Volcanoes
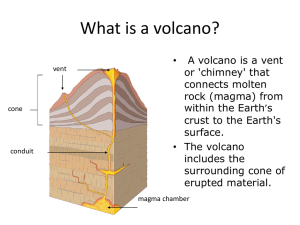
... 6. Often the volcano sides will be higher than the vent forming a depression called a crater ...
... 6. Often the volcano sides will be higher than the vent forming a depression called a crater ...
iss__st4_files/Comenius Volcanoes
... European Space Agency, with the mission to observe and monitor the surface of the Earth. Together with Sentinel-1B, it can create better pictures of the surface of the Earth than the similar InSAR satellites, due to the fact that they can create images in a much shorter time interval. ESA’s Volcanic ...
... European Space Agency, with the mission to observe and monitor the surface of the Earth. Together with Sentinel-1B, it can create better pictures of the surface of the Earth than the similar InSAR satellites, due to the fact that they can create images in a much shorter time interval. ESA’s Volcanic ...
Volcanoes PPT - Van Buren Public Schools
... – Mainly water vapor and carbon dioxide – Gases expand near the surface – A vent is an opening in the surface of Earth through which molten rock and gases are released. – Provide the force to extrude lava – Violence of an eruption is related to how easily gases escape from magma – Gases escape easil ...
... – Mainly water vapor and carbon dioxide – Gases expand near the surface – A vent is an opening in the surface of Earth through which molten rock and gases are released. – Provide the force to extrude lava – Violence of an eruption is related to how easily gases escape from magma – Gases escape easil ...
Учитель: Размахнина О
... underneath. About 30 km beneath your feet is the Earth's 2_______________. It's a region of superhot rock that extends down to the Earth's 3_____________. This region is so hot that molten rock can squeeze out and form giant bubbles of liquid 4______________ called magma 5_______________. This magma ...
... underneath. About 30 km beneath your feet is the Earth's 2_______________. It's a region of superhot rock that extends down to the Earth's 3_____________. This region is so hot that molten rock can squeeze out and form giant bubbles of liquid 4______________ called magma 5_______________. This magma ...
Volcano Vocab.
... • Felsic: Term used to describe volcanic rock or lava composed largely of silica. (ex. Aa) • Mafic: Term used to describe volcanic rock or lava that does not have much silica. (ex. Pahoehoe) ...
... • Felsic: Term used to describe volcanic rock or lava composed largely of silica. (ex. Aa) • Mafic: Term used to describe volcanic rock or lava that does not have much silica. (ex. Pahoehoe) ...
Volcanoes
... that shoot small pieces of magma and ash into the air. O The magma then cools and hardens as it falls back to the Earth, forming a cinder cone. O In many cases, cinder cones form on the sides of a larger volcano. ...
... that shoot small pieces of magma and ash into the air. O The magma then cools and hardens as it falls back to the Earth, forming a cinder cone. O In many cases, cinder cones form on the sides of a larger volcano. ...
Volcanoes
... • The danger is mostly from lahars traveling down river valleys at a speed of 25mph and destroying ...
... • The danger is mostly from lahars traveling down river valleys at a speed of 25mph and destroying ...
Putting the Lava in the Lava Beds
... quartzes, or mineral ores. We have one basic rock to study and that is lava. While there are four types of lava (basalt, andesite, dacite, and rhyolite), it takes a trained geologist to tell one from the other; to most of us, they are all just lava. They differ only in the amounts of silica they con ...
... quartzes, or mineral ores. We have one basic rock to study and that is lava. While there are four types of lava (basalt, andesite, dacite, and rhyolite), it takes a trained geologist to tell one from the other; to most of us, they are all just lava. They differ only in the amounts of silica they con ...
Document
... _____ 12. The underground body of molten rock that feeds a volcano is a(n) a. vent. c. lava chamber. b. magma chamber. d. ash chamber. _____ 13. An opening in the Earth's surface through which volcanic material passes is a(n) a. vent. c. lava chamber. b. magma chamber. d. ash chamber. 14. What about ...
... _____ 12. The underground body of molten rock that feeds a volcano is a(n) a. vent. c. lava chamber. b. magma chamber. d. ash chamber. _____ 13. An opening in the Earth's surface through which volcanic material passes is a(n) a. vent. c. lava chamber. b. magma chamber. d. ash chamber. 14. What about ...
Document
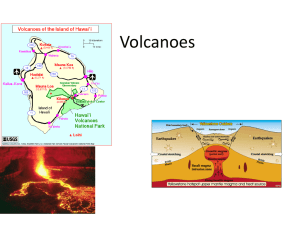
... • The summit of Hualalai rises to an elevation of 2523m (8271ft) above sea level. • Hualalai is well-known in Hawaii as a good source for mantle xenoliths. • The surface of Hualalai is entirely composed of post-shield alkalic basalts. • The last historical eruption at Hualalai ended in 1801. This e ...
... • The summit of Hualalai rises to an elevation of 2523m (8271ft) above sea level. • Hualalai is well-known in Hawaii as a good source for mantle xenoliths. • The surface of Hualalai is entirely composed of post-shield alkalic basalts. • The last historical eruption at Hualalai ended in 1801. This e ...
Lab 5 Lecture
... Viscosity: The ability for lava to flow. Reflective of the amount of silica present in the magma. ...
... Viscosity: The ability for lava to flow. Reflective of the amount of silica present in the magma. ...
01 - Mayfield City Schools
... _____ 12. The underground body of molten rock that feeds a volcano is a(n) a. vent. c. lava chamber. b. magma chamber. d. ash chamber. _____ 13. An opening in the Earth's surface through which volcanic material passes is a(n) a. vent. c. lava chamber. b. magma chamber. d. ash chamber. 14. What about ...
... _____ 12. The underground body of molten rock that feeds a volcano is a(n) a. vent. c. lava chamber. b. magma chamber. d. ash chamber. _____ 13. An opening in the Earth's surface through which volcanic material passes is a(n) a. vent. c. lava chamber. b. magma chamber. d. ash chamber. 14. What about ...
volcanic activity guided notes
... Characteristics of Magma __________ content, how __________ or _________ the magma is, temperature and silica contents are important factors as to the __________ of a volcanic eruptions. The amount of ___________ in magma helps to determine how easily the magma flows. Silica is formed from the el ...
... Characteristics of Magma __________ content, how __________ or _________ the magma is, temperature and silica contents are important factors as to the __________ of a volcanic eruptions. The amount of ___________ in magma helps to determine how easily the magma flows. Silica is formed from the el ...
Volcanoes - PrinceBwis
... more easily because gas dissolved in the magma bubbles • When the lava is thick and sticky the gas continues to store increasing pressure – When the pressure becomes so great an explosion takes place when the gas pushes the magma out with incredible force ...
... more easily because gas dissolved in the magma bubbles • When the lava is thick and sticky the gas continues to store increasing pressure – When the pressure becomes so great an explosion takes place when the gas pushes the magma out with incredible force ...
Volcanoes
... • The danger is mostly from lahars traveling down river valleys at a speed of 25mph and destroying ...
... • The danger is mostly from lahars traveling down river valleys at a speed of 25mph and destroying ...
volcanoes
... A volcano is a location on the surface of the Earth where magma has erupted out of the interior of the planet. Magma is molten rock, which has melted from the extreme heat (2200°C to 5000°C) and pressure that exists inside the Earth. Once molten rock has erupted onto the Earth’s surface, it is calle ...
... A volcano is a location on the surface of the Earth where magma has erupted out of the interior of the planet. Magma is molten rock, which has melted from the extreme heat (2200°C to 5000°C) and pressure that exists inside the Earth. Once molten rock has erupted onto the Earth’s surface, it is calle ...
File
... 1. A shield volcano is formed when a large amount of free-flowing lava, or molten rock, spills from a vent, or opening in the earth, and spreads widely. The lava gradually builds up a low, broad, dome-shaped mountain. (Example: Mauna Loa in Hawaii.) 2. A cinder cone builds up when mostly ash erupts ...
... 1. A shield volcano is formed when a large amount of free-flowing lava, or molten rock, spills from a vent, or opening in the earth, and spreads widely. The lava gradually builds up a low, broad, dome-shaped mountain. (Example: Mauna Loa in Hawaii.) 2. A cinder cone builds up when mostly ash erupts ...
Section 9.2
... Lahar: is a type of mudflow or debris dense, destructive mass flow composed of a slurry of pyroclastic material, rocky debris, and of very hot ash, lava water. The material flows down from a fragments, and gases ejected explosively volcano, typically along a river valley. (Volcano peaks often have i ...
... Lahar: is a type of mudflow or debris dense, destructive mass flow composed of a slurry of pyroclastic material, rocky debris, and of very hot ash, lava water. The material flows down from a fragments, and gases ejected explosively volcano, typically along a river valley. (Volcano peaks often have i ...
geothermal activity - Madison County Schools
... • Sometimes lava forms a plateau instead of a mountain. A lava plateau is a high, level area. If forms when thin lava flows out of many long cracks. ...
... • Sometimes lava forms a plateau instead of a mountain. A lava plateau is a high, level area. If forms when thin lava flows out of many long cracks. ...
Volcanoes
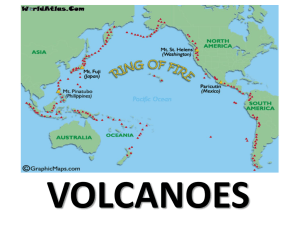
... How are they formed? What are the types of volcanoes? How do volcanoes change the Earth’s surface? Stages of a volcano? What is the ring of fire? What are the differences between quiet eruptions and explosive eruptions? What are the volcanic related landforms? ...
... How are they formed? What are the types of volcanoes? How do volcanoes change the Earth’s surface? Stages of a volcano? What is the ring of fire? What are the differences between quiet eruptions and explosive eruptions? What are the volcanic related landforms? ...