
biologically important molecules
... Because CELLULOSE has alternating glucose orientation, we do not have an enzyme that can break it down. So we cannot eat grass for energy like cows (ruminants) who have the enzyme CELLULASE due to microorganisms in their guts that create it. ...
... Because CELLULOSE has alternating glucose orientation, we do not have an enzyme that can break it down. So we cannot eat grass for energy like cows (ruminants) who have the enzyme CELLULASE due to microorganisms in their guts that create it. ...
Biochemistry with Elements of Chemistry - Collegium Medicum
... 18. The structure of the active site and models for substrate binding. The specificity of enzymes to the substrates and the catalysed reaction. 19. The catalytic mechanisms of the enzymatic reactions. 20. The influence of physical and chemical factors on the enzyme activity (temperature, pH, the enz ...
... 18. The structure of the active site and models for substrate binding. The specificity of enzymes to the substrates and the catalysed reaction. 19. The catalytic mechanisms of the enzymatic reactions. 20. The influence of physical and chemical factors on the enzyme activity (temperature, pH, the enz ...
Chapter 2 : The Chemistry of Life Section 3 : Carbon
... • Catalyst – a substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction • Enzyme – Proteins that speed up chemical reactions by reducing the activation energy (amount of energy needed to start the chemical reaction) • Enzymes are biological catalyst ...
... • Catalyst – a substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction • Enzyme – Proteins that speed up chemical reactions by reducing the activation energy (amount of energy needed to start the chemical reaction) • Enzymes are biological catalyst ...
Fuel Metabolism
... that is found in large masses in the interscapular region, the perirenal area, and surrounds the aorta and heart of the hibernator. BAT proliferation and differentiation is responsive to multiple signals including insulin and insulin-dependent growth factor (IGF-I) that are particularly involved i ...
... that is found in large masses in the interscapular region, the perirenal area, and surrounds the aorta and heart of the hibernator. BAT proliferation and differentiation is responsive to multiple signals including insulin and insulin-dependent growth factor (IGF-I) that are particularly involved i ...
Polony - OpenWetWare
... • Acrylamide polymerized in a solution containing standard PCR reagents (primers, template, dNTPs, enzyme, buffer). • Up to 360 DNA/RNA molecules of starting template per reaction • Glass microscope slide (treated with bind-silane) ...
... • Acrylamide polymerized in a solution containing standard PCR reagents (primers, template, dNTPs, enzyme, buffer). • Up to 360 DNA/RNA molecules of starting template per reaction • Glass microscope slide (treated with bind-silane) ...
Brookfield Academy Upper School SMART Team
... milestones, myopia, dislocation of the eye lens, osteoporosis, mental retardation, and increased risk of blood clotting. Major causes of homocystinuria are mutations in the enzyme cystathionine ß-synthase (CBS), which catalyzes the condensation of serine and homocysteine to cystathionine, an interme ...
... milestones, myopia, dislocation of the eye lens, osteoporosis, mental retardation, and increased risk of blood clotting. Major causes of homocystinuria are mutations in the enzyme cystathionine ß-synthase (CBS), which catalyzes the condensation of serine and homocysteine to cystathionine, an interme ...
Quiz #3 - San Diego Mesa College
... glucose is _______ by a class of enzymes called ________ . A) reduced ….. dehydrogenases B) oxidized …… dehydrogenases C) oxidized ……. reductases D) reduced …… oxidases E) none of the above Q. 9: Which of the following is/are (a) molecule(s) involved in metabolic redox reactions in living organisms? ...
... glucose is _______ by a class of enzymes called ________ . A) reduced ….. dehydrogenases B) oxidized …… dehydrogenases C) oxidized ……. reductases D) reduced …… oxidases E) none of the above Q. 9: Which of the following is/are (a) molecule(s) involved in metabolic redox reactions in living organisms? ...
Biochemistry 2000 Sample Question Protein
... (b) If a Trp residue has = 60º , = 120º, is it in an energetically favorable conformation? (c) If a Gly residue has = 120º , = 60º, is it in an energetically favorable conformation? (5) Pauling predicted the structures of both -helices and -sheets from modeling studies. What physiochemic ...
... (b) If a Trp residue has = 60º , = 120º, is it in an energetically favorable conformation? (c) If a Gly residue has = 120º , = 60º, is it in an energetically favorable conformation? (5) Pauling predicted the structures of both -helices and -sheets from modeling studies. What physiochemic ...
Basic Strategies of Cell Metabolism
... can be carried out by the cell. It is essential for the biotechnologist to fully understand these basic metabolic processes, as every present and future biotechnological industry can be economically feasible only if full advantage is taken of the cell’s capacity to convert substrate into the desired ...
... can be carried out by the cell. It is essential for the biotechnologist to fully understand these basic metabolic processes, as every present and future biotechnological industry can be economically feasible only if full advantage is taken of the cell’s capacity to convert substrate into the desired ...
Exam 4 KEY
... A. (4 pts) The conversion of phosphoenolpyruvate to pyruvate in the cytosol is an exergonic reaction catalyzed by the enzyme pyruvate kinase (ΔGº' = -31.4 kJ/mol). Since the reverse of this reaction is highly unfavorable (ΔGº' = +31.4 kJ/mol), explain how it is possible that the conversion of pyruva ...
... A. (4 pts) The conversion of phosphoenolpyruvate to pyruvate in the cytosol is an exergonic reaction catalyzed by the enzyme pyruvate kinase (ΔGº' = -31.4 kJ/mol). Since the reverse of this reaction is highly unfavorable (ΔGº' = +31.4 kJ/mol), explain how it is possible that the conversion of pyruva ...
HEMOGLOBIN
... Iron is found in the ferrous form (Fe++) in both hemoglobin and oxyhemoglobin. Iron is in the oxidised form (Fe+++) in ...
... Iron is found in the ferrous form (Fe++) in both hemoglobin and oxyhemoglobin. Iron is in the oxidised form (Fe+++) in ...
Heine - MrZitarelli
... B. amino acids. C. carbohydrates. D. nucleic acids. 4. Nucleotides consist of a phosphate group, a nitrogenous base, and a A. fatty acid. B. 5-carbon sugar. C. 6-carbon sugar. D. lipid. ...
... B. amino acids. C. carbohydrates. D. nucleic acids. 4. Nucleotides consist of a phosphate group, a nitrogenous base, and a A. fatty acid. B. 5-carbon sugar. C. 6-carbon sugar. D. lipid. ...
File - singhscience
... (ii) Genetically different organisms contain different DNA codes that produce different proteins. Describe the process that takes place in the nucleus during the first stage of protein synthesis. ...
... (ii) Genetically different organisms contain different DNA codes that produce different proteins. Describe the process that takes place in the nucleus during the first stage of protein synthesis. ...
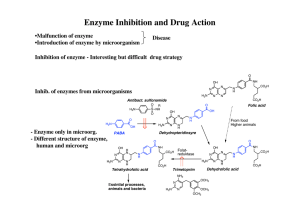
Enzyme Inhibition and Drug Action
... •Affinity labels and active site directed irreversible inhibitors •Mechanism based irreversible enzyme inactivators Suicide substrate - kcat inhibitors - Trojan horse inhib. - latent alkylating agent ≈ Pro-drug, must be activated by the enzyme Penicillins are cleaved by β-lactamase ...
... •Affinity labels and active site directed irreversible inhibitors •Mechanism based irreversible enzyme inactivators Suicide substrate - kcat inhibitors - Trojan horse inhib. - latent alkylating agent ≈ Pro-drug, must be activated by the enzyme Penicillins are cleaved by β-lactamase ...
Chapter 17 (part 2) - University of Nevada, Reno
... ubiquitinates several proteins involved in DNA repair. • Activation of this E3 enzyme is observed in 90% of cervical carcinomas. ...
... ubiquitinates several proteins involved in DNA repair. • Activation of this E3 enzyme is observed in 90% of cervical carcinomas. ...
b) How many electrons are in carbons 2nd energy
... 8 of 20) Which category of organic molecules contains the amount of C, H, and O in a 1: 2: 1 ...
... 8 of 20) Which category of organic molecules contains the amount of C, H, and O in a 1: 2: 1 ...
Ch.9cellrespiration
... 2 ATP, CO2, NADH, FADH Enzymes not embedded Energy carriers Escort molecule to Krebs cycle ...
... 2 ATP, CO2, NADH, FADH Enzymes not embedded Energy carriers Escort molecule to Krebs cycle ...
Lecture 33
... pathways. For example, when energy charge in the cell is low, AMP levels are high leading to activation of PFK-1 (increased flux through glycolysis) and inhibition of FBPase-1 (decreased flux through gluconeogenesis). This makes sense because the pyruvate generated by glycolysis can then be used in ...
... pathways. For example, when energy charge in the cell is low, AMP levels are high leading to activation of PFK-1 (increased flux through glycolysis) and inhibition of FBPase-1 (decreased flux through gluconeogenesis). This makes sense because the pyruvate generated by glycolysis can then be used in ...
Elegant Molecules: [Dr. Stanford Moore]
... carbonate because of their various molecular characters, separated into bands of different colors as they moved down the column. The bands could then be washed OUt of the column, color by color. Tswett's column was later adapted for colorless compounds through the use of specific methods of detectio ...
... carbonate because of their various molecular characters, separated into bands of different colors as they moved down the column. The bands could then be washed OUt of the column, color by color. Tswett's column was later adapted for colorless compounds through the use of specific methods of detectio ...
Novel Specific Halogenating Enzymes from Bacteria
... All isolated bacterial and eukaryotic halo peroxidases only showed very low or no substrate specificity at all (Franssen, 1994). However, as haloperoxidases were the only halogenating enzymes known, with the exception of some Sadenosyl methionine transferases that are involved in the formation of m ...
... All isolated bacterial and eukaryotic halo peroxidases only showed very low or no substrate specificity at all (Franssen, 1994). However, as haloperoxidases were the only halogenating enzymes known, with the exception of some Sadenosyl methionine transferases that are involved in the formation of m ...
How Did Life Begin? And What is Life?
... As a community committed to the Augustinian ideals of truth, unity and love, God School prides itself on maintaining the highest standards of academic integrity and does not tolerate any forms of academic dishonesty or misconduct. ...
... As a community committed to the Augustinian ideals of truth, unity and love, God School prides itself on maintaining the highest standards of academic integrity and does not tolerate any forms of academic dishonesty or misconduct. ...
Figure 5-2
... c. hydrogen atoms b. side groups d. carboxyl groups 32. An amino group is written as: a. –COOH b. –NH2 ...
... c. hydrogen atoms b. side groups d. carboxyl groups 32. An amino group is written as: a. –COOH b. –NH2 ...
Repression of Glutaminase I in the rat Retina by
... sodium glutamate would suppress the increase of glutaminase I in the rat called forth by ammonium chloride. It should be emphasized that our assumption about the effect of glutamate involves one further postulate, namely, that repression of the specific enzyme in question results in cell death or fa ...
... sodium glutamate would suppress the increase of glutaminase I in the rat called forth by ammonium chloride. It should be emphasized that our assumption about the effect of glutamate involves one further postulate, namely, that repression of the specific enzyme in question results in cell death or fa ...
Problem Set 5 (Due February 25th) 1. Show how glucose can be
... coefficient of 1 means that there is no cooperativity in the interactions of the substrate and the effector molecule. A Hill coefficient > 1 means positive cooperativity and less than one is negative cooperativity. This protein is a tetramer, so it’s very possible that there are multiple active si ...
... coefficient of 1 means that there is no cooperativity in the interactions of the substrate and the effector molecule. A Hill coefficient > 1 means positive cooperativity and less than one is negative cooperativity. This protein is a tetramer, so it’s very possible that there are multiple active si ...
Enzyme

Enzymes /ˈɛnzaɪmz/ are macromolecular biological catalysts. Enzymes accelerate, or catalyze, chemical reactions. The molecules at the beginning of the process are called substrates and the enzyme converts these into different molecules, called products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. The set of enzymes made in a cell determines which metabolic pathways occur in that cell. The study of enzymes is called enzymology.Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Most enzymes are proteins, although a few are catalytic RNA molecules. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures.Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the rate of a reaction by lowering its activation energy. Some enzymes can make their conversion of substrate to product occur many millions of times faster. An extreme example is orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase, which allows a reaction that would otherwise take millions of years to occur in milliseconds. Chemically, enzymes are like any catalyst and are not consumed in chemical reactions, nor do they alter the equilibrium of a reaction. Enzymes differ from most other catalysts by being much more specific. Enzyme activity can be affected by other molecules: inhibitors are molecules that decrease enzyme activity, and activators are molecules that increase activity. Many drugs and poisons are enzyme inhibitors. An enzyme's activity decreases markedly outside its optimal temperature and pH.Some enzymes are used commercially, for example, in the synthesis of antibiotics. Some household products use enzymes to speed up chemical reactions: enzymes in biological washing powders break down protein, starch or fat stains on clothes, and enzymes in meat tenderizer break down proteins into smaller molecules, making the meat easier to chew.

















![Elegant Molecules: [Dr. Stanford Moore]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/004414324_1-0b8950e0ece9c8d7bb29eebcb756237c-300x300.png)




