Equation Editor 1. To open the `Equation Editor,` select `Insert`. 2
... 3. Click on the page where you wish to insert the equation. The 'Equation Editor' will open. Choose the desired equation symbols and templates. Click OK to add the equation to your flipchart page. 4. To edit an existing equation, with the 'Equation Editor' tool selected click on the equation or doub ...
... 3. Click on the page where you wish to insert the equation. The 'Equation Editor' will open. Choose the desired equation symbols and templates. Click OK to add the equation to your flipchart page. 4. To edit an existing equation, with the 'Equation Editor' tool selected click on the equation or doub ...
Name _ Date Period 1 3 4 5 6 7 Semester 1 Exam Study Guide The
... at the supermarket. Since his birthday, he has saved more than enough money to buy a game system that costs $450. How many weeks ago was Luc’s birthday? 40. After purchasing the game system, will Luc have any money left over? How do you know? 41. The starting balance of Adam’s saving account is $575 ...
... at the supermarket. Since his birthday, he has saved more than enough money to buy a game system that costs $450. How many weeks ago was Luc’s birthday? 40. After purchasing the game system, will Luc have any money left over? How do you know? 41. The starting balance of Adam’s saving account is $575 ...
problem-set-7c-cal-2016
... b) The amount of heat absorbed by the water was the amount of heat lost by the iron. If the piece of iron was 35 g and the specific heat of iron is 0.451 J/g . Co what was the original temperature of the iron? (hint: the iron was dropped into the water, so you know the final temperature of the iron) ...
... b) The amount of heat absorbed by the water was the amount of heat lost by the iron. If the piece of iron was 35 g and the specific heat of iron is 0.451 J/g . Co what was the original temperature of the iron? (hint: the iron was dropped into the water, so you know the final temperature of the iron) ...
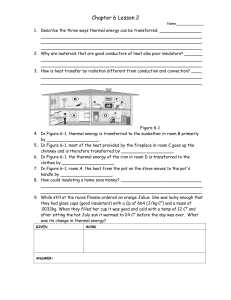
Chapter 6 Lesson 2 Name_____________ Describe the three ways
... In Figure 6-1, thermal energy is transferred to the sunbather in room B primarily by ____________________. In Figure 6-1, most of the heat provided by the fireplace in room C goes up the chimney and is therefore transferred by ____________________. In Figure 6-1, the thermal energy of the iron in ro ...
... In Figure 6-1, thermal energy is transferred to the sunbather in room B primarily by ____________________. In Figure 6-1, most of the heat provided by the fireplace in room C goes up the chimney and is therefore transferred by ____________________. In Figure 6-1, the thermal energy of the iron in ro ...
Document
... Plains, Lines and Automobiles 1. Mr. Slater paid $32,000 for a car. Suppose that the car depreciates linearly at the rate of 15% per year. a. Write an equation for the value, V, of the car after t years. V(t) = _______________________________ b. Graph the equation – be very careful to use appropriat ...
... Plains, Lines and Automobiles 1. Mr. Slater paid $32,000 for a car. Suppose that the car depreciates linearly at the rate of 15% per year. a. Write an equation for the value, V, of the car after t years. V(t) = _______________________________ b. Graph the equation – be very careful to use appropriat ...
File
... A 9.84 oz ingot of unknown metal is heated from 73.2 °F to 191.2 °F. This requires 3.91 kcal of energy. Calculate the specific heat of the metal and determine its identity. ...
... A 9.84 oz ingot of unknown metal is heated from 73.2 °F to 191.2 °F. This requires 3.91 kcal of energy. Calculate the specific heat of the metal and determine its identity. ...
Worksheet 6a
... standard enthalpy of formation – heat associated with the formation of one mole of a compound from its elements in their standard state (way they occur at 1 atm and 25 oC). ...
... standard enthalpy of formation – heat associated with the formation of one mole of a compound from its elements in their standard state (way they occur at 1 atm and 25 oC). ...
Document
... a. Write an equation to model the trout population in any year between 1995 and 2005. Let t be the number of years since 1995. ...
... a. Write an equation to model the trout population in any year between 1995 and 2005. Let t be the number of years since 1995. ...
5,6 Quiz - mvhs
... b. Condensed Orbital Notation c. Number of valence electrons 5. A student is asked to determine the molar enthalpy of neutralization, ∆Hneut, for the neutralization of HCl(aq) with NaOH(aq). The student combines equal volumes of 1.0 M HCl and 1.0 M NaOH in an open polystyrene cup calorimeter. The he ...
... b. Condensed Orbital Notation c. Number of valence electrons 5. A student is asked to determine the molar enthalpy of neutralization, ∆Hneut, for the neutralization of HCl(aq) with NaOH(aq). The student combines equal volumes of 1.0 M HCl and 1.0 M NaOH in an open polystyrene cup calorimeter. The he ...
Lecture 2 Intro to Heat Flow
... (1 day ≈ 80,000 s) surface area: 2 m x 1 m = 2 m2 50 W/m2 ! — or one lightbulb Types of Heat Transport conduction convection radiation—electromagnetic radiation advection Relationship Between Heat Flow & T Gradient: Fourier’s Law The rate of heat flow is proportional to the difference in heat betwee ...
... (1 day ≈ 80,000 s) surface area: 2 m x 1 m = 2 m2 50 W/m2 ! — or one lightbulb Types of Heat Transport conduction convection radiation—electromagnetic radiation advection Relationship Between Heat Flow & T Gradient: Fourier’s Law The rate of heat flow is proportional to the difference in heat betwee ...
Exponential Function and Physical Examples . Applied Math
... only fresh water is introduced (and mixes immediately) and the rate of inflow and outflow are same. [see also the problem (l).] (d) The amount of ultraviolet radiation being absorbed by O3 is proportional to the intensity of the ultraviolet radiation. [Why does the maximum UV radiation absorption by ...
... only fresh water is introduced (and mixes immediately) and the rate of inflow and outflow are same. [see also the problem (l).] (d) The amount of ultraviolet radiation being absorbed by O3 is proportional to the intensity of the ultraviolet radiation. [Why does the maximum UV radiation absorption by ...
Heat equation

The heat equation is a parabolic partial differential equation that describes the distribution of heat (or variation in temperature) in a given region over time.