Article Lateral Gene Transfer and Gene
... 2007). However, to date, the presence of the sulfate activation pathway, ATP synthesis and the fate of acetyl-CoA in the M. balamuthi organelles have not been investigated. Here, we analyze the M. balamuthi genome sequence to identify the components of extended glycolysis and energy metabolism in th ...
... 2007). However, to date, the presence of the sulfate activation pathway, ATP synthesis and the fate of acetyl-CoA in the M. balamuthi organelles have not been investigated. Here, we analyze the M. balamuthi genome sequence to identify the components of extended glycolysis and energy metabolism in th ...
Determine the blood glucose level
... catalyzes the oxidation of -D glucose to gluconolactone. It is isolated from molds, which aIso contain the mutarotase enzyme which enhances the conversion of -D glucose into the ß-D glucose form. As shown in the reaction scheme below, stoichiometric amount of H202 is also formed in the reaction. W ...
... catalyzes the oxidation of -D glucose to gluconolactone. It is isolated from molds, which aIso contain the mutarotase enzyme which enhances the conversion of -D glucose into the ß-D glucose form. As shown in the reaction scheme below, stoichiometric amount of H202 is also formed in the reaction. W ...
Hydroxy carboxylic acids
... Maleic acid and fumaric acid can normally not be interconverted because rotation around a carbon carbon double bond is not energetically favourable. In the laboratory, conversion of the cis isomer into the trans isomer is possible by application of light and a small amount of bromine. Light converts ...
... Maleic acid and fumaric acid can normally not be interconverted because rotation around a carbon carbon double bond is not energetically favourable. In the laboratory, conversion of the cis isomer into the trans isomer is possible by application of light and a small amount of bromine. Light converts ...
1 - Free
... compound activates or inhibits the enzyme. 8. which lipoprotein contain the highest percentage of triaglycerols? 9. write with names the overall equation of the B-oxidation of octanoyl-CoA. 10. list the allosteric regulators of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Indicate whether the given compound acti ...
... compound activates or inhibits the enzyme. 8. which lipoprotein contain the highest percentage of triaglycerols? 9. write with names the overall equation of the B-oxidation of octanoyl-CoA. 10. list the allosteric regulators of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Indicate whether the given compound acti ...
FREE Sample Here
... dissociate. The association rate will be larger than the dissociation rate when complex formation is favorable. The energy that drives this process is referred to as ___________. (a) dissociation energy. ...
... dissociate. The association rate will be larger than the dissociation rate when complex formation is favorable. The energy that drives this process is referred to as ___________. (a) dissociation energy. ...
DIETARY FAT
... • There are no UL’s set for Total Fat, Fatty Acids and Cholesterol because there are insufficient data to use the model of risk assessment to set a UL for total fat, monounsaturated fatty acids, and n-6 and n3 polyunsaturated fatty acids ...
... • There are no UL’s set for Total Fat, Fatty Acids and Cholesterol because there are insufficient data to use the model of risk assessment to set a UL for total fat, monounsaturated fatty acids, and n-6 and n3 polyunsaturated fatty acids ...
Document
... Micelle Formation Complex of lipid materials soluble in water Contains bile salts, phospholipids & cholesterol Combines with 2-monoglycerides, free fatty acids ...
... Micelle Formation Complex of lipid materials soluble in water Contains bile salts, phospholipids & cholesterol Combines with 2-monoglycerides, free fatty acids ...
Part A: Amino Acids and Peptides
... • Parts of a large polypeptide chain will spontaneously organize into α-helices, βpleated sheets and sometimes other less common sub-structures. • These "sub-structures" will organize themselves into a specific 3D super-structure, which is mostly held together by non-covalent interactions like hydro ...
... • Parts of a large polypeptide chain will spontaneously organize into α-helices, βpleated sheets and sometimes other less common sub-structures. • These "sub-structures" will organize themselves into a specific 3D super-structure, which is mostly held together by non-covalent interactions like hydro ...
Chapter 14
... • Oxidative phosphorylation is the process by which NADH and QH2 are oxidized and ATP is formed Prentice Hall c2002 ...
... • Oxidative phosphorylation is the process by which NADH and QH2 are oxidized and ATP is formed Prentice Hall c2002 ...
Isomerisms
... The two carboxylic groups in cis—isomers are on the side so that it is easier to under dehydration to give acid anhydride. However, higher temperature is required to cause the bond between the carbon atoms for the trans—isomers to give the cis—isomers which can subsequently undergo dehydration. Th ...
... The two carboxylic groups in cis—isomers are on the side so that it is easier to under dehydration to give acid anhydride. However, higher temperature is required to cause the bond between the carbon atoms for the trans—isomers to give the cis—isomers which can subsequently undergo dehydration. Th ...
Chemical Properties of Amino Acids
... low pH – maybe 0 or 1) and calculate its net charge 4. Slowly move up in pH to the first ionizable group’s pKa and deprotonate it (reduce charge by 1) 5. Do this until each group is deprotonated. Now you have identified all charged forms and at which pH each transition occurs. 6. Identify the fo ...
... low pH – maybe 0 or 1) and calculate its net charge 4. Slowly move up in pH to the first ionizable group’s pKa and deprotonate it (reduce charge by 1) 5. Do this until each group is deprotonated. Now you have identified all charged forms and at which pH each transition occurs. 6. Identify the fo ...
2566 Part 1
... 7 - ATP - ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATE 8 - ATP - RESYNTHESIS OF ATP 9 - ATP / PC ALACTIC SYSTEM 10 - ATP / PC ALACTIC SYSTEM - THE COUPLED REACTION ...
... 7 - ATP - ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATE 8 - ATP - RESYNTHESIS OF ATP 9 - ATP / PC ALACTIC SYSTEM 10 - ATP / PC ALACTIC SYSTEM - THE COUPLED REACTION ...
Untitled
... The [H3O+] of any aqueous solution is a very important characteristic, and we often need to talk about it. It is inconvenient to talk about the concentration in units such as 4.50 x 10-12 M or numbers similar to this form. So scientist defined a new number called _____ to talk about the concentratio ...
... The [H3O+] of any aqueous solution is a very important characteristic, and we often need to talk about it. It is inconvenient to talk about the concentration in units such as 4.50 x 10-12 M or numbers similar to this form. So scientist defined a new number called _____ to talk about the concentratio ...
Chapter 13 Lecture Notes: Peptides, Proteins
... is so large that it dominates the interactions, making the side-chain hydrophobic. For this reason, tryptophan is put into the nonpolar class. 2) Polar Neutral Amino Acids Polar neutral amino acids have polar (hydrophilic) side-chains and their predominant forms have uncharged side-chains at physiol ...
... is so large that it dominates the interactions, making the side-chain hydrophobic. For this reason, tryptophan is put into the nonpolar class. 2) Polar Neutral Amino Acids Polar neutral amino acids have polar (hydrophilic) side-chains and their predominant forms have uncharged side-chains at physiol ...
High-resolution analysis of metabolic cycles in the intertidal mussel
... aspartate are fermented to produce succinate and alanine via the glucose-succinate and aspartate-succinate pathways, respectively (24). If the duration of hypoxia extends for days then succinate is further converted to propionate, which yields additional ATP and aids in acid-base balance via the pro ...
... aspartate are fermented to produce succinate and alanine via the glucose-succinate and aspartate-succinate pathways, respectively (24). If the duration of hypoxia extends for days then succinate is further converted to propionate, which yields additional ATP and aids in acid-base balance via the pro ...
Bio251 07 HW2 1-26-0..
... The Oxygen atom attracts electrons much more forcefully than does a Hydrogen atom. In this way, oxygen is a strongly electronegative atom. As a result the O-H bond is said to be polarized, such that one of the atoms has a partial negative charge, and the other a partial positive charge. Molecules, s ...
... The Oxygen atom attracts electrons much more forcefully than does a Hydrogen atom. In this way, oxygen is a strongly electronegative atom. As a result the O-H bond is said to be polarized, such that one of the atoms has a partial negative charge, and the other a partial positive charge. Molecules, s ...
Purification and characterization of the 1-3
... coenzymes were determined at 37°C with potassium carbonate buffer (pH 9.7 for the oxidative reactions and pH 9.1 for the reductive reactions). They were determined from the results of experiments in which a fixed concentration of the substrate or coenzyme and an appropriate range of concentrations o ...
... coenzymes were determined at 37°C with potassium carbonate buffer (pH 9.7 for the oxidative reactions and pH 9.1 for the reductive reactions). They were determined from the results of experiments in which a fixed concentration of the substrate or coenzyme and an appropriate range of concentrations o ...
Amino Acids in Dairy Nutrition – Where Do They Fit?
... the tissues of the cow actually require amino acids for protein synthesis, rather than protein per se. The purpose of this paper is to provide some perspective to amino acid balancing together with the underlying biology supporting amino acid balancing and our current recommendations for amino acids ...
... the tissues of the cow actually require amino acids for protein synthesis, rather than protein per se. The purpose of this paper is to provide some perspective to amino acid balancing together with the underlying biology supporting amino acid balancing and our current recommendations for amino acids ...
4. AMINO ACIDS
... into two groups essential amino acids (EAA), and the non-essential amino acids (NEAA). • Essential amino acids • The essential amino acids are that cannot be synthesized within the animal body or rate sufficient to meet the physiological needs of the growing animal, therefore be supplied in a ready ...
... into two groups essential amino acids (EAA), and the non-essential amino acids (NEAA). • Essential amino acids • The essential amino acids are that cannot be synthesized within the animal body or rate sufficient to meet the physiological needs of the growing animal, therefore be supplied in a ready ...
Industrial Biotechnology
... • The final product of metabolic pathway inhibits the action of earlier enzymes (usually the first) of that sequence. • The inhibitor and the substrate need not resemble each other, hence the inhibition is often called allosteric. • In case of isosteic inhibition the inhibitor and substrate have the ...
... • The final product of metabolic pathway inhibits the action of earlier enzymes (usually the first) of that sequence. • The inhibitor and the substrate need not resemble each other, hence the inhibition is often called allosteric. • In case of isosteic inhibition the inhibitor and substrate have the ...
Metabolism
... • Glycolysis generates 2 ATP and 2 NADH • Two ATP are used in energy-investment to add phosphate groups to glucose and fructose-6-phosphate • Four ATP are formed in energy-generation by direct transfers of phosphate groups to four ADP. Glucose + 2ADP + 2Pi + 2NAD+ 2Pyruvate + 2ATP + 2NADH + 4H+ ...
... • Glycolysis generates 2 ATP and 2 NADH • Two ATP are used in energy-investment to add phosphate groups to glucose and fructose-6-phosphate • Four ATP are formed in energy-generation by direct transfers of phosphate groups to four ADP. Glucose + 2ADP + 2Pi + 2NAD+ 2Pyruvate + 2ATP + 2NADH + 4H+ ...
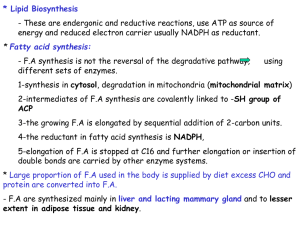
13synthesis
... occurs in cytosol - Acetate is shuttled out of mitochondria as citrate because membrane is NOT permeable for acetate. ...
... occurs in cytosol - Acetate is shuttled out of mitochondria as citrate because membrane is NOT permeable for acetate. ...
Citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle – also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or the Krebs cycle – is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest established components of cellular metabolism and may have originated abiogenically.The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from citric acid (a type of tricarboxylic acid) that is consumed and then regenerated by this sequence of reactions to complete the cycle. In addition, the cycle consumes acetate (in the form of acetyl-CoA) and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and produces carbon dioxide as a waste byproduct. The NADH generated by the TCA cycle is fed into the oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport) pathway. The net result of these two closely linked pathways is the oxidation of nutrients to produce usable chemical energy in the form of ATP.In eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion. In prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria which lack mitochondria, the TCA reaction sequence is performed in the cytosol with the proton gradient for ATP production being across the cell's surface (plasma membrane) rather than the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.