* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Heat Calculations with Specific Heat
Heat exchanger wikipedia , lookup
Intercooler wikipedia , lookup
Solar water heating wikipedia , lookup
Thermoregulation wikipedia , lookup
R-value (insulation) wikipedia , lookup
Heat equation wikipedia , lookup
Solar air conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Copper in heat exchangers wikipedia , lookup
Cogeneration wikipedia , lookup
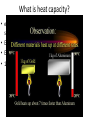
Heat Calculations with Specific Heat What is heat? What is energy? How are they both measured? What is heat? • (q) – transfer of energy from one object to another because of temperature difference between objects • form of energy • flows from warmer to cooler object • measured in joules What is energy? • (E) – ability or capacity to do work • measured in joules • detected by effects What is temperature? • (T) – NOT a form of energy • thought of as intensity of heat • measured in C, F, or K • amount of heat per unit of substance What is a Joule? • (J) – amount of energy produced when a force of 1 Newton acts over a distance of 1 meter • small amount of energy • 1 Newton ~ amount of force 40 pennies exerts on the palm of your hand • striking a match releases 1050 J What is thermodynamics? • THERMODYNAMICS deals with energy changes (∆ E) that accompany chemical and physical properties • TELL US whether a reaction is possible depending on: - whether reaction occurs by itself (spontaneously) OR - if reaction needs outside source of energy to proceed Laws of Thermodynamics What is heat capacity? • energy required to raise temperature of substance by 1 °C • Every pure substance has unique heat capacity • Expressed as Joules • 1 Calorie = 4.184 Joule What is specific heat? • (Cp) energy required to raise temperature of substance by 1 °C • • • • Specific Heat varies depending on: Type of substance State of matter of substance (s, l, g) Temperature of the reaction • S.H. of ICE = 2060 J/kg°C • S.H. of liquid water = 4180 J/kg°C How do you measure heat? 1. Mathematically using HEAT EQUATION • q = m x Cp x ∆T • How much energy would be needed to heat .450 kg of Copper metal from a temperature of 25 °C to 75 °C? • Specific Heat of Copper at 25 °C = 385 J/kg °C • q = m (Cp) ∆T PLUG AND CHUG! What is a Calorimeter? • You are boiling water to make spaghetti. When the water boils, does it all instantly vaporize? Why not, after all – it’s reached the boiling point? • Video Animation Heating Curve in Motion • EX. How much heat is necessary to totally melt 5 g of ice at 0 C to liquid water at 0 C? • EX. How much heat is necessary to change 5 g of water at 100 C to steam at 100 C? • • • • • HEAT CALCULATIONS q = m Cp △T for substance WITHOUT a phase change q = m △Hfus when a substances freezes/melts q = m △Hvap when a substance evaporates/condenses If a substances undergoes a phase change and changes temperature, you must add all the heats together.