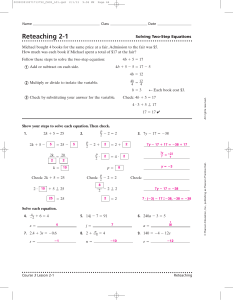
Ch. 2 REVIEW ANSWERS - Lewis
... © Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall. ...
... © Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall. ...
Physical chemistry advanced laboratory course
... The Eq.(2) can also be reformulated in differential form and the mole fraction can be replaced with molality mS (where S refers to saturated solution): d ln mS = ...
... The Eq.(2) can also be reformulated in differential form and the mole fraction can be replaced with molality mS (where S refers to saturated solution): d ln mS = ...
Section 2.4 - Analytic Methods for Special Systems
... 3. A system of differential equations is said to decouple if the rate of change of one or more of the dependent variables depends only on its own value. If the equation for dx involves only x dt dy and the equation for dt involves only y, we say that the system is completely decoupled, and we can so ...
... 3. A system of differential equations is said to decouple if the rate of change of one or more of the dependent variables depends only on its own value. If the equation for dx involves only x dt dy and the equation for dt involves only y, we say that the system is completely decoupled, and we can so ...
specific heat
... A. When you touch ice, 1) heat is transferred from your hand to the ice 2) coldness flows from the ice to your ...
... A. When you touch ice, 1) heat is transferred from your hand to the ice 2) coldness flows from the ice to your ...
physics of foil - P1 International
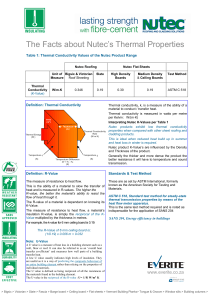
... transfer which is mainly affected by differences in: density, weight, shape, permeability and molecular structure, Materials which transfer heat slowly can be said to RESIST heat flow. ...
... transfer which is mainly affected by differences in: density, weight, shape, permeability and molecular structure, Materials which transfer heat slowly can be said to RESIST heat flow. ...
ME 433 Combustion Engine Systems
... (iv) Shade the area on the P-V diagram which represents the NET work output. (v) Shade the area on the T-S diagram which represents heat transfer INTO the cycle. (vi) Shade the area on the T-S diagram which represent the NET work output. (vii) Explain how to use data from the T-S diagram to estimate ...
... (iv) Shade the area on the P-V diagram which represents the NET work output. (v) Shade the area on the T-S diagram which represents heat transfer INTO the cycle. (vi) Shade the area on the T-S diagram which represent the NET work output. (vii) Explain how to use data from the T-S diagram to estimate ...
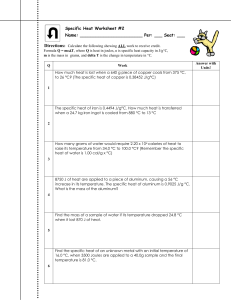
Specific Heat WS #2 - My Chemistry Class
... How many grams of water would require 2.20 x 104 calories of heat to raise its temperature from 34.0 °C to 100.0 °C? (Remember the specific heat of water is 1.00 cal/g x °C) ...
... How many grams of water would require 2.20 x 104 calories of heat to raise its temperature from 34.0 °C to 100.0 °C? (Remember the specific heat of water is 1.00 cal/g x °C) ...
Schaums Heat
... 5. A thermos bottle contains 250 g of coffee at 900C. To this is added 20g of milk at 50C. After equilibrium is established, what is the temperature of the liquid? 6. A thermos bottle contains 150 g of water at 40C. Into this is placed 90g of metal at 1000C. After equilibrium is established, the tem ...
... 5. A thermos bottle contains 250 g of coffee at 900C. To this is added 20g of milk at 50C. After equilibrium is established, what is the temperature of the liquid? 6. A thermos bottle contains 150 g of water at 40C. Into this is placed 90g of metal at 1000C. After equilibrium is established, the tem ...
Heat equation

The heat equation is a parabolic partial differential equation that describes the distribution of heat (or variation in temperature) in a given region over time.