Proteins
... • 8. Regulation: Certain proteins not only control the expression of genes, but also control when gene expression takes place. • Proteins are divided into two types: • Fibrous proteins • Globular proteins ...
... • 8. Regulation: Certain proteins not only control the expression of genes, but also control when gene expression takes place. • Proteins are divided into two types: • Fibrous proteins • Globular proteins ...
Venice, Sep 2010 - Theoretical Biochemistry Group
... control and DNA structure in the living cell. ...
... control and DNA structure in the living cell. ...
Structure of mitochondrial ADP/ATP carrier in complex with
... ADP is imported into the matrix. The exchange is accomplished by a single protein, the ADP/ATP carrier. Here we have solved the bovine carrier structure at a resolution of 2.2 Å by X-ray crystallography in complex with an inhibitor, carboxyatractyloside. Six a-helices form a compact transmembrane d ...
... ADP is imported into the matrix. The exchange is accomplished by a single protein, the ADP/ATP carrier. Here we have solved the bovine carrier structure at a resolution of 2.2 Å by X-ray crystallography in complex with an inhibitor, carboxyatractyloside. Six a-helices form a compact transmembrane d ...
Document
... keep cellular respiration going? • Your body will continue by using glycolysis and fermentation ...
... keep cellular respiration going? • Your body will continue by using glycolysis and fermentation ...
a review on biochemical mechanism of fatty acids synthesis and oil
... A four possible pathways for the biosynthesis of acetyl-CoA in plastids was proposed (Rawsthorne, 2002). (1) Acetyl-CoA synthesis from free acetate after enzymatic reaction with Acetyl-CoA Synthetase (ACS). This is an ATP-dependent reaction; several authors measured the ACS activities in the chlorop ...
... A four possible pathways for the biosynthesis of acetyl-CoA in plastids was proposed (Rawsthorne, 2002). (1) Acetyl-CoA synthesis from free acetate after enzymatic reaction with Acetyl-CoA Synthetase (ACS). This is an ATP-dependent reaction; several authors measured the ACS activities in the chlorop ...
Haemoglobin.
... four nitrogens in the center of the ring, which all lie in one plane. 3) The Globin of each Hb mole consist of a tetramers with two polypeptide chains of one kind & two of another . Globin helps heam to keep iron in ferrous state & combine loosely & reversibly with O2. In ...
... four nitrogens in the center of the ring, which all lie in one plane. 3) The Globin of each Hb mole consist of a tetramers with two polypeptide chains of one kind & two of another . Globin helps heam to keep iron in ferrous state & combine loosely & reversibly with O2. In ...
Journal of Biological Chemistry
... upon amino acid incorporation into protein of the liver ribosome system (Table II) just as effectively as it does the decrease in hepatic ATP concentration induced by the same analogue (3). These results tend to implicate cellular BTP deficiency as being important in the inhibition of protein synthe ...
... upon amino acid incorporation into protein of the liver ribosome system (Table II) just as effectively as it does the decrease in hepatic ATP concentration induced by the same analogue (3). These results tend to implicate cellular BTP deficiency as being important in the inhibition of protein synthe ...
MCB Lecture 2 – Protein Metabolism
... o It is an upper respiratory tract illness that causes significant neck swelling. o It inactivates eEF2 (which causes a stop of translocation) What is Ricin? What does it do? o Ricin is a toxic protein that inactivates the 28S Subunit, which stops peptidyl transferase activity. ...
... o It is an upper respiratory tract illness that causes significant neck swelling. o It inactivates eEF2 (which causes a stop of translocation) What is Ricin? What does it do? o Ricin is a toxic protein that inactivates the 28S Subunit, which stops peptidyl transferase activity. ...
Neonatal Glucose Homeostasis
... maternal supply and placental transfer of glucose, amino acids, free fatty acids, ketones, and glycerol for energy needs. Normal lower limit of fetal glucose concentration remains around 3 mmol/L (54 mg/dL) over most of gestation, particularly after 20 weeks Enzymes for gluconeogenesis are present b ...
... maternal supply and placental transfer of glucose, amino acids, free fatty acids, ketones, and glycerol for energy needs. Normal lower limit of fetal glucose concentration remains around 3 mmol/L (54 mg/dL) over most of gestation, particularly after 20 weeks Enzymes for gluconeogenesis are present b ...
polymers - wellswaysciences
... © Pearson Education Ltd 2009 This document may have been altered from the original ...
... © Pearson Education Ltd 2009 This document may have been altered from the original ...
Ninety-nine Point Nine Percent of the Time, Nature Uses the... Acids, and We Don’t Know Exactly Why
... code; the arrangement was merely the first to be stumbled across by evolution. Once it had been solidified, “any further changes would have been catastrophic (Freeland 2004, 87).” This assumption dominated conventional wisdom for several decades. Problematically, this assumption also predated—by sev ...
... code; the arrangement was merely the first to be stumbled across by evolution. Once it had been solidified, “any further changes would have been catastrophic (Freeland 2004, 87).” This assumption dominated conventional wisdom for several decades. Problematically, this assumption also predated—by sev ...
Hyaluronic Acid in Dermatology and Dermocosmetics
... extensive and damaging exposure to the sun. The changes that occur inside connective tissue also reduce the strength and elasticity of the skin: this process is known as elastosis. The way in which the effects of chronoageing and photoageing both accelerate the appearance of the signs of ageing is a ...
... extensive and damaging exposure to the sun. The changes that occur inside connective tissue also reduce the strength and elasticity of the skin: this process is known as elastosis. The way in which the effects of chronoageing and photoageing both accelerate the appearance of the signs of ageing is a ...
Ch 6 LIPID METABOLISM - FORMATTED - NSDL
... transport chain to ensure complete oxidation to CO2 and H2O and concomitant production of ATP. If required, acetyl-CoA can also be diverted to biosynthesis. When fatty acid oxidation exceeds normal levels ketogenesis takes place, a process on which we will elaborate in section 3 of this chapter. ...
... transport chain to ensure complete oxidation to CO2 and H2O and concomitant production of ATP. If required, acetyl-CoA can also be diverted to biosynthesis. When fatty acid oxidation exceeds normal levels ketogenesis takes place, a process on which we will elaborate in section 3 of this chapter. ...
Regulation of carbohydrate metabolism
... role of Fructose 2,6-P in the regulation of glycolysis and gluconeogenesis. 2. 3 key sites for the regulation of gluconeogenesis (their activation). 3. The signal pathway for the activation of glycogen degradation by ...
... role of Fructose 2,6-P in the regulation of glycolysis and gluconeogenesis. 2. 3 key sites for the regulation of gluconeogenesis (their activation). 3. The signal pathway for the activation of glycogen degradation by ...
Załącznik nr 3 do Zarządzenia Rektora PUM…………………….. z
... of DNA and RNA (primary and secondary) and chromatin structure knows functions of genome, transcriptome and proteome as well as basic methods applied to investigate these; describes processes of DNA replication, repair and recombination, processes of transcription and translation also the processes ...
... of DNA and RNA (primary and secondary) and chromatin structure knows functions of genome, transcriptome and proteome as well as basic methods applied to investigate these; describes processes of DNA replication, repair and recombination, processes of transcription and translation also the processes ...
Anaerobic Glucose and Serine Metabolism in Staphy
... at 12000 g for 15 min on a Sorvall RC-5 Superspeed centrifuge, washed twice with 02-free 67 mM-Na+/K-lphosphate buffer pH 6.8 (referred to as phosphate buffer) and resuspended to the required concentration in the same buffer. Bacterial suspensions used in anaerobic experiments were held under 0,-fre ...
... at 12000 g for 15 min on a Sorvall RC-5 Superspeed centrifuge, washed twice with 02-free 67 mM-Na+/K-lphosphate buffer pH 6.8 (referred to as phosphate buffer) and resuspended to the required concentration in the same buffer. Bacterial suspensions used in anaerobic experiments were held under 0,-fre ...
Mitochondrial metabolite transport
... now, 22 MC subfamilies, which are well conserved throughout evolution, have been functionally characterized, mainly by transport assays upon heterologous gene expression, purification and reconstitution into liposomes. Given the significant sequence conservation, it is thought that all MCs use the s ...
... now, 22 MC subfamilies, which are well conserved throughout evolution, have been functionally characterized, mainly by transport assays upon heterologous gene expression, purification and reconstitution into liposomes. Given the significant sequence conservation, it is thought that all MCs use the s ...
EXERCISE 7 Cellular Respiration
... Name 2 molecules that are used as the final electron acceptor if oxygen is not available. State the products formed in each case. ...
... Name 2 molecules that are used as the final electron acceptor if oxygen is not available. State the products formed in each case. ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Mediterranean Emergency Medicine
... Poorly absorbed in the presence of ethanol. J Nutr 1965;85:297-304. ...
... Poorly absorbed in the presence of ethanol. J Nutr 1965;85:297-304. ...
Major roles of isocitrate lyase and malate synthase in
... carbon from C2 compounds, allowing micro-organisms to replenish the pool of TCA cycle intermediates necessary for gluconeogenesis and other biosynthetic processes. The net result of the glyoxylate cycle is the production of malate and succinate from two molecules of acetyl-CoA derived from acetate o ...
... carbon from C2 compounds, allowing micro-organisms to replenish the pool of TCA cycle intermediates necessary for gluconeogenesis and other biosynthetic processes. The net result of the glyoxylate cycle is the production of malate and succinate from two molecules of acetyl-CoA derived from acetate o ...
substances that target tumor metabolism
... Normally, lipid and muscle protein stores decrease after fasting for example, when one needs to synthesize nutriments: ketone bodies and glucose by neoglucogenesis. However, tumors utilize such stores for supporting an elevated very special glycolysis, with lactate production and release, a process ...
... Normally, lipid and muscle protein stores decrease after fasting for example, when one needs to synthesize nutriments: ketone bodies and glucose by neoglucogenesis. However, tumors utilize such stores for supporting an elevated very special glycolysis, with lactate production and release, a process ...
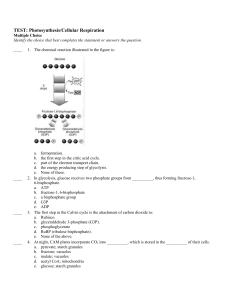
Use to make Test Corrections (Answer in complete sentence +10 pts
... During the reactions of photosynthesis, __________ is reduced and __________ is oxidized. a. CO2; H2O b. CO2; C6H12O6 c. H2O; C6H12O6 d. O2; H2O e. O2; C6H12O6 12 H2O + 12 NADP+ + 18 ADP + Pi 6 O2 + 12 NADPH + 18 ATP summarizes the __________ reactions of photosynthesis. a. light-independent b. CA ...
... During the reactions of photosynthesis, __________ is reduced and __________ is oxidized. a. CO2; H2O b. CO2; C6H12O6 c. H2O; C6H12O6 d. O2; H2O e. O2; C6H12O6 12 H2O + 12 NADP+ + 18 ADP + Pi 6 O2 + 12 NADPH + 18 ATP summarizes the __________ reactions of photosynthesis. a. light-independent b. CA ...
Citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle – also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or the Krebs cycle – is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest established components of cellular metabolism and may have originated abiogenically.The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from citric acid (a type of tricarboxylic acid) that is consumed and then regenerated by this sequence of reactions to complete the cycle. In addition, the cycle consumes acetate (in the form of acetyl-CoA) and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and produces carbon dioxide as a waste byproduct. The NADH generated by the TCA cycle is fed into the oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport) pathway. The net result of these two closely linked pathways is the oxidation of nutrients to produce usable chemical energy in the form of ATP.In eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion. In prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria which lack mitochondria, the TCA reaction sequence is performed in the cytosol with the proton gradient for ATP production being across the cell's surface (plasma membrane) rather than the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.