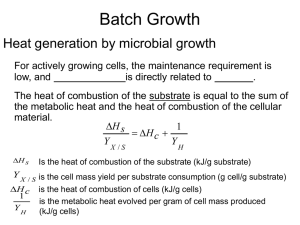
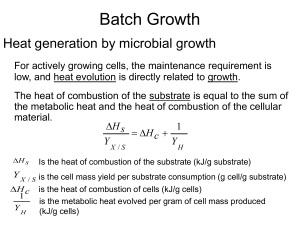
Calorimetry Lab
... Part III: Calibration of the Calorimeter In order to account for all of the heat produced by a reaction in the calorimeter, it is important to determine how much heat the calorimeter itself absorbs. This can be accomplished by combining two masses of water, one “hot” and one “cold”. If the coffee cu ...
... Part III: Calibration of the Calorimeter In order to account for all of the heat produced by a reaction in the calorimeter, it is important to determine how much heat the calorimeter itself absorbs. This can be accomplished by combining two masses of water, one “hot” and one “cold”. If the coffee cu ...
Test 3
... Potential vs. Kinetic Energy Heat : involves transfer of energy Flows from high temp. to low temp. Describe changes to motion of particles when heat added or taken away Temperature - measure of average KE Conversions between Kelvin & Celsius Absolute zero (0 Kelvin) Endothermic vs. Exothermic Change ...
... Potential vs. Kinetic Energy Heat : involves transfer of energy Flows from high temp. to low temp. Describe changes to motion of particles when heat added or taken away Temperature - measure of average KE Conversions between Kelvin & Celsius Absolute zero (0 Kelvin) Endothermic vs. Exothermic Change ...
Pre-Calculus 12A Section 7.3 Solving Exponential Equations
... The student council of a school notices that their membership is growing by 3% per year. a. The membership is currently 350 students. Write an exponential function to model the size of the student council. Define your variables. b. Use your equation to determine the time needed until the student cou ...
... The student council of a school notices that their membership is growing by 3% per year. a. The membership is currently 350 students. Write an exponential function to model the size of the student council. Define your variables. b. Use your equation to determine the time needed until the student cou ...
thermodynamics, heat and mass transfer
... 5. Two blocks A and B which are initially at 950C and 5400C, respectively are brought together into contact and isolated from the surroundings. They are allowed to reach a final state of thermal equilibrium. Determine the entropy change of each block and of the isolated system. Block A is aluminium ...
... 5. Two blocks A and B which are initially at 950C and 5400C, respectively are brought together into contact and isolated from the surroundings. They are allowed to reach a final state of thermal equilibrium. Determine the entropy change of each block and of the isolated system. Block A is aluminium ...
Specific Heat Capacity - Tasker Milward
... Specific Heat Capacity • The specific heat capacity is the amount of energy required to increase the temperature of 1kg of a substance by 1˚C • We will calculate the specific heat capacity of water by heating it with an electrical heater and measuring the energy required for a fixed temperature ris ...
... Specific Heat Capacity • The specific heat capacity is the amount of energy required to increase the temperature of 1kg of a substance by 1˚C • We will calculate the specific heat capacity of water by heating it with an electrical heater and measuring the energy required for a fixed temperature ris ...
Solution - Illustrative Mathematics
... c. In order to solve this equation with pictures, you have to have some way of representing the subtraction in 2x– 4. If students have experience with integer chips, they can transfer that knowledge to this situation to show 2x + −4, but otherwise they may struggle with the idea. The pictures give u ...
... c. In order to solve this equation with pictures, you have to have some way of representing the subtraction in 2x– 4. If students have experience with integer chips, they can transfer that knowledge to this situation to show 2x + −4, but otherwise they may struggle with the idea. The pictures give u ...
2 Pieces - cloudfront.net
... Insulators serve to (increase, decrease or not change) the transfer of heat energy. ...
... Insulators serve to (increase, decrease or not change) the transfer of heat energy. ...
Thermodynamics: Lecture 2
... equation of state is complex and involves approximations, which may not be justified. Therefore, it is essential to experimentally establish an empirical the equation of state as shown in figure 2.3. Once one has an equation of state, we can predict how the state will change as the state variables a ...
... equation of state is complex and involves approximations, which may not be justified. Therefore, it is essential to experimentally establish an empirical the equation of state as shown in figure 2.3. Once one has an equation of state, we can predict how the state will change as the state variables a ...
CCD Apologia Chemistry Syllabus 2011-12
... Define Energy: The ability to do work – to cause motion. Work: The force applied to an object times the distance that the object travels parallel to that force. For work to occur, there must be motion. Heat: Energy transferred as a consequence of temperature differences. It is energy on its way from ...
... Define Energy: The ability to do work – to cause motion. Work: The force applied to an object times the distance that the object travels parallel to that force. For work to occur, there must be motion. Heat: Energy transferred as a consequence of temperature differences. It is energy on its way from ...
Solutions
... for integers m, n, p, q such that the above formulae yield integers. [Hint: Use the previous exercise.] Proof. Rewrite the equation as x2 − t2 = z 2 − y 2 which is equivalent to (x + t)(x − t) = (y + z)(z − y) From the previous exercise there exist integers m, n, p, q such that x + t = mn x − t = pq ...
... for integers m, n, p, q such that the above formulae yield integers. [Hint: Use the previous exercise.] Proof. Rewrite the equation as x2 − t2 = z 2 − y 2 which is equivalent to (x + t)(x − t) = (y + z)(z − y) From the previous exercise there exist integers m, n, p, q such that x + t = mn x − t = pq ...
Document
... The Multiplication Property of Equality For any numbers a, b and c: If a = b, then a · c = b · c ...
... The Multiplication Property of Equality For any numbers a, b and c: If a = b, then a · c = b · c ...
Calorimetry: Heat of Fusion of Ice Procedure In a 250 mL beaker
... Immediately add 2-3 ice cubes. Stir the mixture carefully. The cup should contain ice at all times. If the last of the ice is about to melt, add another ice cube. Monitor the temperature of the mixture as you stir. Continue stirring until the temperature no longer drops. Record this final temperatur ...
... Immediately add 2-3 ice cubes. Stir the mixture carefully. The cup should contain ice at all times. If the last of the ice is about to melt, add another ice cube. Monitor the temperature of the mixture as you stir. Continue stirring until the temperature no longer drops. Record this final temperatur ...
WORKSHOP 2: Dimensional Analysis and
... object in g/mL. 0.884 g/cm3 7. A rubber stopper weighing 65.4 g is immersed into a graduated cylinder filled with 30.0 mL of liquid. The liquid level then rises to 48.8 mL. Calculate the density of the stopper. 3.48 g/mL 8. If the density of a liquid is known to be 0.785 g/mL, calculate the mass of ...
... object in g/mL. 0.884 g/cm3 7. A rubber stopper weighing 65.4 g is immersed into a graduated cylinder filled with 30.0 mL of liquid. The liquid level then rises to 48.8 mL. Calculate the density of the stopper. 3.48 g/mL 8. If the density of a liquid is known to be 0.785 g/mL, calculate the mass of ...
Heat equation

The heat equation is a parabolic partial differential equation that describes the distribution of heat (or variation in temperature) in a given region over time.