Course ME 32200 – Heat Transfer Laboratory Type of Course
... systems and computers, and to improve students’ written communication, teamwork, and experimental skills. ...
... systems and computers, and to improve students’ written communication, teamwork, and experimental skills. ...
CS 626 project III (folding of hetero
... 4. A function that evaluates the heat capacity at a specific temperature 5. A function that performs a complete simulated annealing run To simulate the folding of the polymer start at a high temperature of and decrease the temperature (while computing the heat capacity for each temperature). You wil ...
... 4. A function that evaluates the heat capacity at a specific temperature 5. A function that performs a complete simulated annealing run To simulate the folding of the polymer start at a high temperature of and decrease the temperature (while computing the heat capacity for each temperature). You wil ...
Equations with Many Solutions or No Solution
... You can write an equation with one solution, no solution, or infinitely many solutions. One solution: Start with a variable on one side and a constant on the other. This is your solution. Add, subtract, multiply or divide both sides of the equation by the same constant(s). Your equation has one solu ...
... You can write an equation with one solution, no solution, or infinitely many solutions. One solution: Start with a variable on one side and a constant on the other. This is your solution. Add, subtract, multiply or divide both sides of the equation by the same constant(s). Your equation has one solu ...
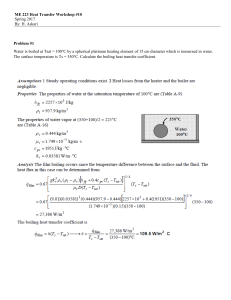
Specific Heat Lab Experiment Sixteen p
... Purpose: To determine the identity of an unknown metal by determining its specific heat capacity, “c” Materials: unknown metal sample, calorimeter, styrofoam cup, water, beaker, hot plate, string, thermometer, balance Background: If substances of different temperatures are in contact with each other ...
... Purpose: To determine the identity of an unknown metal by determining its specific heat capacity, “c” Materials: unknown metal sample, calorimeter, styrofoam cup, water, beaker, hot plate, string, thermometer, balance Background: If substances of different temperatures are in contact with each other ...
specific heat
... How much energy would be needed to heat 450 g of copper metal from 25.0 ºC to 75.0 ºC? The specific heat of copper at 25.0 ºC is 0.385 J/g ºC. ...
... How much energy would be needed to heat 450 g of copper metal from 25.0 ºC to 75.0 ºC? The specific heat of copper at 25.0 ºC is 0.385 J/g ºC. ...
y=f(x)
... 1) Find out what you are being asked to find. Set a variable to this unknown quantity. Make sure you know the units of this unknown (miles?, hours? ounces?) 2) If there is another unknown quantity, use the given information to put that unknown quantity in terms of the variable you have chosen. (For ...
... 1) Find out what you are being asked to find. Set a variable to this unknown quantity. Make sure you know the units of this unknown (miles?, hours? ounces?) 2) If there is another unknown quantity, use the given information to put that unknown quantity in terms of the variable you have chosen. (For ...
First Law of Thermodynamics
... Boiling •Is not a temperature •It is a pressure •Pressure above the liquid=pressure from particles leaving the surface ...
... Boiling •Is not a temperature •It is a pressure •Pressure above the liquid=pressure from particles leaving the surface ...
Equation-Based Modeling: Building your Equations from scratch
... in the Coefficient Form Interface ...
... in the Coefficient Form Interface ...
NUMERICAL MODELING OF GEOTHERMAL FIELDS IN BLACK SEA
... means extrapolating the measured on the sea bottom heat flow in accordance with assumptions concerning the deep structure of the main geological provinces (based on the explosion seismology), the depth distribution of the heat sources, and the thermal conductivity coefficient. Up to now in Black Sea ...
... means extrapolating the measured on the sea bottom heat flow in accordance with assumptions concerning the deep structure of the main geological provinces (based on the explosion seismology), the depth distribution of the heat sources, and the thermal conductivity coefficient. Up to now in Black Sea ...
module 2
... We have set up a differential equation, with T as the dependent variable. The solution will give us T(x,y,z). Solution depends on boundary conditions (BC) and initial conditions (IC). How many BC’s and IC’s ? - Heat equation is second order in spatial coordinate. Hence, 2 BC’s needed for each coordi ...
... We have set up a differential equation, with T as the dependent variable. The solution will give us T(x,y,z). Solution depends on boundary conditions (BC) and initial conditions (IC). How many BC’s and IC’s ? - Heat equation is second order in spatial coordinate. Hence, 2 BC’s needed for each coordi ...
ppt
... From a calorimetry experiment, a student determines that the specific heat of solution of KBrO3 (s) is an endothermic 0.25 kJ/g. Calculate the molar heat of solution and write the ...
... From a calorimetry experiment, a student determines that the specific heat of solution of KBrO3 (s) is an endothermic 0.25 kJ/g. Calculate the molar heat of solution and write the ...
Heat equation

The heat equation is a parabolic partial differential equation that describes the distribution of heat (or variation in temperature) in a given region over time.