* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Presentation
Axial Seamount wikipedia , lookup
Mono–Inyo Craters wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pinatubo wikipedia , lookup
Mount Garibaldi wikipedia , lookup
Itcha Range wikipedia , lookup
Llullaillaco wikipedia , lookup
Mount Meager massif wikipedia , lookup
Nevado del Ruiz wikipedia , lookup
Cascade Volcanoes wikipedia , lookup
Olympus Mons wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Level Mountain wikipedia , lookup
Mount St. Helens wikipedia , lookup
Lascar (volcano) wikipedia , lookup
Shield volcano wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pelée wikipedia , lookup
Cerro Blanco (volcano) wikipedia , lookup
Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field wikipedia , lookup
Mount Vesuvius wikipedia , lookup
Craters of the Moon National Monument and Preserve wikipedia , lookup
Mount Edziza volcanic complex wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pleasant Caldera wikipedia , lookup
Cerro Azul (Chile volcano) wikipedia , lookup
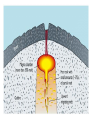
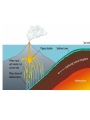
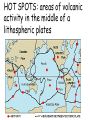
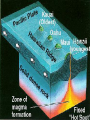
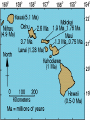
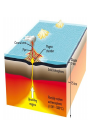
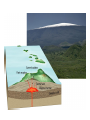
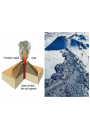
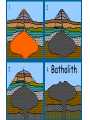
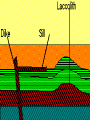
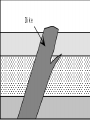
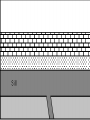
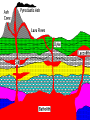
What are volcanoes? volcanism:any activity that includes the movement of magma toward the surface of the Earth volcano: place where magma reaches the surface MID-OCEAN RIDGE: occurs where plates are moving apart •lava flows out smoothly and fluidly from cracks SUBDUCTION ZONE: occurs at subduction boundaries •usually explosive and erupted material is mostly lava HOT SPOTS: areas of volcanic activity in the middle of a lithospheric plates Hawaiian Islands are an example What are the factors that determine the violence of the eruption? • Composition of the magma • Temperature of the magma • Dissolved gases in the magma What is magma & lava? magma: liquid, molten rock underground lava: magma that reaches the surface • • the measure of a material's resistance to flow. Factors affecting viscosity - Temperature (hotter magmas are less viscous) - Composition (silica content) 1. High silica—high viscosity 2. Low silica—more fluid (e.g., basaltic lava) What are the two types of lava? •felsic: much silica, lightcolored, slow moving (continental crust) •mafic: low silica, dark-colored, fast moving (oceanic crust) Aa Lava Pahoehoe Lava Pahoehoe Aa Aa Pillow lava from Hawaii How do gases affect magma? •many magmas contain dissolved gases that are given off •water vapor, carbon dioxide (CO2), sulfur (S) •magmas with more gases have more explosive eruptions What is pyroclastic material? solid fragments ejected from a volcano ash (fine, glassy fragments) lapilli (walnut sized particles) blocks (hardened lava) bombs (ejected as hot lava) lapilli bombs bombs blocks What is the anatomy of a volcano? •Vent: opening from which lava flows •Crater: funnel-shaped pit or depression at top of volcano •Caldera:craters whose walls have collapsed What are the 3 different types of volcanoes? • Shield • Cinder Cone • Composite •composed of quiet lava flows •form gently sloping, domeshaped mountain •basaltic (mafic) magma largest = Mauna Loa in Hawaii •Made mostly of tephra and other rock particle •Formed from explosive eruptions •Not very high, narrow base, steep sides •Grantic (felsic) magma •built up of alternating layers of rock and lava •explosive eruptions at first with tephra, then quiet with lava •forms large, cone-shaped mountains •made of grantic and basaltic magma Mount Fuji Mount St. Helens Before and After the May 18, 1980, Eruption What are Igneous Rock Structures? • Intrusions – • Extrusions – underground surface rock masses rock masses What are the different types of INTRUSIONS? • 1. Batholiths – largest igneous intrusions – Form when huge bodies of magma cool underground – Cover 1000 km Batholith INTRUSIONS •2. Laccoliths – Domelike masses formed from magma bulging upward This laccolith in Red and White Mountain, Colorado, is of Tertiary age. Overlying layers of rock have been eroded. INTRUSIONS •3. Dike – Sheets of igneous rocks that cut across the rock layer Dike Dike INTRUSIONS •4. Sill – Sheet of hardened magma that forms between and parallel to layers of rock Sill Sill INTRUSIONS •5Stock – Similar to batholiths but less than 100 km What are EXTRUSIONS? •1. Volcanic neck: – The plug of hardened magma left in the vent from which lava flowed Volcanic neck: EXTRUSIONS •2. Caldera Aniakchak Caldera formed during an enormous explosive eruption that expelled more than 50 km3 of magma about 3,450 years ago. The caldera is 10 km in diameter and 500-1,000 m deep.