Enzymes
... • The synthesis of isoleucine from threonine is an example of allosteric regulation. – Threonine deaminase, which acts in the first step of the conversion pathway, is inhibited by the isoleucine product. – When isoleucine builds up, it binds to the allosteric site on threonine deaminase, changing i ...
... • The synthesis of isoleucine from threonine is an example of allosteric regulation. – Threonine deaminase, which acts in the first step of the conversion pathway, is inhibited by the isoleucine product. – When isoleucine builds up, it binds to the allosteric site on threonine deaminase, changing i ...
Section 3. Antimicrobial Sulfonamides and Antibacterial Synergists
... efficiently catalyze the conversion of dihydrofolic to tetrahydrofiolic acid , the bacteria enzyme is sensitive to inhibition by trimethoprim by up to 40,000 times lower concentration than the mouse enzyme. This difference explains the useful selective toxicity of trimethoprim. TMP is frequently use ...
... efficiently catalyze the conversion of dihydrofolic to tetrahydrofiolic acid , the bacteria enzyme is sensitive to inhibition by trimethoprim by up to 40,000 times lower concentration than the mouse enzyme. This difference explains the useful selective toxicity of trimethoprim. TMP is frequently use ...
ЛЕКЦІЯ 2
... Molecular Characteristics of the Actin Filament The actin filament is also complex. It is composed of three protein components: actin, tropomyosin, and troponin. The backbone of the actin filament is a double stranded F-actin protein molecule. The two strands are wound in a helix in the same manner ...
... Molecular Characteristics of the Actin Filament The actin filament is also complex. It is composed of three protein components: actin, tropomyosin, and troponin. The backbone of the actin filament is a double stranded F-actin protein molecule. The two strands are wound in a helix in the same manner ...
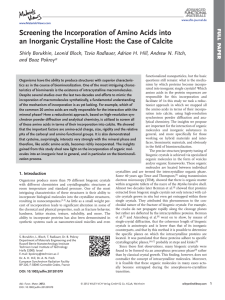
Screening the Incorporation of Amino Acids into an Inorganic
... counterparts, and that by this method it is possible to determine the specific planes on which the intracrystalline proteins are located. It was postulated that these proteins adhere to specific crystallographic planes,[4,6,7] probably at steps and kinks.[8] Since those first observations, many biog ...
... counterparts, and that by this method it is possible to determine the specific planes on which the intracrystalline proteins are located. It was postulated that these proteins adhere to specific crystallographic planes,[4,6,7] probably at steps and kinks.[8] Since those first observations, many biog ...
Agonism with the omega-3 fatty acids α-linolenic acid
... quences (NCBI ID: BC101175 and NM_181745, respectively) to predict intra- and extra- cellular domains as well as membranespanning regions and their orientations. Protein sequences were aligned and examined using Vector NTI 10.0 software (Invitrogen). 2.4. Immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting Forty ...
... quences (NCBI ID: BC101175 and NM_181745, respectively) to predict intra- and extra- cellular domains as well as membranespanning regions and their orientations. Protein sequences were aligned and examined using Vector NTI 10.0 software (Invitrogen). 2.4. Immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting Forty ...
New Advances in Catalytic Systems for Conversion of CH4 and CO2
... akin to the reductive acetyl-coenzyme A (CoA) pathway. The key enzyme in this pathway, acetyl-CoA synthane, contains an [Ni-Fe] reaction center and can catalyze reactions for the synthesis of acetic acid. The net reaction (Equation (8)) may be summarized as follows: CH3 SH + CO + H2 O −→ CH3 COOH + ...
... akin to the reductive acetyl-coenzyme A (CoA) pathway. The key enzyme in this pathway, acetyl-CoA synthane, contains an [Ni-Fe] reaction center and can catalyze reactions for the synthesis of acetic acid. The net reaction (Equation (8)) may be summarized as follows: CH3 SH + CO + H2 O −→ CH3 COOH + ...
Application of Synthetic Biology for Biopolymer
... Aiming at reducing the cost of xylose-based processes other improvements were investigated. Modified S. cerevisiae strains consume xylose when oxygen is available; however, their performance is not optimal anaerobic conditions. As pumping air into bioreactors is expensive, one of our goals was to im ...
... Aiming at reducing the cost of xylose-based processes other improvements were investigated. Modified S. cerevisiae strains consume xylose when oxygen is available; however, their performance is not optimal anaerobic conditions. As pumping air into bioreactors is expensive, one of our goals was to im ...
The Metabolic Network of Synechocystis sp. PCC
... Similarly, the scheme described above was applied to test and complete the pathways for de novo synthesis of cofactors, including CoA, NADs (NAD/ NADH), NADPs (NADP/NADPH), FADs (FAD/ FADH), and tetrahydrofolate. Again, the initial draft network had to be supplemented with additional reactions. A co ...
... Similarly, the scheme described above was applied to test and complete the pathways for de novo synthesis of cofactors, including CoA, NADs (NAD/ NADH), NADPs (NADP/NADPH), FADs (FAD/ FADH), and tetrahydrofolate. Again, the initial draft network had to be supplemented with additional reactions. A co ...
Slide 1
... 3. Unassigned Codon – The loss happens before the gain. There is a period when the loss is fixed in the population and the codon is unassigned. 4. Compensatory Change – The gain and loss are fixed in the population simultaneously (although they do not arise at the same time). There is no intermediat ...
... 3. Unassigned Codon – The loss happens before the gain. There is a period when the loss is fixed in the population and the codon is unassigned. 4. Compensatory Change – The gain and loss are fixed in the population simultaneously (although they do not arise at the same time). There is no intermediat ...
formula writing and nomenclature of inorganic - Parkway C-2
... 2 Na + Cl2 → 2 Na+ClIn this reaction, each sodium atom is considered to have transferred one electron to each chlorine atom forming, as a result, charged atoms or ions. Since each sodium atom has lost one electron, it is assigned an oxidation number of +1, while each chlorine atom has gained one ele ...
... 2 Na + Cl2 → 2 Na+ClIn this reaction, each sodium atom is considered to have transferred one electron to each chlorine atom forming, as a result, charged atoms or ions. Since each sodium atom has lost one electron, it is assigned an oxidation number of +1, while each chlorine atom has gained one ele ...
Carbon Metabolism in Spores of the Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungus
... Representative 13C-NMR spectra obtained for the MeOH/H2O extracts from each treatment are shown in Figure 2. Peaks at 94.1, 73.4, 72.9, 71.9, 70.5, and 61.4 ppm correspond to the chemical shifts of carbons (1,19), (3,39), (5,59), (2,29), (4,49), and (6,69) of trehalose (Fig. 2, T1–T6, compare with F ...
... Representative 13C-NMR spectra obtained for the MeOH/H2O extracts from each treatment are shown in Figure 2. Peaks at 94.1, 73.4, 72.9, 71.9, 70.5, and 61.4 ppm correspond to the chemical shifts of carbons (1,19), (3,39), (5,59), (2,29), (4,49), and (6,69) of trehalose (Fig. 2, T1–T6, compare with F ...
Nonenzymatic, Self-Elimination Degradation
... cytoplasm and the major reducing agent for almost all biochemical processes. GSH is important in the synthesis of proteins and DNA, transport, enzyme activity, metabolism, and protection of cells [1]. Cellular GSH levels must be maintained, since they are constantly fluctuating due to degradation an ...
... cytoplasm and the major reducing agent for almost all biochemical processes. GSH is important in the synthesis of proteins and DNA, transport, enzyme activity, metabolism, and protection of cells [1]. Cellular GSH levels must be maintained, since they are constantly fluctuating due to degradation an ...
BCMB 3100 – Chapters 6,7,8 Enzyme Basics • Six Classes (IUBMB
... Find a minimum of three examples of enzymes and their reactions for each of the 6 classes of enzymes. (You should be able to find all or most of these in your book) Label an individual page with one of each of the names of the 6 classes of enzymes. On each page for that particular class of enzymes, ...
... Find a minimum of three examples of enzymes and their reactions for each of the 6 classes of enzymes. (You should be able to find all or most of these in your book) Label an individual page with one of each of the names of the 6 classes of enzymes. On each page for that particular class of enzymes, ...
End-product control of enzymes of branched
... In streptomycetes, the branched-chain amino acids leucine, isoleucine and valine may serve as precursors for commercially important polyketides, and it is of interest to investigate whether the availability of these amino acids affects the production of the secondary metabolites derived from them. T ...
... In streptomycetes, the branched-chain amino acids leucine, isoleucine and valine may serve as precursors for commercially important polyketides, and it is of interest to investigate whether the availability of these amino acids affects the production of the secondary metabolites derived from them. T ...
1 Acids and Bases
... Identifying Arrhenius Acids and Bases How can we identify an acid or a base simply by looking at the chemical formula? Since we have defined acids and bases by the ions they release in solution, the first requirement is that they contain H or OH, respectively. However, there are plenty of compounds ...
... Identifying Arrhenius Acids and Bases How can we identify an acid or a base simply by looking at the chemical formula? Since we have defined acids and bases by the ions they release in solution, the first requirement is that they contain H or OH, respectively. However, there are plenty of compounds ...
Effect of Alanine-293 Replacement on the Activity, ATP Binding, and
... aminoacylation activity of LeuRS than any of the other substitutions A293D, A293R, A293G, A293I, A293Y and A293F. 293A is only involved in the binding of ATP, and all amino acid substitutions above caused stronger binding of ATP. Moreover, the negative charge at this site, induced by mutation A293D, ...
... aminoacylation activity of LeuRS than any of the other substitutions A293D, A293R, A293G, A293I, A293Y and A293F. 293A is only involved in the binding of ATP, and all amino acid substitutions above caused stronger binding of ATP. Moreover, the negative charge at this site, induced by mutation A293D, ...
Carbon isotope analysis of bulk keratin and single amino acids from
... different geographical locations,23,24 and on different diets within the same population.10,25,26 A number of animalfeeding studies have also been conducted.15–17 O’Connell and Hedges found that the hair of vegans was significantly depleted in 15N compared with that of omnivores and ovolacto vegetar ...
... different geographical locations,23,24 and on different diets within the same population.10,25,26 A number of animalfeeding studies have also been conducted.15–17 O’Connell and Hedges found that the hair of vegans was significantly depleted in 15N compared with that of omnivores and ovolacto vegetar ...
Nutritional Aspects of Inborn Errors of Metabolism
... growth period and the first two years of life, the human brain grows at an impressive rate. This brain growth spurt period (1) is associated with a very high rate of protein synthesis that makes the central nervous system vulnérable to any interférence with protein synthesis. Biochemical insuit at t ...
... growth period and the first two years of life, the human brain grows at an impressive rate. This brain growth spurt period (1) is associated with a very high rate of protein synthesis that makes the central nervous system vulnérable to any interférence with protein synthesis. Biochemical insuit at t ...
Bil 255 – CMB
... derivation of equation occurs at a time when the rate of formation of ES complex is equal to rate of destruction (break down), – i.e., at equilibrium, when [S] >>>> [E] so that total E is bound in ES complex – as a 1st order reaction enzyme catalyzed reaction ...
... derivation of equation occurs at a time when the rate of formation of ES complex is equal to rate of destruction (break down), – i.e., at equilibrium, when [S] >>>> [E] so that total E is bound in ES complex – as a 1st order reaction enzyme catalyzed reaction ...
Biochemistry - Textbooks Online
... Functions The hydrolytic enzymes of lysosome completely destroy the foreign materials like bacteria. They also serve to digest cell components after cell death. Inside the macrophages these lysosomes combine with vecuole which has engulfed the foreign particles and form phagolysosomes. Inside these ...
... Functions The hydrolytic enzymes of lysosome completely destroy the foreign materials like bacteria. They also serve to digest cell components after cell death. Inside the macrophages these lysosomes combine with vecuole which has engulfed the foreign particles and form phagolysosomes. Inside these ...
22: Peptides, Proteins, and α
... peptide because they cleave different C-terminal amino acids at different rates. As a result, C-terminal amino acids of shortened chains formed during the analysis procedure may cleave more rapidly than those of the original polypeptide. This can quickly complicate the reaction mixture with a variet ...
... peptide because they cleave different C-terminal amino acids at different rates. As a result, C-terminal amino acids of shortened chains formed during the analysis procedure may cleave more rapidly than those of the original polypeptide. This can quickly complicate the reaction mixture with a variet ...
Citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle – also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or the Krebs cycle – is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest established components of cellular metabolism and may have originated abiogenically.The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from citric acid (a type of tricarboxylic acid) that is consumed and then regenerated by this sequence of reactions to complete the cycle. In addition, the cycle consumes acetate (in the form of acetyl-CoA) and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and produces carbon dioxide as a waste byproduct. The NADH generated by the TCA cycle is fed into the oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport) pathway. The net result of these two closely linked pathways is the oxidation of nutrients to produce usable chemical energy in the form of ATP.In eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion. In prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria which lack mitochondria, the TCA reaction sequence is performed in the cytosol with the proton gradient for ATP production being across the cell's surface (plasma membrane) rather than the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.