Modification of halogen specificity of a vanadium‐dependent
... residue located at the chlorine binding site of various amylases (Machius et al. 1995). In the case of BPO from C. pilulifera, the substituted tryptophan or phenylalanine residues at position 397 could participate in chloride binding. In the native BPO enzyme the active site cavity provides the corr ...
... residue located at the chlorine binding site of various amylases (Machius et al. 1995). In the case of BPO from C. pilulifera, the substituted tryptophan or phenylalanine residues at position 397 could participate in chloride binding. In the native BPO enzyme the active site cavity provides the corr ...
Crystal Structures of the Oxidized and Reduced Forms of UDP
... either side by R-helices. The C-terminal domain contains three strands of β-pleated sheet, two major R-helices, and one helical turn. In addition to allowing for a threedimensional structure of the enzyme to be modeled, this X-ray crystallographic investigation proved that the protein binds two NAD+ ...
... either side by R-helices. The C-terminal domain contains three strands of β-pleated sheet, two major R-helices, and one helical turn. In addition to allowing for a threedimensional structure of the enzyme to be modeled, this X-ray crystallographic investigation proved that the protein binds two NAD+ ...
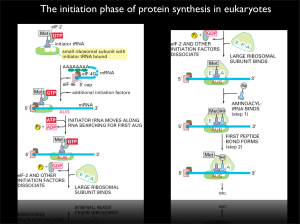
The initiation phase of protein synthesis in eukaryotes
... protein kinase-1(MNK1; also called MAP kinase signal-integrating kinase). MNK1 was identified independently by two groups as a substrate for ERK1 and ...
... protein kinase-1(MNK1; also called MAP kinase signal-integrating kinase). MNK1 was identified independently by two groups as a substrate for ERK1 and ...
Protein content and amino acids profile of
... Quality control results for protein and amino acid analysis are indicated in Table 2. The analytical values are within the certified ranges for all amino acids and macronutrients. The sum of individual amino acids agree with protein content determined by Kjeldahl. For each amino acid analysis the var ...
... Quality control results for protein and amino acid analysis are indicated in Table 2. The analytical values are within the certified ranges for all amino acids and macronutrients. The sum of individual amino acids agree with protein content determined by Kjeldahl. For each amino acid analysis the var ...
Case Study 5 Literature - Department of Chemistry
... purposes by supplying NADPH for anabolic reactions or in serine biosynthesis (10, 13, 14). Sequence analyses of the genes encoding GAPN of pea and maize, as well as of the bacterium Streptococcus mutans, indicated that GAPN enzymes are not related to phosphorylating GAPDH at all, but belong to the s ...
... purposes by supplying NADPH for anabolic reactions or in serine biosynthesis (10, 13, 14). Sequence analyses of the genes encoding GAPN of pea and maize, as well as of the bacterium Streptococcus mutans, indicated that GAPN enzymes are not related to phosphorylating GAPDH at all, but belong to the s ...
STEROIDS, BILE ACIDS, STEROID HORMONES
... CHOLESTEROL FACTS synthesized from acetyl CoA and eliminated as bile acids precursor of all other steroids in the body product of animal metabolism - in foods of animal origin amphipathic lipid (hydrophobic and hydrophilic portions) storage form is cholesterol ester found in most tissues. ...
... CHOLESTEROL FACTS synthesized from acetyl CoA and eliminated as bile acids precursor of all other steroids in the body product of animal metabolism - in foods of animal origin amphipathic lipid (hydrophobic and hydrophilic portions) storage form is cholesterol ester found in most tissues. ...
(pdf)
... yielded maximum cellular amino acid turnover times of ~89 years for 1 km depth and 27 °C and 1–2 years for 3 km depth and 54 °C. The latter turnover times are much shorter than previously estimated cellular turnover times based upon geochemical arguments. The aspartic acid racemization rate at highe ...
... yielded maximum cellular amino acid turnover times of ~89 years for 1 km depth and 27 °C and 1–2 years for 3 km depth and 54 °C. The latter turnover times are much shorter than previously estimated cellular turnover times based upon geochemical arguments. The aspartic acid racemization rate at highe ...
Gene7-07
... cause the replacement of one amino acid by another in a protein sequence. Nonsense codon means a termination codon. Suppressor (extragenic) is usually a gene coding a mutant tRNA that reads the mutated codon either in the sense of the original codon or to give an acceptable substitute for the origin ...
... cause the replacement of one amino acid by another in a protein sequence. Nonsense codon means a termination codon. Suppressor (extragenic) is usually a gene coding a mutant tRNA that reads the mutated codon either in the sense of the original codon or to give an acceptable substitute for the origin ...
Rooting the Ribosomal Tree of Life Research article
... ribosomal RNAs) have remained unrooted. Individual core ribosomal proteins are short in length, each containing few phylogenetically informative positions. As such, although universal phylogenies generated from alignments of individual ribosomal proteins generally do not show significant conflict, t ...
... ribosomal RNAs) have remained unrooted. Individual core ribosomal proteins are short in length, each containing few phylogenetically informative positions. As such, although universal phylogenies generated from alignments of individual ribosomal proteins generally do not show significant conflict, t ...
Integration of carbohydrate and lipid metabolism in skeletal
... from animals shortly after birth, subsequently rates of glucose transport decrease by 60-70 % over the first 40 days of post-natal development (fig. 1 ). The total pool size of glucose transporter units (sarcolemmal plus microsomal) also declines by about 60 % over a similar time period (Wang, 1985) ...
... from animals shortly after birth, subsequently rates of glucose transport decrease by 60-70 % over the first 40 days of post-natal development (fig. 1 ). The total pool size of glucose transporter units (sarcolemmal plus microsomal) also declines by about 60 % over a similar time period (Wang, 1985) ...
Environmental enteric dysfunction is associated with carnitine
... palmitoyltransferase II. Carnitine is then free to cycle back to the cytosol through the transporter (Fig. 1). Secondary carnitine deficiency is characterized by increases in serum acylcarnitines, fatty acid intermediates associated with blocked β-oxidation, and dicarboxylic acids produced by ω-oxida ...
... palmitoyltransferase II. Carnitine is then free to cycle back to the cytosol through the transporter (Fig. 1). Secondary carnitine deficiency is characterized by increases in serum acylcarnitines, fatty acid intermediates associated with blocked β-oxidation, and dicarboxylic acids produced by ω-oxida ...
BCMB 3100 – Chapters 6,7,8 Enzyme Basics • Six Classes (IUBMB
... Challenge of the Weekend, Due September 13, 2016 ...
... Challenge of the Weekend, Due September 13, 2016 ...
Phar 722 Pharmacy Practice III
... • There does not seem to be a cofactor form different from the basic structure. • The carboxyl chain forms an amide linkage with the ε-amino nitrogen of lysine which binds the vitamin to the enzyme's active site. • Biotin is required for the addition of carbon dioxide in many, but not all, carboxyla ...
... • There does not seem to be a cofactor form different from the basic structure. • The carboxyl chain forms an amide linkage with the ε-amino nitrogen of lysine which binds the vitamin to the enzyme's active site. • Biotin is required for the addition of carbon dioxide in many, but not all, carboxyla ...
THE SHIKIMATE PATHWAY: AROMATIC AMINO ACIDS AND
... AROMATIC AMINO ACIDS AND SIMPLE BENZOIC ACIDS The shikimate pathway begins with a coupling of phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) and D-erythrose 4-phosphate to give the seven-carbon 3-deoxyD-arabino-heptulosonic acid 7-phosphate (DAHP) (Figure 4.1). This reaction, shown here as an aldol-type condensation, is ...
... AROMATIC AMINO ACIDS AND SIMPLE BENZOIC ACIDS The shikimate pathway begins with a coupling of phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) and D-erythrose 4-phosphate to give the seven-carbon 3-deoxyD-arabino-heptulosonic acid 7-phosphate (DAHP) (Figure 4.1). This reaction, shown here as an aldol-type condensation, is ...
Fatigue During Muscular Exercise
... physiological pH range - Fig 2-7 – also depends on ATP/ADP ratio – consequence-less energy available for work with given VO2 flux – fatigue also influences ATP binding in X-bridge cycle ...
... physiological pH range - Fig 2-7 – also depends on ATP/ADP ratio – consequence-less energy available for work with given VO2 flux – fatigue also influences ATP binding in X-bridge cycle ...
Enzymes in jasmonate biosynthesis – Structure, function, regulation
... 2002)) mediates import of OPDA, and thus contributes to the biosynthesis of JAs (Theodoulou et al., 2005). CTS catalyzes the ATPdependent uptake of multiple b-oxidation substrates into peroxisomes. Reduced levels of JAs, impaired wound-induced JA accumulation, and reduced expression of the JA-depend ...
... 2002)) mediates import of OPDA, and thus contributes to the biosynthesis of JAs (Theodoulou et al., 2005). CTS catalyzes the ATPdependent uptake of multiple b-oxidation substrates into peroxisomes. Reduced levels of JAs, impaired wound-induced JA accumulation, and reduced expression of the JA-depend ...
Vitamins
... Vitamins are required to perform specific cellular functions, for example, many of the water-soluble vitamins are precursors of coenzymes for the enzymes of intermediary metabolism. In contrast to the water-soluble vitamins, only one fat soluble vitamin (vitamin K) has a coenzyme function. These vit ...
... Vitamins are required to perform specific cellular functions, for example, many of the water-soluble vitamins are precursors of coenzymes for the enzymes of intermediary metabolism. In contrast to the water-soluble vitamins, only one fat soluble vitamin (vitamin K) has a coenzyme function. These vit ...
Reading materials 511/rumen microbes/rumen
... mitochondria, they accumulate this intracellular messenger (Biagini et al., 1997). Both organelles have a double membrane and use the same import pathway for proteins (see van der Giezen et al., 2002 and references therein). The major function of mitochondria, the conversion of pyruvate to acetylCoA ...
... mitochondria, they accumulate this intracellular messenger (Biagini et al., 1997). Both organelles have a double membrane and use the same import pathway for proteins (see van der Giezen et al., 2002 and references therein). The major function of mitochondria, the conversion of pyruvate to acetylCoA ...
MS Word
... Basal GTP binding and hydrolysis (K1, k2 and K1’, k2’). The chemical step is rate-limiting for the basal GTPase reaction of cpSRP54, because the maximal rate constant of GTP hydrolysis (0.017 min-1; Figure 2A) is 4 104 -fold slower than the rate at which GTP dissociates from the enzyme active site ...
... Basal GTP binding and hydrolysis (K1, k2 and K1’, k2’). The chemical step is rate-limiting for the basal GTPase reaction of cpSRP54, because the maximal rate constant of GTP hydrolysis (0.017 min-1; Figure 2A) is 4 104 -fold slower than the rate at which GTP dissociates from the enzyme active site ...
Glucose Homeostasis
... They play an important role in glucose homeostatic mechanisms. If blood glucose level increases, decreases it through The uptake of glucose by tissues Glucose oxidation ...
... They play an important role in glucose homeostatic mechanisms. If blood glucose level increases, decreases it through The uptake of glucose by tissues Glucose oxidation ...
PAGE PROOFS
... Hydrochloric acid is found in our stomachs, where it is used to help break down food. It is also used in industry, where it is sometimes called ‘spirit of salts’, to clean bricks and to clean off the coating of oxide on corroded iron or steel before plating the metal with a protective layer of zinc ...
... Hydrochloric acid is found in our stomachs, where it is used to help break down food. It is also used in industry, where it is sometimes called ‘spirit of salts’, to clean bricks and to clean off the coating of oxide on corroded iron or steel before plating the metal with a protective layer of zinc ...
Citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle – also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or the Krebs cycle – is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest established components of cellular metabolism and may have originated abiogenically.The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from citric acid (a type of tricarboxylic acid) that is consumed and then regenerated by this sequence of reactions to complete the cycle. In addition, the cycle consumes acetate (in the form of acetyl-CoA) and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and produces carbon dioxide as a waste byproduct. The NADH generated by the TCA cycle is fed into the oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport) pathway. The net result of these two closely linked pathways is the oxidation of nutrients to produce usable chemical energy in the form of ATP.In eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion. In prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria which lack mitochondria, the TCA reaction sequence is performed in the cytosol with the proton gradient for ATP production being across the cell's surface (plasma membrane) rather than the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.