized; covalent covalent modification; modification; interaction interaction with with metabolic metabolic inhibitors inhibitors and and activators; activators; comparmentation; comparmentation; etc. etc. ...
... enzyme synthesized; synthesized; covalent covalent modification; modification; interaction interaction with with metabolic metabolic inhibitors inhibitors and and activators; activators; comparmentation; comparmentation; etc. etc. ...
Acid Carboxypeptidases: Their Occurrence in Plants, Intracellular
... which has not passed through further development) and of the Angiosperms. Carboxypeptidase activity, finally, is present in the thermophilic fungi Talaromyces duponti (Ascomycetes) Humicula lanuginosa (Deuteromycetes); these enzymes, however, belong to a different family of alkaline carboxypeptidase ...
... which has not passed through further development) and of the Angiosperms. Carboxypeptidase activity, finally, is present in the thermophilic fungi Talaromyces duponti (Ascomycetes) Humicula lanuginosa (Deuteromycetes); these enzymes, however, belong to a different family of alkaline carboxypeptidase ...
Profile #78
... produce newly developed Spirulina sp. cyanobacterium in pilot-plant scale in one of the Mediterranean areas. • One SME and/or one applied research group from food & nutrition research institutes or universities from any country to develop new and innovative ready-toeat products and semi-prepared foo ...
... produce newly developed Spirulina sp. cyanobacterium in pilot-plant scale in one of the Mediterranean areas. • One SME and/or one applied research group from food & nutrition research institutes or universities from any country to develop new and innovative ready-toeat products and semi-prepared foo ...
Gold Biotechnology Enzyme and Antibody Immobilization
... • Glyoxal Agarose Beads: Supports with an aldehyde group that covalently reacts with the lysine groups in the biomolecules. • Aminoethyl Agarose Beads: Supports with an amino group that covalently reacts with acidic amino acids like aspartic acid or glutamic acid. Both types of resins give the biomo ...
... • Glyoxal Agarose Beads: Supports with an aldehyde group that covalently reacts with the lysine groups in the biomolecules. • Aminoethyl Agarose Beads: Supports with an amino group that covalently reacts with acidic amino acids like aspartic acid or glutamic acid. Both types of resins give the biomo ...
Chapter 3 Review Questions
... 8. Nucleic acids are important because they contain your __genetic information__________. 9. ___Proteins______________ build living tissue and help in chemical reactions. 10. _____Lipids___________ are a source of long-term stored energy. 11. Organic molecules that have the same chemical formula but ...
... 8. Nucleic acids are important because they contain your __genetic information__________. 9. ___Proteins______________ build living tissue and help in chemical reactions. 10. _____Lipids___________ are a source of long-term stored energy. 11. Organic molecules that have the same chemical formula but ...
Gene Cloning, Expression, and Substrate Specificity of an Imidase
... amino acids with a calculated molecular weight of 33712.6 kDa. The deduced amino-acid sequence showed 78% identity with the imidase from Alcaligenes eutrophus 112R4 and 80% identity with Nterminal 20 amino-acid imidase from Blastobacter sp. A17p-4. Next, the ORF was subcloned into vector pET32a to f ...
... amino acids with a calculated molecular weight of 33712.6 kDa. The deduced amino-acid sequence showed 78% identity with the imidase from Alcaligenes eutrophus 112R4 and 80% identity with Nterminal 20 amino-acid imidase from Blastobacter sp. A17p-4. Next, the ORF was subcloned into vector pET32a to f ...
File
... • A protein’s subunit arrangement (not all proteins have a quarternary structure). Occurs when 2 or more polypeptide chains form a functional protein. • E.g. hemoglobin is a protein composed of two alpha-chain subunits and two betachain subunits. Quarternary structure can bind prosthetic groups such ...
... • A protein’s subunit arrangement (not all proteins have a quarternary structure). Occurs when 2 or more polypeptide chains form a functional protein. • E.g. hemoglobin is a protein composed of two alpha-chain subunits and two betachain subunits. Quarternary structure can bind prosthetic groups such ...
Marine Biotechnology
... Baja California Peninsula have both ecological and economic interest. Panulirus interruptus is one of the most important fisheries of the regional economy. This study describes the first known work on the proteases for digesting food protein in this species. The main objective was to provide descrip ...
... Baja California Peninsula have both ecological and economic interest. Panulirus interruptus is one of the most important fisheries of the regional economy. This study describes the first known work on the proteases for digesting food protein in this species. The main objective was to provide descrip ...
Chapter 5
... can occur when atoms, ions, and molecules collide Activation energy is needed to disrupt electronic configurations Reaction rate is the frequency of collisions with enough energy to bring about a reaction. Reaction rate can be increased by enzymes or by increasing temperature or pressure ...
... can occur when atoms, ions, and molecules collide Activation energy is needed to disrupt electronic configurations Reaction rate is the frequency of collisions with enough energy to bring about a reaction. Reaction rate can be increased by enzymes or by increasing temperature or pressure ...
G 0 - Lucinda Supernavage
... • May be inorganic (such as a metal in ionic form) or organic • An organic cofactor is called a coenzyme – Coenzymes include vitamins ...
... • May be inorganic (such as a metal in ionic form) or organic • An organic cofactor is called a coenzyme – Coenzymes include vitamins ...
Station #2: Biomolecules, Enzymes, Photosynthesis and Respiration
... 2. Cells break down lipids/fats to provide __________and_____________ that the cell requires. a. energy, simple sugars b. DNA, nucleotides c. proteins, energy d. energy, fatty acids 3. Cells require energy to build _________________that they require for cellular functions. a. proteins b. carbohydrat ...
... 2. Cells break down lipids/fats to provide __________and_____________ that the cell requires. a. energy, simple sugars b. DNA, nucleotides c. proteins, energy d. energy, fatty acids 3. Cells require energy to build _________________that they require for cellular functions. a. proteins b. carbohydrat ...
BIOL 303 Cell Biology Test preparation questionnaire # 1
... 1. How does the sign and magnitude of the ∆G for a reaction indicate whether it can occur spontaneously? 55. By what means can cells carry out chemical transformations that are thrmodynamically unfavorable? 56. Can enzymes change the ∆G for a reaction and thus make an unfavorable reaction happen? 57 ...
... 1. How does the sign and magnitude of the ∆G for a reaction indicate whether it can occur spontaneously? 55. By what means can cells carry out chemical transformations that are thrmodynamically unfavorable? 56. Can enzymes change the ∆G for a reaction and thus make an unfavorable reaction happen? 57 ...
Compare and Contrast table for Photosynthesis and Cellular
... 4. Explain how different environmental conditions effect enzyme productivity? 5. What are characteristics of enzymes? 6. Explain the relationship between ATP synthesis and degradation and endergonic and exergonic reactions. 7. Write the formula for Gibbs free energy and understand how variations in ...
... 4. Explain how different environmental conditions effect enzyme productivity? 5. What are characteristics of enzymes? 6. Explain the relationship between ATP synthesis and degradation and endergonic and exergonic reactions. 7. Write the formula for Gibbs free energy and understand how variations in ...
Compare and Contrast table for Photosynthesis and Cellular
... 4. Explain how different environmental conditions effect enzyme productivity? 5. What are characteristics of enzymes? 6. Explain the relationship between ATP synthesis and degradation and endergonic and exergonic reactions. 7. Write the formula for Gibbs free energy and understand how variations in ...
... 4. Explain how different environmental conditions effect enzyme productivity? 5. What are characteristics of enzymes? 6. Explain the relationship between ATP synthesis and degradation and endergonic and exergonic reactions. 7. Write the formula for Gibbs free energy and understand how variations in ...
Enzyme

Enzymes /ˈɛnzaɪmz/ are macromolecular biological catalysts. Enzymes accelerate, or catalyze, chemical reactions. The molecules at the beginning of the process are called substrates and the enzyme converts these into different molecules, called products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. The set of enzymes made in a cell determines which metabolic pathways occur in that cell. The study of enzymes is called enzymology.Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Most enzymes are proteins, although a few are catalytic RNA molecules. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures.Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the rate of a reaction by lowering its activation energy. Some enzymes can make their conversion of substrate to product occur many millions of times faster. An extreme example is orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase, which allows a reaction that would otherwise take millions of years to occur in milliseconds. Chemically, enzymes are like any catalyst and are not consumed in chemical reactions, nor do they alter the equilibrium of a reaction. Enzymes differ from most other catalysts by being much more specific. Enzyme activity can be affected by other molecules: inhibitors are molecules that decrease enzyme activity, and activators are molecules that increase activity. Many drugs and poisons are enzyme inhibitors. An enzyme's activity decreases markedly outside its optimal temperature and pH.Some enzymes are used commercially, for example, in the synthesis of antibiotics. Some household products use enzymes to speed up chemical reactions: enzymes in biological washing powders break down protein, starch or fat stains on clothes, and enzymes in meat tenderizer break down proteins into smaller molecules, making the meat easier to chew.