Biomolecules
... form a major portion of our food. Honey has been used for a long time as an instant source of energy by ‘Vaids’ in ayurvedic system of medicine. Carbohydrates are used as storage molecules as starch in plants and glycogen in animals. Cell wall of bacteria and plants is made up of cellulose. We build ...
... form a major portion of our food. Honey has been used for a long time as an instant source of energy by ‘Vaids’ in ayurvedic system of medicine. Carbohydrates are used as storage molecules as starch in plants and glycogen in animals. Cell wall of bacteria and plants is made up of cellulose. We build ...
Probing peroxisomal β-oxidation and the labelling of acetyl
... which very-long-chain n-fatty acids are partially shortened to long-chain acyl-CoAs which are transferred to the mitochondria for complete β-oxidation [1]. Based on the relative activities of enzymes of mitochondrial compared with peroxisomal β-oxidation, the latter appears to contribute only a smal ...
... which very-long-chain n-fatty acids are partially shortened to long-chain acyl-CoAs which are transferred to the mitochondria for complete β-oxidation [1]. Based on the relative activities of enzymes of mitochondrial compared with peroxisomal β-oxidation, the latter appears to contribute only a smal ...
as a PDF
... fall far short of those observed. Moreover, if any incorporation of activity into carbon dioxide occurred by mechanisms other than recycling, even less recycling could have taken place. It therefore appears impossible that the radioactivity of carboxyls 2 and 3 is due solely to recycling. A similar ...
... fall far short of those observed. Moreover, if any incorporation of activity into carbon dioxide occurred by mechanisms other than recycling, even less recycling could have taken place. It therefore appears impossible that the radioactivity of carboxyls 2 and 3 is due solely to recycling. A similar ...
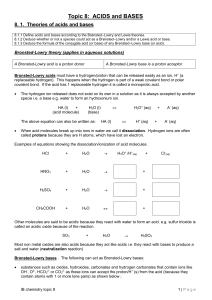
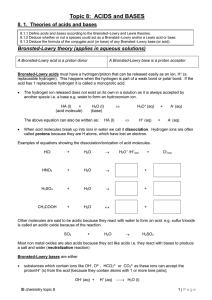
Topic 8: ACIDS and BASES
... molecules containing positive centres (mostly organic molecules) as a result of polar bonds within the molecule e.g. C in CO2 or in halogenalkanes and S in SO2. All Bronsted-Lowry acids are Lewis acids but not vice versa; Although strictly speaking dissociation needs to occur first before a Br ...
... molecules containing positive centres (mostly organic molecules) as a result of polar bonds within the molecule e.g. C in CO2 or in halogenalkanes and S in SO2. All Bronsted-Lowry acids are Lewis acids but not vice versa; Although strictly speaking dissociation needs to occur first before a Br ...
Topic 3 The chemistry of life
... the reactions may occur faster. Enzymes are organic catalysts. They are proteins. The amino acids that make up these enzymes allow a tertiary and/or quaternary structure. Because each enzyme has a specific amino acid sequence, enzymes have a specific three-dimensional shape. The molecule an enzy ...
... the reactions may occur faster. Enzymes are organic catalysts. They are proteins. The amino acids that make up these enzymes allow a tertiary and/or quaternary structure. Because each enzyme has a specific amino acid sequence, enzymes have a specific three-dimensional shape. The molecule an enzy ...
Structural Biochemistry/Proteins/Synthesis
... Peptide synthesis can be specific; meaning specific/desired products can be formed. To make unique products and to prevent side reactions, protecting groups such as tert-butyloxycarbonyl (t-Boc) are used. T-Boc is used in the first step of the formation of simple peptides. This protecting group, in ...
... Peptide synthesis can be specific; meaning specific/desired products can be formed. To make unique products and to prevent side reactions, protecting groups such as tert-butyloxycarbonyl (t-Boc) are used. T-Boc is used in the first step of the formation of simple peptides. This protecting group, in ...
Biological monomers and polymers (1)
... There are thousands of enzyme-catalyzed reactions in a cell. If the biochemical reactions involved in this process were reversible, we would convert our macromolecules back to metabolites if we stop eating even for a short period of time. To prevent this from happening, our metabolism is organized i ...
... There are thousands of enzyme-catalyzed reactions in a cell. If the biochemical reactions involved in this process were reversible, we would convert our macromolecules back to metabolites if we stop eating even for a short period of time. To prevent this from happening, our metabolism is organized i ...
Quinolizidine Alkaloids
... responsible for the toxic properties associated with lupins, are characterized by a quinolizidine skeleton (figure below, fused piperideine rings ) ,This bicyclic ring system is closely related to the ornithine-derived pyrrolizidine system, but is formed from two molecules of lysine. ...
... responsible for the toxic properties associated with lupins, are characterized by a quinolizidine skeleton (figure below, fused piperideine rings ) ,This bicyclic ring system is closely related to the ornithine-derived pyrrolizidine system, but is formed from two molecules of lysine. ...
Chapter 10. Delivering Oxygen.
... When GB is skateboarding or mountain climbing, GB.’s muscles need more ATP and to make ATP in the mitochondria O2 is needed. There is a sensor for O2 in the carotid artery. When O2 in the blood gets low and CO2 produced from metabolism gets high, a signal gets sent from chemical sensors in the carot ...
... When GB is skateboarding or mountain climbing, GB.’s muscles need more ATP and to make ATP in the mitochondria O2 is needed. There is a sensor for O2 in the carotid artery. When O2 in the blood gets low and CO2 produced from metabolism gets high, a signal gets sent from chemical sensors in the carot ...
intermediate chemistry may 2011 marking scheme
... which are at 120o to each other and overlap of these orbitals with each other and the 1s orbital of H forms the sigma bonding of the molecule (2). The remaining 2p orbital on each C, having a single electron, interact together to form molecular orbitals in which the 6 electrons are shared (1) (stude ...
... which are at 120o to each other and overlap of these orbitals with each other and the 1s orbital of H forms the sigma bonding of the molecule (2). The remaining 2p orbital on each C, having a single electron, interact together to form molecular orbitals in which the 6 electrons are shared (1) (stude ...
enzyme substrate
... Most of the ATP made by the cell is used in the production of new cellular components Amphibolic pathways bridge the reactions that lead to the breakdown and synthesis of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleus. These pathways allow for the simultaneous reactions to occur in which the breakdown ...
... Most of the ATP made by the cell is used in the production of new cellular components Amphibolic pathways bridge the reactions that lead to the breakdown and synthesis of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleus. These pathways allow for the simultaneous reactions to occur in which the breakdown ...
Scheme I Supplementary Material Available: Detailed
... as well as the importance of the approximately 20 amino acids common in proteins has stimulated recent work on asymmetric synthesis of such compounds.1-3 Their structural analogues, a-hydrazino acids (l),are effective inhibitors of certain amino acid metabolizing enzymes, especially ammonia lyases4 ...
... as well as the importance of the approximately 20 amino acids common in proteins has stimulated recent work on asymmetric synthesis of such compounds.1-3 Their structural analogues, a-hydrazino acids (l),are effective inhibitors of certain amino acid metabolizing enzymes, especially ammonia lyases4 ...
The Reactions of Diazonium Compounds with Amino Acids and
... in the normal manner, gave a product with an unchanged As/N quotient of 0-842, but the other, kept at 370 for the same time, gave a product with a diminished As/N quotient of 0-765. A product obtained from bovine-plasma albumin, having an initial As/N quotient of 0 774, was also dissolved in NaHCO2. ...
... in the normal manner, gave a product with an unchanged As/N quotient of 0-842, but the other, kept at 370 for the same time, gave a product with a diminished As/N quotient of 0-765. A product obtained from bovine-plasma albumin, having an initial As/N quotient of 0 774, was also dissolved in NaHCO2. ...
lec 7 Metabolism of purine nucleotides
... AMP or GMP is metabolized to give hypoxanthine which is then converted into xanthine and finally into uric acid as in the next slide. Most of uric acid is excreted by the kidney. The remaining uric acid travels through the intestines, where bacteria help break it down. Normally these actions keep th ...
... AMP or GMP is metabolized to give hypoxanthine which is then converted into xanthine and finally into uric acid as in the next slide. Most of uric acid is excreted by the kidney. The remaining uric acid travels through the intestines, where bacteria help break it down. Normally these actions keep th ...
ATP-binding site as a further application of neural network
... not show a high propensity for His, which is observed in ATP-binding sites. This anomaly i. e. a similarity with Arg and Lys and difference from His residues may be either due to different oxidation states of His in the two cases or due to structural requirements of DNA, which may be absent in case ...
... not show a high propensity for His, which is observed in ATP-binding sites. This anomaly i. e. a similarity with Arg and Lys and difference from His residues may be either due to different oxidation states of His in the two cases or due to structural requirements of DNA, which may be absent in case ...
B1 - BBS Biology Revision
... a) Protein molecules are made up of long chains of amino acids. These long chains are folded to produce a specific shape that enables other molecules to fit into the protein. Proteins act as: ■ structural components of tissues such as muscles ■ hormones, ■ antibodies ■ catalysts. b) Catalysts increa ...
... a) Protein molecules are made up of long chains of amino acids. These long chains are folded to produce a specific shape that enables other molecules to fit into the protein. Proteins act as: ■ structural components of tissues such as muscles ■ hormones, ■ antibodies ■ catalysts. b) Catalysts increa ...
the incorporation of c from sodium acetate- 2
... of minced mouse brain taken from the day-old mouse. They found to their surprise that 14C from uniformly labelled glucose was incorporated into all the amino acids, both essential and non-essential for the mouse, except threonine and proline (Rafelson et al. 1951). Following up this discovery they s ...
... of minced mouse brain taken from the day-old mouse. They found to their surprise that 14C from uniformly labelled glucose was incorporated into all the amino acids, both essential and non-essential for the mouse, except threonine and proline (Rafelson et al. 1951). Following up this discovery they s ...
Chapter 3
... • _________ is an end point of glycolysis. • At normal body pH ______, lactic acid will rapidly dissociate to form lactate. • Therefore, the terms lactate and lactic acid are commonly used interchangeably. ...
... • _________ is an end point of glycolysis. • At normal body pH ______, lactic acid will rapidly dissociate to form lactate. • Therefore, the terms lactate and lactic acid are commonly used interchangeably. ...
Archive Microbiology
... of the pyruvate synthesis both in Anacystis nidulans and Azotobacter vinelandii (Table 2). The significance of this finding is not yet clear in the moment. In all other organisms tested, no significant activity was found for either the exchange or the synthesis reaction. The pyruvate dehydrogenase c ...
... of the pyruvate synthesis both in Anacystis nidulans and Azotobacter vinelandii (Table 2). The significance of this finding is not yet clear in the moment. In all other organisms tested, no significant activity was found for either the exchange or the synthesis reaction. The pyruvate dehydrogenase c ...
Citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle – also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or the Krebs cycle – is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest established components of cellular metabolism and may have originated abiogenically.The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from citric acid (a type of tricarboxylic acid) that is consumed and then regenerated by this sequence of reactions to complete the cycle. In addition, the cycle consumes acetate (in the form of acetyl-CoA) and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and produces carbon dioxide as a waste byproduct. The NADH generated by the TCA cycle is fed into the oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport) pathway. The net result of these two closely linked pathways is the oxidation of nutrients to produce usable chemical energy in the form of ATP.In eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion. In prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria which lack mitochondria, the TCA reaction sequence is performed in the cytosol with the proton gradient for ATP production being across the cell's surface (plasma membrane) rather than the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.