A Diurnal Component to the Variation in Sieve Tube Amino Acid
... 16 amino acids in wheat (Triticum aestivum) sieve tube (ST) samples as small as 2 nL collected by severing the stylets of feeding aphids. The sensitivity of the method was sufficient to determine a quantitative amino acid profile of individual STs without the need to bulk samples to produce larger v ...
... 16 amino acids in wheat (Triticum aestivum) sieve tube (ST) samples as small as 2 nL collected by severing the stylets of feeding aphids. The sensitivity of the method was sufficient to determine a quantitative amino acid profile of individual STs without the need to bulk samples to produce larger v ...
Free Amino Acids Content of Honeys from Poland Katarzyna
... of honey. A specific relation between the amount of this ...
... of honey. A specific relation between the amount of this ...
Received June 19, 1964.
... 275 mg fresh weight for cocklebur and 225 mg for bean tissues) were added to 125 ml Erlenmeyer flasks .containing 5.0 ml 0.01 M phosphate buffer at pH 5.8. These flasks had a 1.5 cm diameter by 2.5 cm long well glued to the inside wall about 3 cm above the bottom. To this well 1.0 ml 3 % KOH was add ...
... 275 mg fresh weight for cocklebur and 225 mg for bean tissues) were added to 125 ml Erlenmeyer flasks .containing 5.0 ml 0.01 M phosphate buffer at pH 5.8. These flasks had a 1.5 cm diameter by 2.5 cm long well glued to the inside wall about 3 cm above the bottom. To this well 1.0 ml 3 % KOH was add ...
Genetic Analysis of Amino Acid Accumulation in
... level of Lys ketoglutarate reductase- saccaropine dehydrogenase is an important factor responsible for the high level of free Lys in mature endosperm. Damerval and Le Guilloux (1998) found that acetohydroxyacid synthase, the enzyme catalyzing the first common step in the synthesis of branched amino ...
... level of Lys ketoglutarate reductase- saccaropine dehydrogenase is an important factor responsible for the high level of free Lys in mature endosperm. Damerval and Le Guilloux (1998) found that acetohydroxyacid synthase, the enzyme catalyzing the first common step in the synthesis of branched amino ...
Biochemical Journal
... with MtIPMS and secondary-structure prediction, LiCMS appears to be composed of an N-terminal catalytic domain (residues 1– 330) and a C-terminal regulatory domain (residues 390–516), connected together by a linker region of approx. 60 amino-acid residues. Although the catalytic reactions catalysed ...
... with MtIPMS and secondary-structure prediction, LiCMS appears to be composed of an N-terminal catalytic domain (residues 1– 330) and a C-terminal regulatory domain (residues 390–516), connected together by a linker region of approx. 60 amino-acid residues. Although the catalytic reactions catalysed ...
Mechanism of citric acid accumulation by Aspergillus niger in solid
... Measurements of intracellular concentrations of products of certain enzymes and adenine nucleotides were conducted in order to assess the in vivo catalytic function of the enzymes of interest. It was concluded that internal accumulation of citrate or oxalate is an immediate cause of its excretion. S ...
... Measurements of intracellular concentrations of products of certain enzymes and adenine nucleotides were conducted in order to assess the in vivo catalytic function of the enzymes of interest. It was concluded that internal accumulation of citrate or oxalate is an immediate cause of its excretion. S ...
Past Exam Questions - Intermediate School Biology
... 42. Name a compound to which pyruvic acid may be converted, in the absence of oxygen. Lactic acid or ethanol + CO2 43. In aerobic respiration, the product of the first stage moves to the mitochondrion. Outline subsequent events in the total breakdown of this product. (Begins with) acetyl co-enzyme A ...
... 42. Name a compound to which pyruvic acid may be converted, in the absence of oxygen. Lactic acid or ethanol + CO2 43. In aerobic respiration, the product of the first stage moves to the mitochondrion. Outline subsequent events in the total breakdown of this product. (Begins with) acetyl co-enzyme A ...
Glucose Polyester Biosynthesis. Purification and
... the formation of diacyl-Glc from 1-O-[1-14C-isobutyryl]-bGlc. Reactions were performed in a 15-mL solution containing 50 mm HEPES-NaOH, pH 7.5, 1 mm 1-O-[1-14Cisobutyryl]-b-d-Glc (105 cpm), and an appropriate amount of protein obtained at different purification steps (approximately 30 mg–50 ng). All ...
... the formation of diacyl-Glc from 1-O-[1-14C-isobutyryl]-bGlc. Reactions were performed in a 15-mL solution containing 50 mm HEPES-NaOH, pH 7.5, 1 mm 1-O-[1-14Cisobutyryl]-b-d-Glc (105 cpm), and an appropriate amount of protein obtained at different purification steps (approximately 30 mg–50 ng). All ...
추가8
... Energy transforming pathways of carbohydrate metabolism include glycolysis, glycogenesis, glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis, and pentose phosphate pathway From McKee and McKee, Biochemistry, International Fifth Edition, © 2012 by Oxford University Press ...
... Energy transforming pathways of carbohydrate metabolism include glycolysis, glycogenesis, glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis, and pentose phosphate pathway From McKee and McKee, Biochemistry, International Fifth Edition, © 2012 by Oxford University Press ...
Effect of low glycogen on ... metabolism in human muscle during ...
... (AMP deaminase) during the contraction. The larger increases in ADP and AMP during LG exercise are considered necessary to activate phosphofructokinase, the TCA cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation under conditions in which glycolysis does not provide adequate substrate for formation of acetyl CoA a ...
... (AMP deaminase) during the contraction. The larger increases in ADP and AMP during LG exercise are considered necessary to activate phosphofructokinase, the TCA cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation under conditions in which glycolysis does not provide adequate substrate for formation of acetyl CoA a ...
Inhibitors are structural analogs of true substrate
... enzyme of tricarboxylic acid cycle participates in reaction of substrate phosphorylation? In a patient are manifested symptoms of intoxication with arsenic compounds. What metabolic process is damaged taking into account that arsen containing substances inactivate lipoic acid? ...
... enzyme of tricarboxylic acid cycle participates in reaction of substrate phosphorylation? In a patient are manifested symptoms of intoxication with arsenic compounds. What metabolic process is damaged taking into account that arsen containing substances inactivate lipoic acid? ...
Chapter 7 - Metabolism
... a. energy, fatty acids b. glucose, acetyl CoA c. oxygen, lactate d. glycogen, glucose Copyright © 2011, Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings. ...
... a. energy, fatty acids b. glucose, acetyl CoA c. oxygen, lactate d. glycogen, glucose Copyright © 2011, Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings. ...
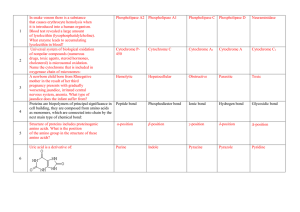
Natural antioxidants
... O Lower, but significant amounts it is possible to found in some vegetables, lower amount in fruits Rutin and its aglycone quercetin are most significant flavonoids from vegetables ...
... O Lower, but significant amounts it is possible to found in some vegetables, lower amount in fruits Rutin and its aglycone quercetin are most significant flavonoids from vegetables ...
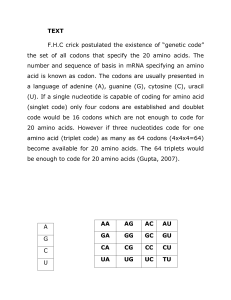
TEXT F.H.C crick postulated the existence of “genetic code” the set
... will prove the relationship between codon and radioactive amino acid. For example, 20 samples of a mixture of all 20 amino acids may be taken and in each sample one amino acid is made radioactive in such a manner that each and every amino acid is made radioactive in one sample or the other, and no t ...
... will prove the relationship between codon and radioactive amino acid. For example, 20 samples of a mixture of all 20 amino acids may be taken and in each sample one amino acid is made radioactive in such a manner that each and every amino acid is made radioactive in one sample or the other, and no t ...
Crystal structure of ATP sulfurylase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae
... (S16±S20), but with a 2-3-1-4-5 topology. This structural classi®cation reveals its close relationship to the superfamily of P-loop-containing nucleotide triphosphate hydrolases and the family of nucleotide kinases, indicating a common evolutionary origin with APS kinase. Typical members of this fam ...
... (S16±S20), but with a 2-3-1-4-5 topology. This structural classi®cation reveals its close relationship to the superfamily of P-loop-containing nucleotide triphosphate hydrolases and the family of nucleotide kinases, indicating a common evolutionary origin with APS kinase. Typical members of this fam ...
Hyperammonemia in review: pathophysiology, diagnosis, and
... the breakdown and catabolism of dietary and bodily proteins, respectively. In healthy individuals, amino acids that are not needed for protein synthesis are metabolized in various chemical pathways, with the rest of the nitrogen waste being converted to urea. Ammonia is important for normal animal a ...
... the breakdown and catabolism of dietary and bodily proteins, respectively. In healthy individuals, amino acids that are not needed for protein synthesis are metabolized in various chemical pathways, with the rest of the nitrogen waste being converted to urea. Ammonia is important for normal animal a ...
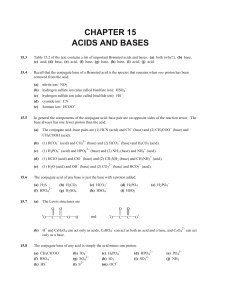
8.4 Weak Acids and Bases, Continued
... • The Brønsted–Lowry definitions of acids and bases imply that a proton is transferred in an acidic or basic solution. • Water can act as an acid or base by donating or accepting a proton. For example, when a hydrochloric acid solution is prepared, water accepts a proton, and is acting as a base. ...
... • The Brønsted–Lowry definitions of acids and bases imply that a proton is transferred in an acidic or basic solution. • Water can act as an acid or base by donating or accepting a proton. For example, when a hydrochloric acid solution is prepared, water accepts a proton, and is acting as a base. ...
a formulation containing silk protein
... total mean NAD/NADH ratios compared to ethanol control at 1 hour post treatment, significant increase in ADH values compared to control at 0.5 hour post treatment and exhibited significant decrease in blood alcohol level at 1 hour post treatment. Similarly, serine showed significant decrease in NAD/ ...
... total mean NAD/NADH ratios compared to ethanol control at 1 hour post treatment, significant increase in ADH values compared to control at 0.5 hour post treatment and exhibited significant decrease in blood alcohol level at 1 hour post treatment. Similarly, serine showed significant decrease in NAD/ ...
Lecture of Enzymes.
... ■ The activities of metabolic pathways in cells are regulated by control of the activities of certain enzymes. ■ In feedback inhibition, the end product of a pathway inhibits the first enzyme of that pathway. ■ The activity of allosteric enzymes is adjusted by reversible binding of a specific modula ...
... ■ The activities of metabolic pathways in cells are regulated by control of the activities of certain enzymes. ■ In feedback inhibition, the end product of a pathway inhibits the first enzyme of that pathway. ■ The activity of allosteric enzymes is adjusted by reversible binding of a specific modula ...
Methylobacterium extorquens AM1
... intracellular metabolites by LC-MS. Sampling for metabolites was performed at three different timepoints during growth with 13C methanol and naturally labeled succinate. The first sample was collected in the middle of the first exponential growth phase, and the second sample was harvested just at th ...
... intracellular metabolites by LC-MS. Sampling for metabolites was performed at three different timepoints during growth with 13C methanol and naturally labeled succinate. The first sample was collected in the middle of the first exponential growth phase, and the second sample was harvested just at th ...
Lactic acid bacteria as a cell factory: rerouting of carbon metabolism
... sugar and at the level of sugar transport. This phosphocarrier protein contains two residues that are target for phosphorylation. A histidine residue in the N-terminal part of the protein, that is a target for enzyme I mediated phosphorylation and the resulting HPr-(His-P) primarily plays a role in ...
... sugar and at the level of sugar transport. This phosphocarrier protein contains two residues that are target for phosphorylation. A histidine residue in the N-terminal part of the protein, that is a target for enzyme I mediated phosphorylation and the resulting HPr-(His-P) primarily plays a role in ...
CHANNELING OF SUBSTRATES AND INTERMEDIATES IN
... regulated by allosteric communication between the active sites. Does the tunneling event also synchronize the enzymatic reactions occurring at the distinct active sites? What is the mechanism of diffusion through a protein tunnel? Is active transport employed? It is not clear in most cases whether t ...
... regulated by allosteric communication between the active sites. Does the tunneling event also synchronize the enzymatic reactions occurring at the distinct active sites? What is the mechanism of diffusion through a protein tunnel? Is active transport employed? It is not clear in most cases whether t ...
chapter 15 acids and bases
... Oftentimes, assumptions such as these are valid if K is very small. A very small value of K means that a very small amount of reactants go to products. Hence, x is small. If we did not make this assumption, we would have to solve a quadratic equation. ...
... Oftentimes, assumptions such as these are valid if K is very small. A very small value of K means that a very small amount of reactants go to products. Hence, x is small. If we did not make this assumption, we would have to solve a quadratic equation. ...
Citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle – also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or the Krebs cycle – is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest established components of cellular metabolism and may have originated abiogenically.The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from citric acid (a type of tricarboxylic acid) that is consumed and then regenerated by this sequence of reactions to complete the cycle. In addition, the cycle consumes acetate (in the form of acetyl-CoA) and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and produces carbon dioxide as a waste byproduct. The NADH generated by the TCA cycle is fed into the oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport) pathway. The net result of these two closely linked pathways is the oxidation of nutrients to produce usable chemical energy in the form of ATP.In eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion. In prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria which lack mitochondria, the TCA reaction sequence is performed in the cytosol with the proton gradient for ATP production being across the cell's surface (plasma membrane) rather than the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.